Basic Auth
Hertz provides an implementation of Basic Auth.
There are various types of Hertz middleware, which are simply divided into two categories.
Server-side middleware is a function in the HTTP request-response cycle that provides a convenient mechanism for inspecting and filtering HTTP requests entering your application, such as logging each request or enabling CORS.
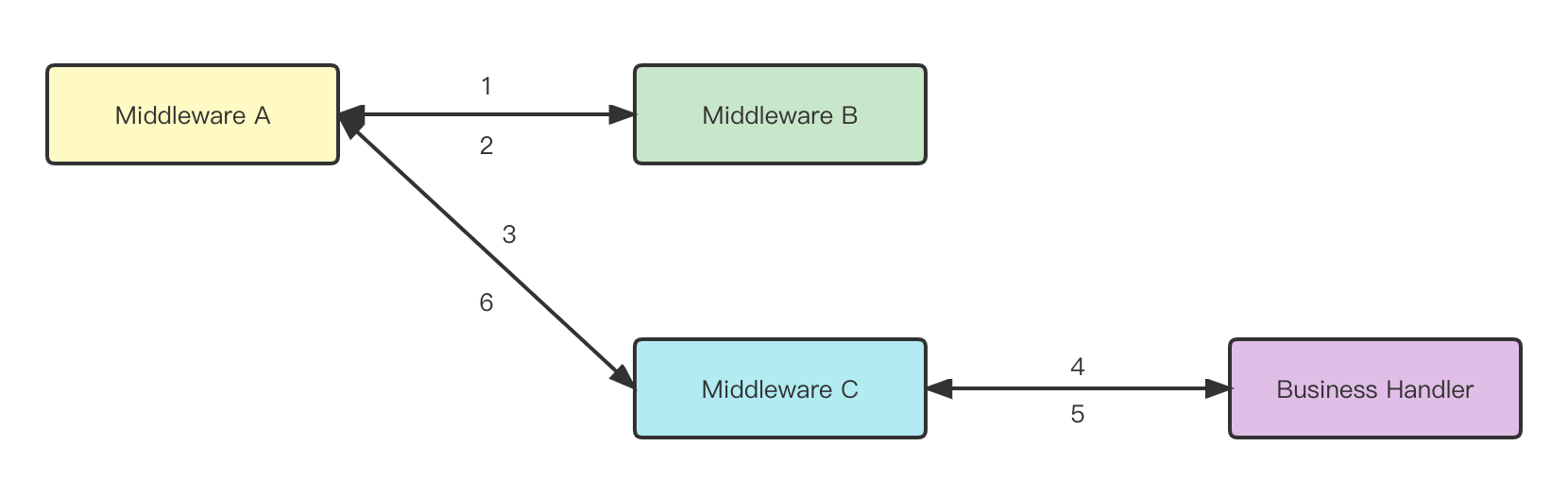 |
|---|
| Figure 1: middleware call chain |
Middleware can perform tasks before or after passing the request deeper into the application:
.Next can be omitted..Next must be called explicitly, see middleware C in Figure 1.// One way
func MyMiddleware() app.HandlerFunc {
return func(ctx context.Context, c *app.RequestContext) {
// pre-handle
// ...
// if there is no 'post-handle' logic, the 'c.Next(ctx)' can be omitted.
c.Next(ctx)
}
}
// The other way
func MyMiddleware() app.HandlerFunc {
return func(ctx context.Context, c *app.RequestContext) {
c.Next(ctx) // call the next middleware(handler)
// post-handle
...
}
}
Server-level middleware will take effect on all routing of the server
h := server.Default()
h.Use(MyMiddleware())
The group-level middleware takes effect on the paths under the current routing group
h := server.Default()
group := h.Group("/group")
group.Use(GroupMiddleware())
or
package main
import (
"context"
"fmt"
"github.com/cloudwego/hertz/pkg/app"
"github.com/cloudwego/hertz/pkg/app/server"
)
func GroupMiddleware() []app.HandlerFunc {
return []app.HandlerFunc{func(ctx context.Context, c *app.RequestContext) {
fmt.Println("group middleware")
c.Next(ctx)
}}
}
func main() {
h := server.Default(server.WithHostPorts("127.0.0.1:8888"))
group := h.Group("/group", append(GroupMiddleware(),
func(ctx context.Context, c *app.RequestContext) {
fmt.Println("group middleware 2")
c.Next(ctx)
})...)
// ...
h.Spin()
}
A route-level middleware only takes effect on the current route
package main
import (
"context"
"fmt"
"net/http"
"github.com/cloudwego/hertz/pkg/app"
"github.com/cloudwego/hertz/pkg/app/server"
)
func PathMiddleware() []app.HandlerFunc {
return []app.HandlerFunc{func(ctx context.Context, c *app.RequestContext) {
fmt.Println("path middleware")
c.Next(ctx)
}}
}
func main() {
h := server.Default(server.WithHostPorts("127.0.0.1:8888"))
h.GET("/path", append(PathMiddleware(),
func(ctx context.Context, c *app.RequestContext) {
c.String(http.StatusOK, "path")
})...)
h.Spin()
}
If you use the hz tool and IDL to develop a project, the router folder will automatically generate group-level middleware and route-level middleware templates based on services and methods. You can add corresponding logic to it and customize your own personalized middleware.
The Hertz framework already presets the commonly used Recover middleware, which can be registered by Default with server.Default().
Hertz provides frequently-used middlewares such as BasicAuth, CORS, JWT etc., more implementations can be found at hertz-contrib. If you need others, please make an issue.
Client-side middleware can be executed before the request is made or after the response is obtained:
The middleware implementation on the Client side is different from that on the Server side. The Client side cannot get the index of the middleware to increase, so the Client middleware uses nested functions to build the middleware in advance. When implementing client-side customized middleware, you can refer to the following code.
func MyMiddleware(next client.Endpoint) client.Endpoint {
return func(ctx context.Context, req *protocol.Request, resp *protocol.Response) (err error) {
// pre-handle
// ...
err = next(ctx, req, resp)
if err != nil {
return
}
// post-handle
// ...
}
}
Note: the next method must be executed to continue calls to the subsequent middleware. If you want to stop the middleware call, just return before next.
Registering custom middleware is the same as on the server side.
c, err := client.NewClient()
c.Use(MyMiddleware)
package main
import (
"context"
"fmt"
"github.com/cloudwego/hertz/pkg/app/client"
"github.com/cloudwego/hertz/pkg/protocol"
)
func MyMiddleware(next client.Endpoint) client.Endpoint {
return func(ctx context.Context, req *protocol.Request, resp *protocol.Response) (err error) {
// pre-handle
// ...
fmt.Println("before request")
req.AppendBodyString("k1=v1&")
err = next(ctx, req, resp)
if err != nil {
return
}
// post-handle
// ...
fmt.Println("after request")
return nil
}
}
func main() {
client, _ := client.NewClient()
client.Use(MyMiddleware)
statusCode, body, err := client.Post(context.Background(),
[]byte{},
"http://httpbin.org/redirect-to?url=http%3A%2F%2Fhttpbin.org%2Fpost&status_code=302",
&protocol.Args{})
fmt.Printf("%d, %s, %s", statusCode, body, err)
}
Middleware may be executed more than once, such as redirect, etc., idempotency needs to be considered
When implementing server-side middleware, the RequestContext related operation is usually used, as shown in RequestContext.
A server-side middleware is a handler, and the related operations of the handler can be found in Handler.
The server-side middleware will be executed in the order defined, if you want to terminate the middleware call quickly, you can use the following methods, noting that the current middleware will still execute.
ctx.Abort():terminate subsequent callsctx.AbortWithMsg(msg string, statusCode int):terminates subsequent calls and sets the body and status code for the Responsectx.AbortWithStatus(code int):terminates subsequent calls and sets the status codeHertz provides an implementation of Basic Auth.
The Recovery middleware is preset by the Hertz framework to provide the feature of Panic recovery for the Hertz framework.