Eino ADK: Agent 抽象
todo:更新 eino-examples 代码的链接引用
Agent 定义
Eino 定义了 Agent 的基础接口,实现此接口的 Struct 可被视为一个 Agent:
// github.com/cloudwego/eino/adk/interface.go
type Agent interface {
Name(ctx context.Context) string
Description(ctx context.Context) string
Run(ctx context.Context, input *AgentInput, opts ...AgentRunOption) *AsyncIterator[*AgentEvent]
}
| Method | 说明 |
| Name | Agent 的名称,作为 Agent 的标识 |
| Description | Agent 的职能描述信息,主要用于让其他的 Agent 了解和判断该 Agent 的职责或功能 |
| Run | Agent 的核心执行方法,返回一个迭代器,调用者可以通过这个迭代器持续接收 Agent 产生的事件 |
ADK 提供了一些常用的 Agent 实现,单 Agent 如:ChatModelAgent;静态路由的多 Agent 如:SequentialAgent;动态路由的多 Agent 如:Supervisor 等。
AgentInput
Run 方法接收 AgentInput 作为 Agent 的输入:
type AgentInput struct {
Messages []_Message_
_ _EnableStreaming bool
}
Agent 通常以 ChatModel 为核心,因此规定 Agent 的输入为 Message List, 与 ChatModel 相同。Message List 中可以包括用户指令、对话历史、背景知识、样例数据等任何你希望传递给 Agent 的数据。例如:
import (
"github.com/cloudwego/eino/adk"
"github.com/cloudwego/eino/schema"
)
input := &adk.AgentInput{
Messages: []adk.Message{
schema.UserMessage("What's the capital of France?"),
schema.AssistantMessage("The capital of France is Paris.", nil),
schema.UserMessage("How far is it from London? "),
},
}
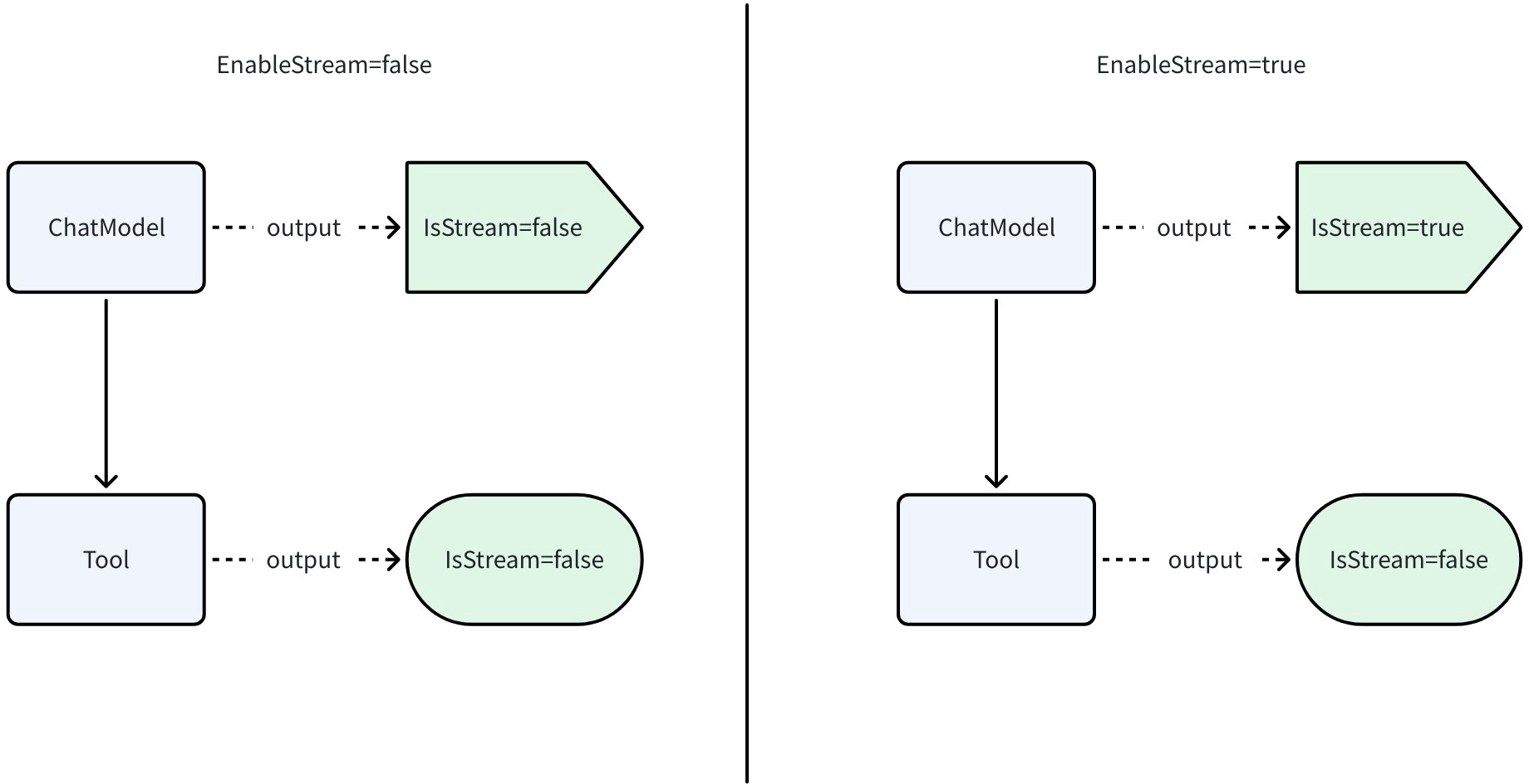
EnableStreaming 用于向 Agent 建议其输出模式,但它并非一个强制性约束。它的核心思想是控制那些同时支持流式和非流式输出的组件的行为,例如 ChatModel,而仅支持一种输出方式的组件,EnableStreaming 不会影响他们的行为。
- 当 EnableStreaming 设置为 true 时,对于 Agent 内部能够流式输出的组件(如 ChatModel 调用),应以流的形式逐步返回结果。如果某个组件天然不支持流式,它仍然可以按其原有的非流式方式工作。
- 当 EnableStreaming 设置为 false 时,对于那些既能流式也能非流式输出的组件,此时会使用一次性返回完整结果的非流式模式。
如下图所示,ChatModel 既可以输出非流也可以输出流,Tool 只能输出非流,当 EnableStream=false 时,二者均输出非流;当 EnableStream=true 时,ChatModel 输出流,Tool 因为不具备输出流的能力,仍然输出非流。
在 AgentOutput 中,会标明实际输出类型。
AgentRunOption
AgentRunOption 由 Agent 实现定义,可以在请求维度修改 Agent 配置或者控制 Agent 行为。Eino ADK 提供了 WrapImplSpecificOptFn 和 GetImplSpecificOptions 两个方法供 Agent 定义、读取 AgentRunOption。例如可以定义 WithModelName,在请求维度修改调用的模型:
// github.com/cloudwego/eino/adk/call_option.go
// func WrapImplSpecificOptFn[T any](optFn func(*T)) AgentRunOption
// func GetImplSpecificOptions[T any](base *T, opts ...AgentRunOption) *T
import "github.com/cloudwego/eino/adk"
type options struct {
modelName string
}
func WithModelName(name string) adk.AgentRunOption {
return adk.WrapImplSpecificOptFn(func(t *options) {
t.modelName = name
})
}
func (m *MyAgent) Run(ctx context.Context, input *adk.AgentInput, opts ...adk.AgentRunOption) *adk.AsyncIterator[*adk.AgentEvent] {
o := &options{}
o = adk.GetImplSpecificOptions(o, opts...)
// run code...
}
使用 GetImplSpecificOptions 方法读取 AgentRunOptions 时,与所需类型(如例子中的 options)不符的 AgentRunOption 会被忽略。
AgentRunOption 具有一个 DesignateAgent 方法,调用该方法可以在调用多 Agent 系统时指定 Option 生效的 Agent。
AsyncIterator
Agent.Run 返回了一个迭代器 AsyncIterator[*AgentEvent]:
// github.com/cloudwego/eino/adk/utils.go
type AsyncIterator[T any] struct {
...
}
func (ai *AsyncIterator[T]) Next() (T, bool) {
...
}
它代表一个异步迭代器(异步指生产与消费之间没有同步控制),允许调用者以一种有序、阻塞的方式消费 Agent 在运行过程中产生的一系列事件。
- AsyncIterator 是一个泛型结构体,可以用于迭代任何类型的数据。但在 Agent 接口中, Run 方法返回的迭代器类型被固定为 AsyncIterator[*AgentEvent] 。这意味着,你从这个迭代器中获取的每一个元素,都将是一个指向 AgentEvent 对象的指针。AgentEvent 会在后续章节中详细说明。
- 迭代器的主要交互方式是通过调用其 Next() 方法。这个方法的行为是 阻塞式 的,每次调用 Next() ,程序会暂停执行,直到以下两种情况之一发生:
- Agent 产生了一个新的 AgentEvent : Next() 方法会返回这个事件,调用者可以立即对其进行处理。
- Agent 主动关闭了迭代器 : 当 Agent 不会再产生任何新的事件时(通常是 Agent 运行结束),它会关闭这个迭代器。此时, Next() 调用会结束阻塞并在第二个返回值返回 false,告知调用者迭代已经结束。
AsyncIterator 常在 for 循环中处理:
iter := myAgent.Run(xxx) // get AsyncIterator from Agent.Run
for {
event, ok := iter.Next()
if !ok {
break
}
// handle event
}
AsyncIterator 可以由 NewAsyncIteratorPair 创建,该函数返回的另一个参数 AsyncGenerator 用来生产数据:
// github.com/cloudwego/eino/adk/utils.go
func NewAsyncIteratorPair[T any]() (*AsyncIterator[T], *AsyncGenerator[T])
Agent.Run 返回 AsyncIterator 旨在让调用者实时地接收到 Agent 产生的一系列 AgentEvent,因此 Agent.Run 通常会在 Goroutine 中运行 Agent 从而立刻返回 AsyncIterator 供调用者监听:
import "github.com/cloudwego/eino/adk"
func (m *MyAgent) Run(ctx context.Context, input *adk.AgentInput, opts ...adk.AgentRunOption) *adk.AsyncIterator[*adk.AgentEvent] {
// handle input
iter, gen := adk.NewAsyncIteratorPair[*adk.AgentEvent]()
go func() {
defer func() {
// recover code
gen.Close()
}()
// agent run code
// gen.Send(event)
}()
return iter
}
AgentWithOptions
使用 AgentWithOptions 方法可以在 Eino ADK Agent 做一些通用配置:
// github.com/cloudwego/eino/adk/flow.go
func AgentWithOptions(ctx context.Context, agent Agent, opts ...AgentOption) Agent
比如 WithDisallowTransferToParent、WithHistoryRewriter 等,具体功能将在相关的章节中详细说明。
AgentEvent
AgentEvent 是 Agent 在其运行过程中产生的核心事件数据结构。其中包含了 Agent 的元信息、输出、行为和报错:
// github.com/cloudwego/eino/adk/interface.go
type AgentEvent struct {
AgentName string
RunPath []string
Output *AgentOutput
Action *AgentAction
Err error
}
AgentName & RunPath
AgentEvent 包含的 AgentName 和 RunPath 字段是由框架自动填充的,它们提供了关于事件来源的重要上下文信息,尤其是在复杂的、由多个 Agent 构成的系统中。
- AgentName 标明了是哪一个 Agent 实例产生了当前的 AgentEvent 。
- RunPath 记录了到达当前 Agent 的完整调用链路。RunPath 是一个字符串切片,它按顺序记录了从最初的入口 Agent 到当前产生事件的 Agent 的所有 AgentName。
Output
AgentOutput 封装了 Agent 产生的输出。Message 输出被设置在 MessageOutput 字段中,其他类型的输出被设置在 CustomizedOutput 字段中:
// github.com/cloudwego/eino/adk/interface.go
type AgentOutput struct {
MessageOutput *MessageVariant
CustomizedOutput any
}
type MessageVariant struct {
IsStreaming bool
Message Message
MessageStream MessageStream
// message role: Assistant or Tool
Role schema.RoleType
// only used when Role is Tool
ToolName string
}
MessageOutput 字段的类型 MessageVariant 是一个核心数据结构,以下是其主要功能的分解说明:
- 统一处理流式与非流式消息
Agent 的输出可能是两种形式:
- 非流式 : 一次性返回一个完整的消息( Message )。
- 流式 : 随着时间的推移,逐步返回一系列消息片段,最终构成一个完整的消息( MessageStream )。
IsStreaming 是一个标志位。它的值为 true 表示当前 MessageVariant 包含的是一个流式消息(应从 MessageStream 读取),为 false 则表示包含的是一个非流式消息(应从 Message 读取)。
- 提供便捷的元数据访问
Message 结构体内部包含了一些重要的元信息,如消息的 Role(Assistant 或 Tool),为了方便快速地识别消息类型和来源, MessageVariant 将这些常用的元数据提升到了顶层:
- Role:消息的角色。
- ToolName:如果消息角色是 Tool ,这个字段会直接提供工具的名称。
这样做的好处是,代码在需要根据消息类型进行路由或决策时, 无需深入解析 Message 对象的具体内容 ,可以直接从 MessageVariant 的顶层字段获取所需信息,从而简化了逻辑,提高了代码的可读性和效率。
AgentAction
Agent 产生包含 AgentAction 的 Event 可以控制多 Agent 协作,比如立刻退出、中断、跳转等:
// github.com/cloudwego/eino/adk/interface.go
type AgentAction struct {
Exit bool
Interrupted *_InterruptInfo_
_ _TransferToAgent *_TransferToAgentAction_
_ _CustomizedAction any
}
比如:当 Agent 产生 Exit Action 时,Multi-Agent 会立刻退出;当 Agent 产生 Transfer Action 时,会跳转到目标 Agent 运行。Action 的具体用法会在相应功能介绍中说明。
多 Agent 协作
Eino ADK 提供了多 Agent 协作能力,包括由 Agent 在运行时动态决定将任务移交给其他 Agent,或者预先决定好 Agent 运行顺序。
上下文传递
在构建多 Agent 系统时,让不同 Agent 之间高效、准确地共享信息至关重要。Eino ADK 提供了两种核心的上下文传递机制,以满足不同的协作需求: History 和 SessionValues。
History
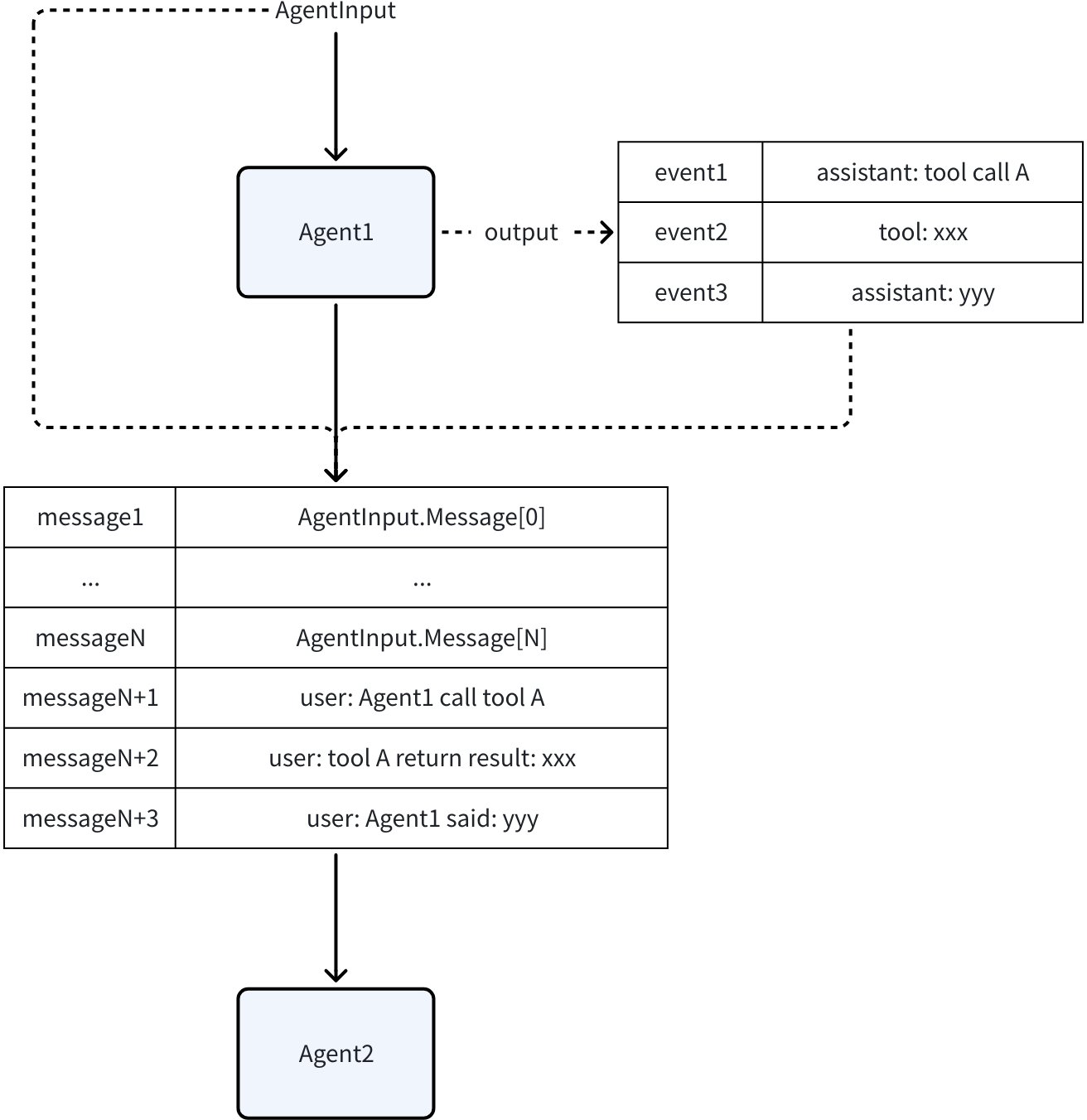
多 Agent 系统中每一个 Agent 产生的 AgentEvent 都会被保存到 History 中,在调用一个新 Agent 时(Workflow/ Transfer),History 中的 AgentEvent 会被转换并拼接到 AgentInput 中。
默认情况下,其他 Agent 的 Assistant 或 Tool Message,被转换为 User Message。这相当于在告诉当前的 LLM:“刚才, Agent_A 调用了 some_tool ,返回了 some_result 。现在,轮到你来决策了。”
通过这种方式,其他 Agent 的行为被当作了提供给当前 Agent 的“外部信息”或“事实陈述”,而不是它自己的行为,从而避免了 LLM 的上下文混乱。
在 Eino ADK 中,当为一个 Agent 构建 AgentInput 时,会对 History 中的 Event 进行过滤,确保 Agent 只会接收到当前 Agent 的直接或间接父 Agent 产生的 Event。换句话说,只有当 Event 的 RunPath “属于”当前 Agent 的 RunPath 时,该 Event 才会参与构建 Agent 的 Input。
💡 RunPathA “属于” RunPathB 定义为 RunPathA 与 RunPathB 相同或者 RunPathA 是 RunPathB 的前缀
WithHistoryRewriter
通过 AgentWithOptions 可以自定义 Agent 从 History 中生成 AgentInput 的方式:
// github.com/cloudwego/eino/adk/flow.go
type HistoryRewriter func(ctx context.Context, entries []*HistoryEntry) ([]Message, error)
func WithHistoryRewriter(h HistoryRewriter) AgentOption
SessionValues
SessionValues 是在一次运行中持续存在的全局临时 KV 存储,一次运行中的任何 Agent 可以在任何时间读写 SessionValues。Eino ADK 提供了三种方法访问 SessionValues:
// github.com/cloudwego/eino/adk/runctx.go
// 获取全部 SessionValues
func GetSessionValues(ctx context.Context) map[string]any
// 设置 SessionValues
func SetSessionValue(ctx context.Context, key string, value any)
// 指定 key 获取 SessionValues 中的一个值,key 不存在时第二个返回值为 false,否则为 true
func GetSessionValue(ctx context.Context, key string) (any, bool)
Transfer SubAgents
Agent 运行时产生带有包含 TransferAction 的 AgentEvent 后,Eino ADK 会调用 Action 指定的 Agent,被调用的 Agent 被称为子 Agent(SubAgent)。TransferAction 可以使用 NewTransferToAgentAction 快速创建:
import "github.com/cloudwego/eino/adk"
event := adk.NewTransferToAgentAction("dest agent name")
为了让 Eino ADK 在接受到 TransferAction 可以找到子 Agent 实例并运行,在运行前需要先调用 SetSubAgents 将可能的子 Agent 注册到 Eino ADK 中:
// github.com/cloudwego/eino/adk/flow.go
func SetSubAgents(ctx context.Context, agent Agent, subAgents []Agent) (Agent, error)
💡 Transfer 的含义是将任务移交给子 Agent,而不是委托或者分配,因此:
- 区别于 ToolCall,通过 Transfer 调用子 Agent,子 Agent 运行结束后,不会再调用父 Agent 总结内容或进行下一步操作。
- 调用子 Agent 时,子 Agent 的输入仍然是原始输入,父 Agent 的输出会作为上下文供子 Agent 参考。
以上描述中,产生 TransferAction Agent 天然清楚自己的子 Agent 有哪些,另外一些 Agent 需要根据不同场景配置不同的子 Agent,比如 Eino ADK 提供的 ChatModelAgent,这是一个通用 Agent 模板,需要根据业务实际场景配置子 Agent。这样的 Agent 需要能动态地注册父子 Agent,Eino 定义了 OnSubAgents 接口,用来支持此功能:
// github.com/cloudwego/eino/adk/interface.go
type OnSubAgents interface {
OnSetSubAgents(ctx context.Context, subAgents []Agent) error
OnSetAsSubAgent(ctx context.Context, parent Agent) error
OnDisallowTransferToParent(ctx context.Context) error
}
如果 Agent 实现了 OnSubAgents 接口,SetSubAgents 中会调用相应的方法向 Agent 注册。
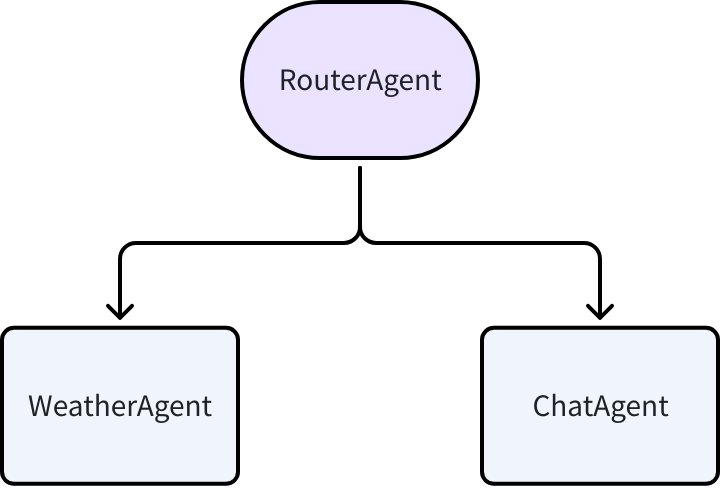
接下来以一个多功能对话 Agent 演示 Transfer 能力,目标是搭建一个可以查询天气或者与用户对话的 Agent,Agent 结构如下:
三个 Agent 均使用 ChatModelAgent 实现:
import (
"context"
"fmt"
"log"
"os"
"github.com/cloudwego/eino-ext/components/model/openai"
"github.com/cloudwego/eino/adk"
"github.com/cloudwego/eino/components/model"
"github.com/cloudwego/eino/components/tool"
"github.com/cloudwego/eino/components/tool/utils"
"github.com/cloudwego/eino/compose"
)
func newChatModel() model.ToolCallingChatModel {
cm, err := openai.NewChatModel(context.Background(), &openai.ChatModelConfig{
APIKey: os.Getenv("OPENAI_API_KEY"),
Model: os.Getenv("OPENAI_MODEL"),
})
if err != nil {
log.Fatal(err)
}
return cm
}
type GetWeatherInput struct {
City string `json:"city"`
}
func NewWeatherAgent() adk.Agent {
weatherTool, err := utils.InferTool(
"get_weather",
"Gets the current weather for a specific city.", // English description
func(ctx context.Context, input *GetWeatherInput) (string, error) {
return fmt.Sprintf(`the temperature in %s is 25°C`, input.City), nil
},
)
if err != nil {
log.Fatal(err)
}
a, err := adk.NewChatModelAgent(context.Background(), &adk.ChatModelAgentConfig{
Name: "WeatherAgent",
Description: "This agent can get the current weather for a given city.",
Instruction: "Your sole purpose is to get the current weather for a given city by using the 'get_weather' tool. After calling the tool, report the result directly to the user.",
Model: newChatModel(),
ToolsConfig: adk.ToolsConfig{
ToolsNodeConfig: compose.ToolsNodeConfig{
Tools: []tool.BaseTool{weatherTool},
},
},
})
if err != nil {
log.Fatal(err)
}
return a
}
func NewChatAgent() adk.Agent {
a, err := adk.NewChatModelAgent(context.Background(), &adk.ChatModelAgentConfig{
Name: "ChatAgent",
Description: "A general-purpose agent for handling conversational chat.", // English description
Instruction: "You are a friendly conversational assistant. Your role is to handle general chit-chat and answer questions that are not related to any specific tool-based tasks.",
Model: newChatModel(),
})
if err != nil {
log.Fatal(err)
}
return a
}
func NewRouterAgent() adk.Agent {
a, err := adk.NewChatModelAgent(context.Background(), &adk.ChatModelAgentConfig{
Name: "RouterAgent",
Description: "A manual router that transfers tasks to other expert agents.",
Instruction: `You are an intelligent task router. Your responsibility is to analyze the user's request and delegate it to the most appropriate expert agent.If no Agent can handle the task, simply inform the user it cannot be processed.`,
Model: newChatModel(),
})
if err != nil {
log.Fatal(err)
}
return a
}
之后使用 Eino ADK 的 Transfer 能力搭建 Multi-Agent 并运行,ChatModelAgent 实现了 OnSubAgent 接口,在 adk.SetSubAgents 方法中会使用此接口向 ChatModelAgent 注册父/子 Agent,不需要用户处理 TransferAction 生成问题:
import (
"context"
"fmt"
"log"
"os"
"github.com/cloudwego/eino/adk"
"github.com/cloudwego/eino-examples/adk/intro/transfer/internal"
)
func main() {
weatherAgent := internal.NewWeatherAgent()
chatAgent := internal.NewChatAgent()
routerAgent := internal.NewRouterAgent()
ctx := context.Background()
a, err := adk.SetSubAgents(ctx, routerAgent, []adk.Agent{chatAgent, weatherAgent})
if err != nil {
log.Fatal(err)
}
runner := adk.NewRunner(ctx, adk.RunnerConfig{
Agent: a,
})
// query weather
println("\n\n>>>>>>>>>query weather<<<<<<<<<")
iter := runner.Query(ctx, "What's the weather in Beijing?")
for {
event, ok := iter.Next()
if !ok {
break
}
if event.Err != nil {
log.Fatal(event.Err)
}
if event.Action != nil {
fmt.Printf("\nAgent[%s]: transfer to %+v\n\n======\n", event.AgentName, event.Action.TransferToAgent.DestAgentName)
} else {
fmt.Printf("\nAgent[%s]:\n%+v\n\n======\n", event.AgentName, event.Output.MessageOutput.Message)
}
}
// failed to route
println("\n\n>>>>>>>>>failed to route<<<<<<<<<")
iter = runner.Query(ctx, "Book me a flight from New York to London tomorrow.")
for {
event, ok := iter.Next()
if !ok {
break
}
if event.Err != nil {
log.Fatal(event.Err)
}
if event.Action != nil {
fmt.Printf("\nAgent[%s]: transfer to %+v\n\n======\n", event.AgentName, event.Action.TransferToAgent.DestAgentName)
} else {
fmt.Printf("\nAgent[%s]:\n%+v\n\n======\n", event.AgentName, event.Output.MessageOutput.Message)
}
}
}
得到结果:
query weather««««<
Agent[RouterAgent]:
assistant:
tool_calls:
{Index:
ID:call_SKNsPwKCTdp1oHxSlAFt8sO6 Type:function Function:{Name:transfer_to_agent Arguments:{“agent_name”:“WeatherAgent”}} Extra:map[]} finish_reason: tool_calls
usage: &{201 17 218}
======
Agent[RouterAgent]: transfer to WeatherAgent
======
Agent[WeatherAgent]:
assistant:
tool_calls:
{Index:
ID:call_QMBdUwKj84hKDAwMMX1gOiES Type:function Function:{Name:get_weather Arguments:{“city”:“Beijing”}} Extra:map[]} finish_reason: tool_calls
usage: &{255 15 270}
======
Agent[WeatherAgent]:
tool: the temperature in Beijing is 25°C
tool_call_id: call_QMBdUwKj84hKDAwMMX1gOiES
tool_call_name: get_weather
======
Agent[WeatherAgent]:
assistant: The current temperature in Beijing is 25°C.
finish_reason: stop
usage: &{286 11 297}
======
failed to route««««<
Agent[RouterAgent]:
assistant: I’m unable to assist with booking flights. Please use a relevant travel service or booking platform to make your reservation.
finish_reason: stop
usage: &{206 23 229}
======
完整示例见:github.com/cloudwego/eino-examples/