Build Your First AI Agent with Eino ADK: Starting from Excel Agent in Practice
Understanding Eino ADK Through the Excel Agent
This article will introduce you to how to build a powerful multi-agent system using Eino ADK (Agent Development Kit). Previous Eino ADK introduction link: Eino ADK: Master AI Agent Core Design Patterns, Build Agent Systems from Scratch
The example is based on the Excel Agent, a real business scenario. The Excel Agent is an intelligent assistant that can “understand your words, read your spreadsheets, and write and execute code”. It breaks down complex Excel processing work into clear steps, completing various Excel data processing tasks reliably through automatic planning, tool calling, and result verification.
Next, we will demonstrate how this Agent is built step by step using Eino ADK, starting from the complete architecture and functionality of the Excel Agent. This will help you understand the core design features of Eino ADK in a simple and accessible way, helping you get started with Eino ADK quickly and move toward building custom agents and AI application systems.
The complete code for this example is located at GitHub, and you can browse and download it at any time.
What is the Excel Agent?
The Excel Agent is an “intelligent assistant that understands Excel”. It first breaks down problems into steps, then executes and verifies results step by step. It can understand user questions and uploaded file content, propose feasible solutions, and select appropriate tools (system commands, generate and run Python code, web queries, etc.) to complete tasks.
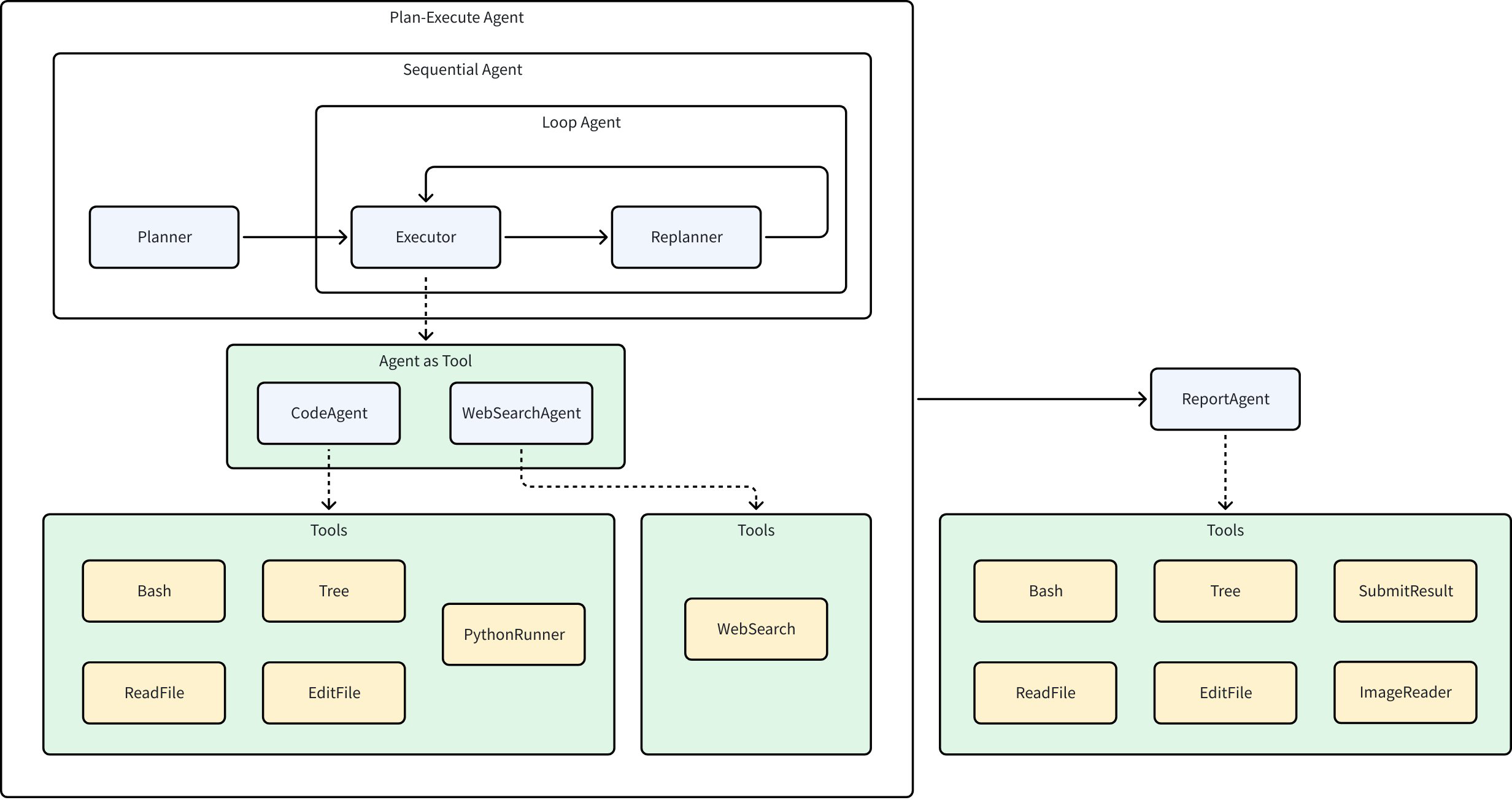
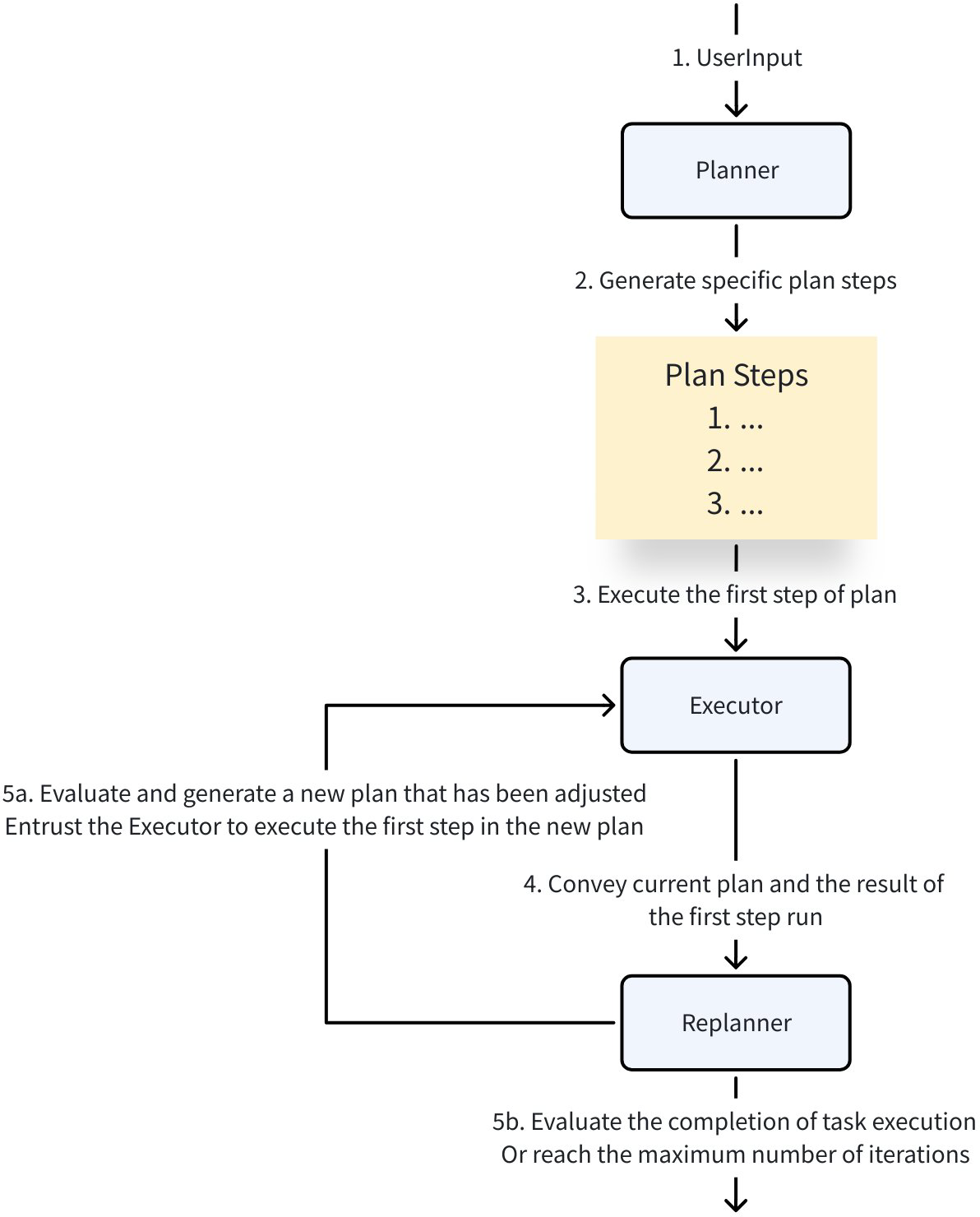
The Excel Agent is a Multi-Agent system built on Eino ADK. The complete architecture is shown in the figure below:
The Excel Agent contains several Agents with the following functions:
- Planner: Analyzes user input and breaks down user problems into executable plans
- Executor: Correctly executes the first step in the current plan
- CodeAgent: Receives instructions from the Executor, calls various tools (such as reading/writing files, running Python code, etc.) to complete tasks
- WebSearchAgent: Receives instructions from the Executor and performs web searches
- Replanner: Based on the Executor’s execution results and existing plans, decides whether to continue execution, adjust the plan, or complete execution
- ReportAgent: Generates summary reports based on the running process and results
Typical Use Cases for the Excel Agent
In real business scenarios, you can treat the Excel Agent as an “Excel expert + automation engineer”. When you provide a raw spreadsheet and target description, it will propose a solution and execute it:
- Data Cleaning and Formatting: Complete deduplication, null value handling, and date format standardization from an Excel file containing large amounts of data.
- Data Analysis and Report Generation: Extract monthly sales totals from sales data, perform aggregation statistics and pivot analysis, and finally generate and export chart reports.
- Automated Budget Calculation: Automatically calculate the total budget based on different departments’ budget requests and generate department budget allocation tables.
- Data Matching and Merging: Match and merge customer information tables from multiple different sources to generate a complete customer information database.
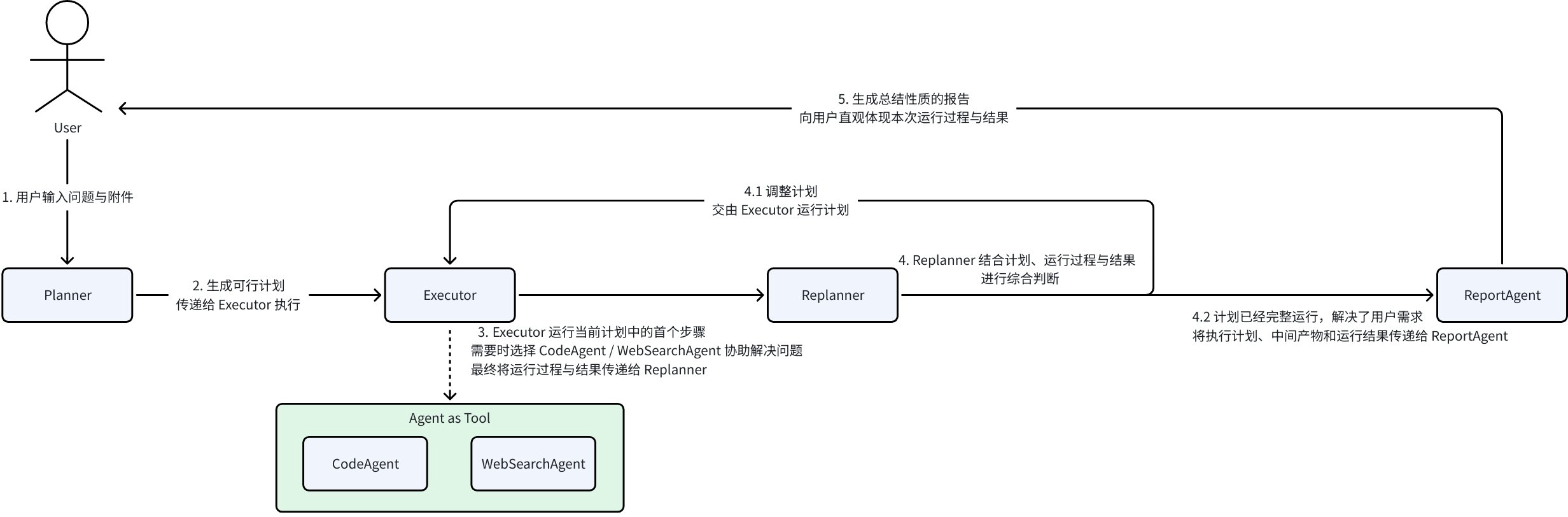
The complete execution flow of the Excel Agent is:
💡 Core Benefits:
- Less manual work, letting the Agent automatically complete complex and tedious Excel processing tasks.
- More stable output quality, reducing omissions and errors through the “plan-execute-reflect” closed loop.
- Stronger scalability, with each Agent built independently, low coupling facilitates iterative updates.
The Excel Agent can be used independently, or as a sub-Agent integrated into a composite multi-expert system, routed to by external systems to solve Excel domain-related problems.
Below, we will gradually break down the Excel Agent to gain an in-depth understanding of the core design features of Eino ADK and how to use these features to build efficient, flexible AI application systems.
ChatModelAgent: The Foundation for Interacting with LLMs
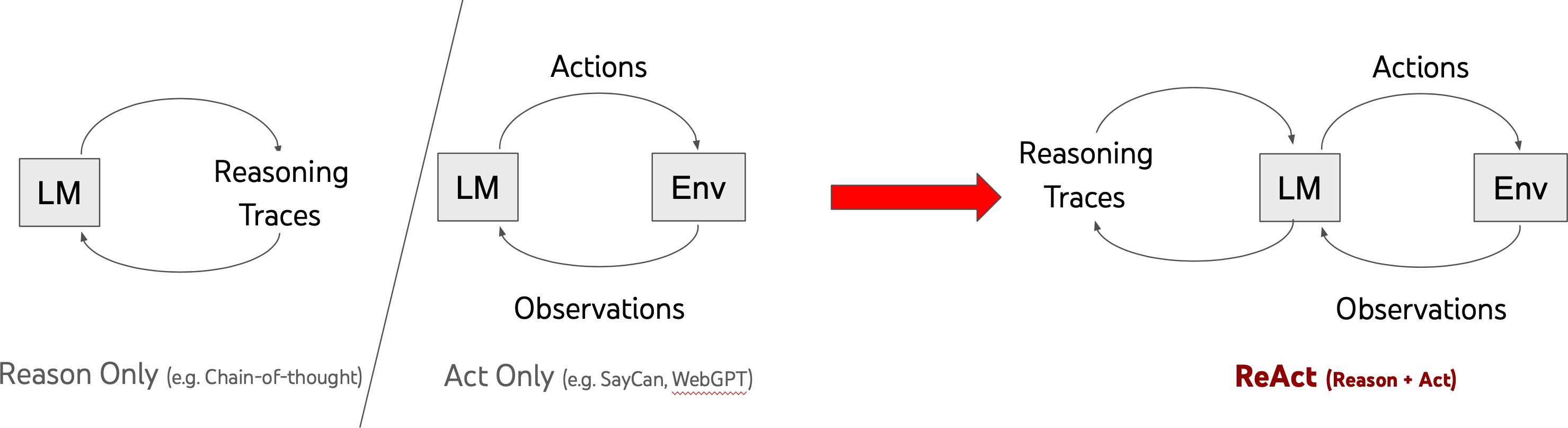
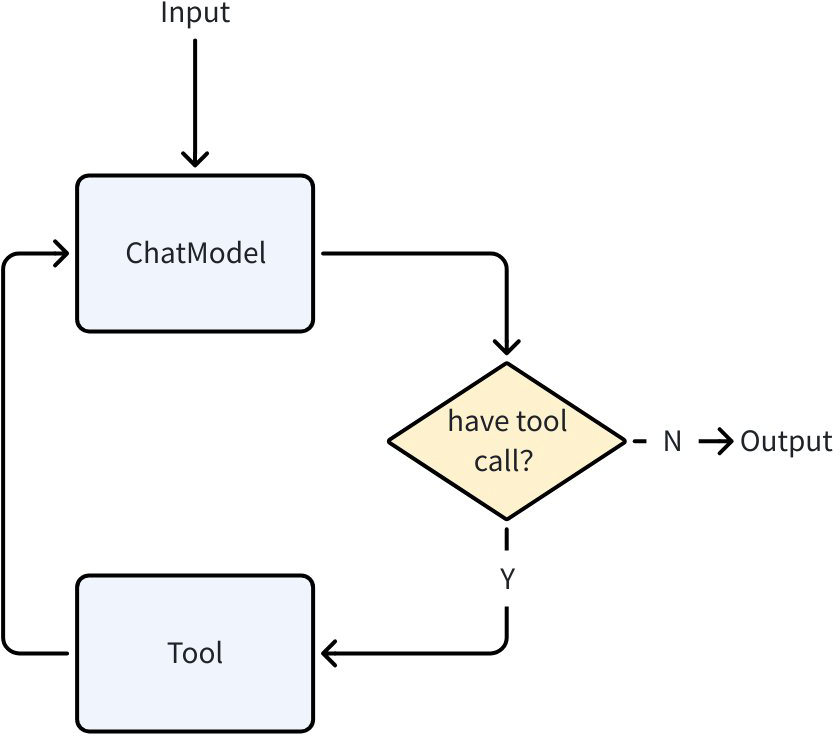
ChatModelAgent is a core pre-built Agent in Eino ADK that internally uses the ReAct pattern (a chain-of-reasoning pattern that lets the model “think-act-observe”):
ChatModelAgent is designed to let ChatModel perform explicit, step-by-step “thinking”, combining the thinking process to drive actions, observing historical thinking processes and action results to continue with the next step of thinking and action, ultimately solving complex problems:
- Call ChatModel (Reason)
- LLM returns tool call requests (Action)
- ChatModelAgent executes tools (Act)
- Return tool results to LLM (Observation), combined with previous context to continue generation until the model determines no more tool calls are needed
In the Excel Agent, the core of each Agent is such a ChatModelAgent. Taking the Executor running the step [Read the header information of the user’s input spreadsheet] as an example, we can understand how the ReAct pattern manifests in ChatModelAgent by observing the complete running process:
- Executor: After judgment, transfers the task to CodeAgent for execution
- CodeAgent: Receives the task [Read the header information of the user’s input spreadsheet]
- Think-1: The context doesn’t provide all files in the working directory, need to check
- Act-1: Call the Bash tool, ls to view all files in the working directory
- Think-2: Found the user’s input file, determines need to write Python code to read the xlsx spreadsheet’s first row
- Act-2: Call the PythonRunner tool, write and run code, get the execution result
- Think-3: Got the xlsx first row, determines task is complete
- Execution complete, return the spreadsheet header information to Executor
Plan-Execute Agent: A Multi-Agent Collaboration Framework Based on “Plan-Execute-Reflect”
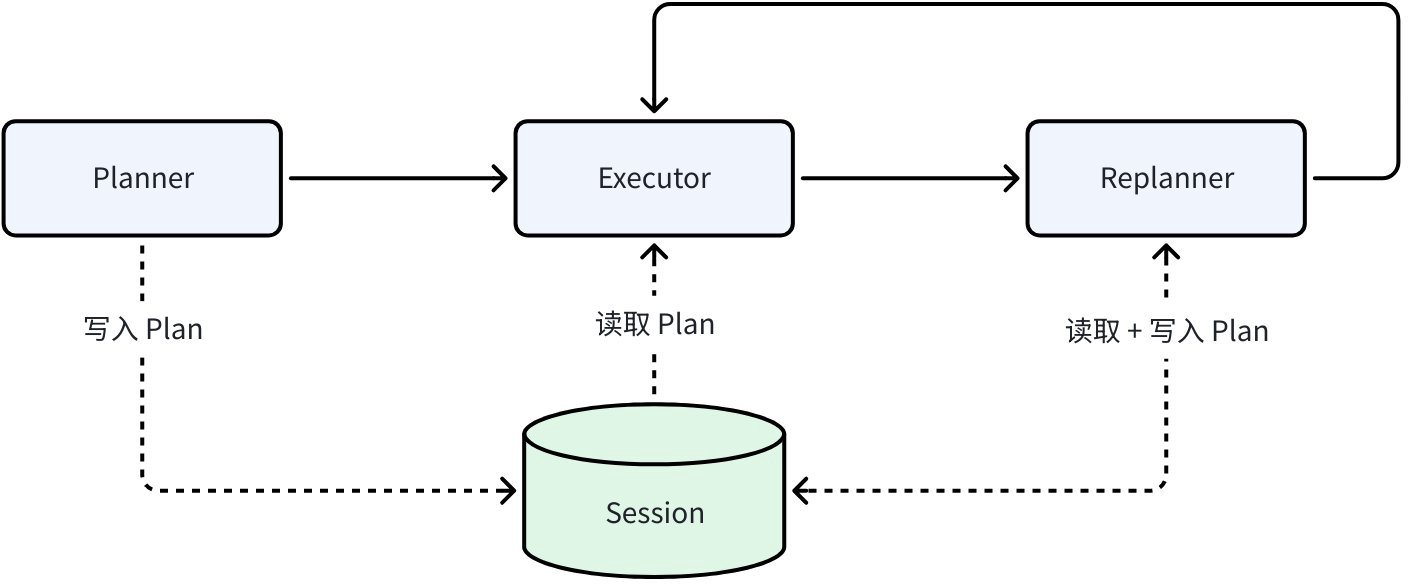
Plan-Execute Agent is a multi-agent collaboration framework in Eino ADK based on the “plan-execute-reflect” paradigm, designed to solve the problems of step-by-step decomposition, execution, and dynamic adjustment of complex tasks. Through the collaborative work of Planner, Executor, and Replanner - three core agents, it achieves structured task planning, tool call execution, progress evaluation, and dynamic replanning, ultimately achieving user goals:
// Complete code: https://github.com/cloudwego/eino/blob/main/adk/prebuilt/planexecute/plan_execute.go
// NewPlanner creates a new planner agent based on the provided configuration.
func NewPlanner(_ context.Context, cfg *PlannerConfig) (adk.Agent, error)
// NewExecutor creates a new executor agent.
func NewExecutor(ctx context.Context, cfg *ExecutorConfig) (adk.Agent, error)
// NewReplanner creates a new replanner agent.
func NewReplanner(_ context.Context, cfg *ReplannerConfig) (adk.Agent, error)
// New creates a new plan-execute-replan agent with the given configuration.
func New(ctx context.Context, cfg *Config) (adk.Agent, error)
The Excel Agent’s core capability is precisely [solving user problems in the Excel domain], which aligns with this agent collaboration framework:
- Planner: Clarifies goals, automatically decomposes into executable steps
- Executor: Calls tools (Excel reading, system commands, Python code) to complete each detailed step in the plan
- Replanner: Decides to continue, adjust the plan, or end based on execution progress
Planner and Replanner break down vague user instructions into clear, executable step lists - plans (Plan) containing multiple steps (Step). Eino ADK provides a flexible Plan interface definition for this, supporting users to customize Plan structure and details:
type Plan interface {
// FirstStep returns the first step to be executed in the plan.
FirstStep() string
// Marshaler serializes the Plan into JSON.
// The resulting JSON can be used in prompt templates.
json.Marshaler
// Unmarshaler deserializes JSON content into the Plan.
// This processes output from structured chat models or tool calls into the Plan structure.
json.Unmarshaler
}
By default, the framework uses the built-in Plan structure as a fallback configuration. For example, here is a complete execution plan generated by the Excel Agent:
### Task Plan
- [x] 1. Read the contents of '模拟出题.csv' from the working directory into a pandas DataFrame.
- [x] 2. Identify the question type (e.g., multiple-choice, short-answer) for each row in the DataFrame.
- [x] 3. For non-short-answer questions, restructure the data to place question, answer, explanation, and options in the same row.
- [x] 4. For short-answer questions, merge the answer content into the explanation column and ensure question and merged explanation are in the same row.
- [x] 5. Verify that all processed rows have question, answer (where applicable), explanation, and options (where applicable) in a single row with consistent formatting.
- [x] 6. Generate a cleaned report presenting the formatted questions with all relevant components (question, answer, explanation, options) in unified rows.
Workflow Agents: Controllable Multi-Agent Execution Pipeline
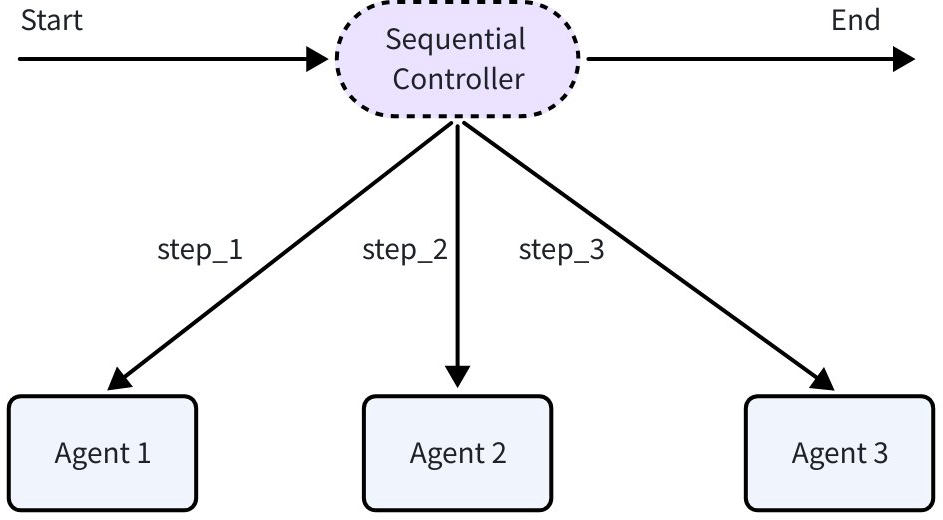
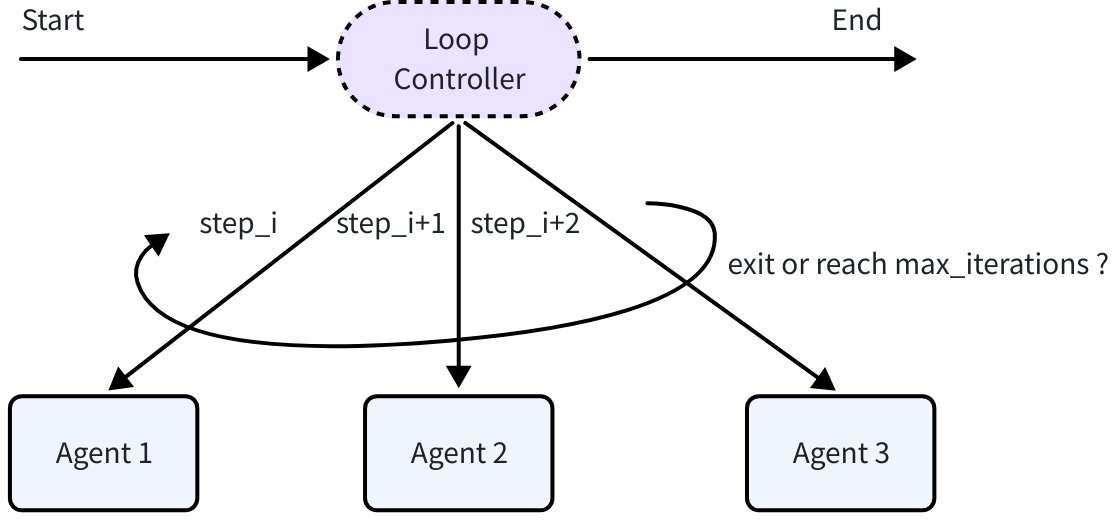
In the Excel Agent, there are situations where agents need to run in a specific order:
- Sequential execution: Run Planner first, then Executor and Replanner; Planner runs only once.
- Loop execution: Executor and Replanner need to run multiple times in a loop as needed, each loop runs Executor first then Replanner
- Sequential execution: After Plan-Executor completes overall execution, run ReportAgent once for summary.
For these scenarios with fixed execution flows, Eino ADK provides three workflow orchestration methods to help users quickly build controllable workflows:
SequentialAgent: Executes a series of sub-Agents sequentially according to the order provided in the configuration. After each sub-Agent completes execution, its output is passed to the next sub-Agent through the History mechanism, forming a linear execution chain.
import github.com/cloudwego/eino/adk // Execute in sequence: Create research plan -> Search materials -> Write report sequential := adk.NewSequentialAgent(ctx, &adk.SequentialAgentConfig{ Name: "research_pipeline", SubAgents: []adk.Agent{ planAgent, // Create research plan searchAgent, // Search materials writeAgent, // Write report }, })
LoopAgent: Repeatedly executes the configured sub-Agent sequence until the maximum number of iterations is reached or a sub-Agent produces an ExitAction. The results of each iteration accumulate, and subsequent iterations can access all historical information. LoopAgent is implemented based on SequentialAgent.
import github.com/cloudwego/eino/adk // Loop execution 5 times, each sequence: Analyze current state -> Propose improvement plan -> Verify improvement results loop := adk.NewLoopAgent(ctx, &adk.LoopAgentConfig{ Name: "iterative_optimization", SubAgents: []adk.Agent{ analyzeAgent, // Analyze current state improveAgent, // Propose improvement plan validateAgent, // Verify improvement results }, MaxIterations: 5, })
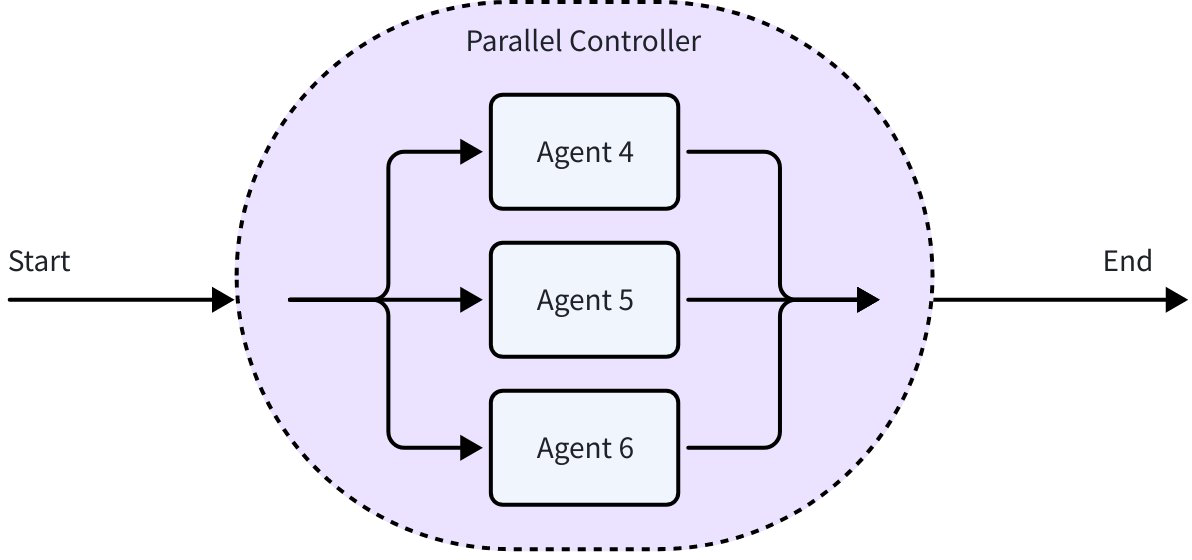
ParallelAgent: Allows multiple sub-Agents to execute concurrently based on the same input context. All sub-Agents receive the same initial input, each running in an independent goroutine (a lightweight concurrent execution unit in Go), finally collecting all sub-Agent execution results and outputting them sequentially to
AsyncIterator.import github.com/cloudwego/eino/adk // Concurrent execution: Sentiment analysis + Keyword extraction + Content summary parallel := adk.NewParallelAgent(ctx, &adk.ParallelAgentConfig{ Name: "multi_analysis", SubAgents: []adk.Agent{ sentimentAgent, // Sentiment analysis keywordAgent, // Keyword extraction summaryAgent, // Content summary }, })
Agent Abstraction: The Foundation for Flexibly Defining Agents
The core of Eino ADK is a simple yet powerful Agent interface. Each Agent has a clear identity (Name), clear responsibilities (Description), and standardized execution methods (Run), providing the foundation for Agent discovery and invocation. Whether it’s a simple Q&A bot or a complex multi-step task processing system, they can all be implemented through this unified interface.
Unified Agent Abstraction: All pre-built Agents provided by ADK (ChatModelAgent, Plan-Execute Agent, Workflow Agents) follow this interface definition. You can also write custom Agents based on this interface to meet customized requirements.
type Agent interface { Name(ctx context.Context) string Description(ctx context.Context) string Run(ctx context.Context, input *AgentInput, options ...AgentRunOption) *AsyncIterator[*AgentEvent] }Standardized Input: Agents typically have LLM as their core, so the Agent input defined by Eino ADK is consistent with LLM input:
type AgentInput struct { Messages []Message EnableStreaming bool } type Message = *schema.Message // *schema.Message is the structure definition for model input and outputAsynchronous Event-Driven Output: The Agent’s output is an asynchronous iterator of AgentEvent, where AgentEvent represents the core event data generated by the Agent during its execution. It contains the Agent’s metadata, output, behavior, and error information:
type AgentEvent struct { AgentName string // Name of the Agent that produced the Event (automatically filled by the framework) RunPath []RunStep // Complete execution trace to reach the current Agent (automatically filled by the framework) Output *AgentOutput // Agent output message content Action *AgentAction // Agent action event content Err error // Agent error } type AgentOutput struct { MessageOutput *MessageVariant // Model message output content CustomizedOutput any // Customized output content } type MessageVariant struct { IsStreaming bool // Whether it's streaming output Message Message // Non-streaming message output MessageStream MessageStream // Streaming message output Role schema.RoleType // Message role ToolName string // Tool name } type AgentAction struct { Exit bool // Agent exit Interrupted *InterruptInfo // Agent interrupted TransferToAgent *TransferToAgentAction // Agent transfer CustomizedAction any // Customized Agent action }
The asynchronous iterator allows the Agent to send messages to the iterator at any time during execution (Agent’s model call results, tool execution results, intermediate states, etc.), while the caller consumes this series of events in an ordered, blocking manner:
iter := myAgent.Run(ctx, "hello") // get AsyncIterator
for {
event, ok := iter.Next()
if !ok {
break
}
// handle event
}
Agent Collaboration: Data Passing Hidden Behind Agents
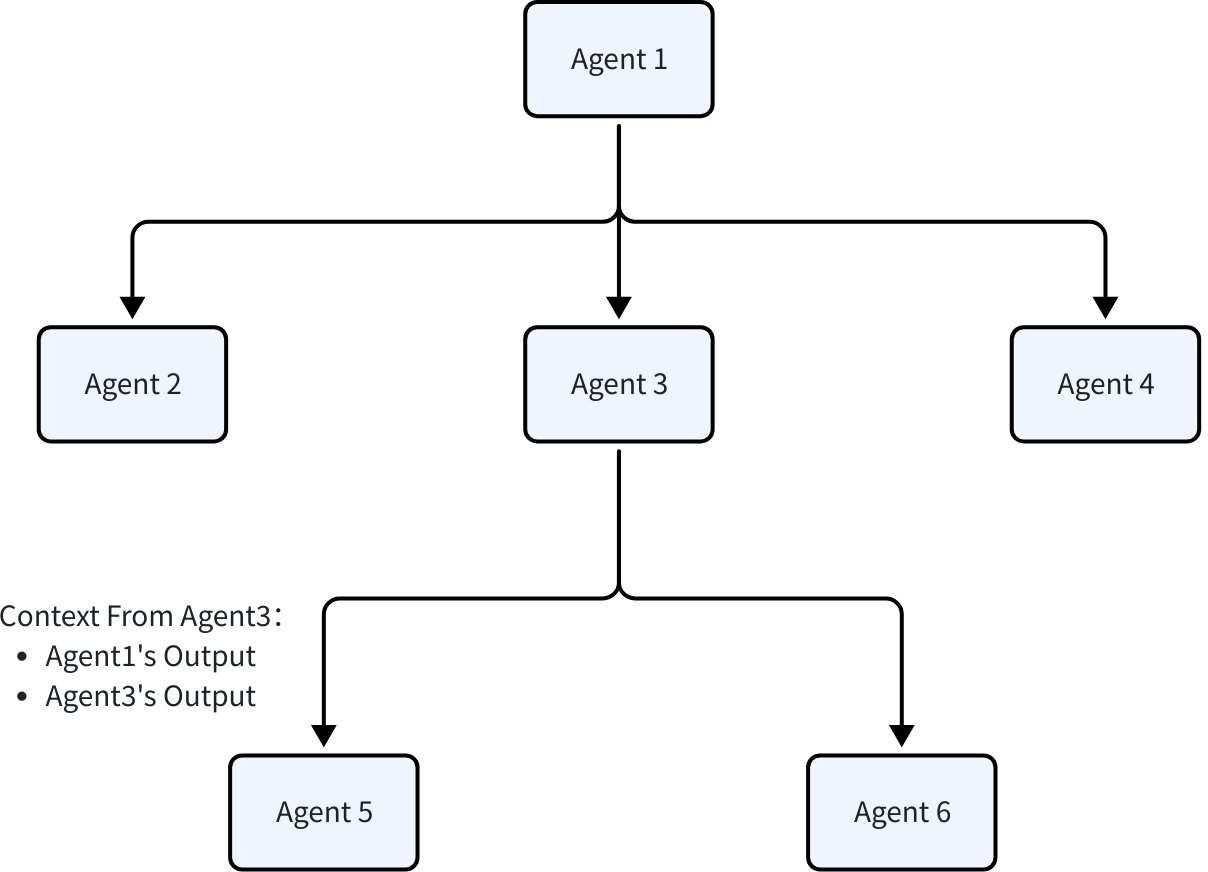
The nodes in the Excel Agent architecture diagram represent each specific Agent, and the edges represent data flow and task transfer. When building multi-Agent systems, it’s crucial to enable efficient and accurate information sharing between different Agents.
This information includes not only the Agent’s input and output, but also various additional information that is global and partially visible, such as:
- Executor execution needs to get a structured plan (Plan) that can be broken down into detailed steps (Step) from Planner/Replanner, rather than an unstructured raw LLM output message.
- ReportAgent needs to get the complete execution plan, execution process, and execution artifacts to correctly generate reports.
Eino ADK includes two basic data passing mechanisms:
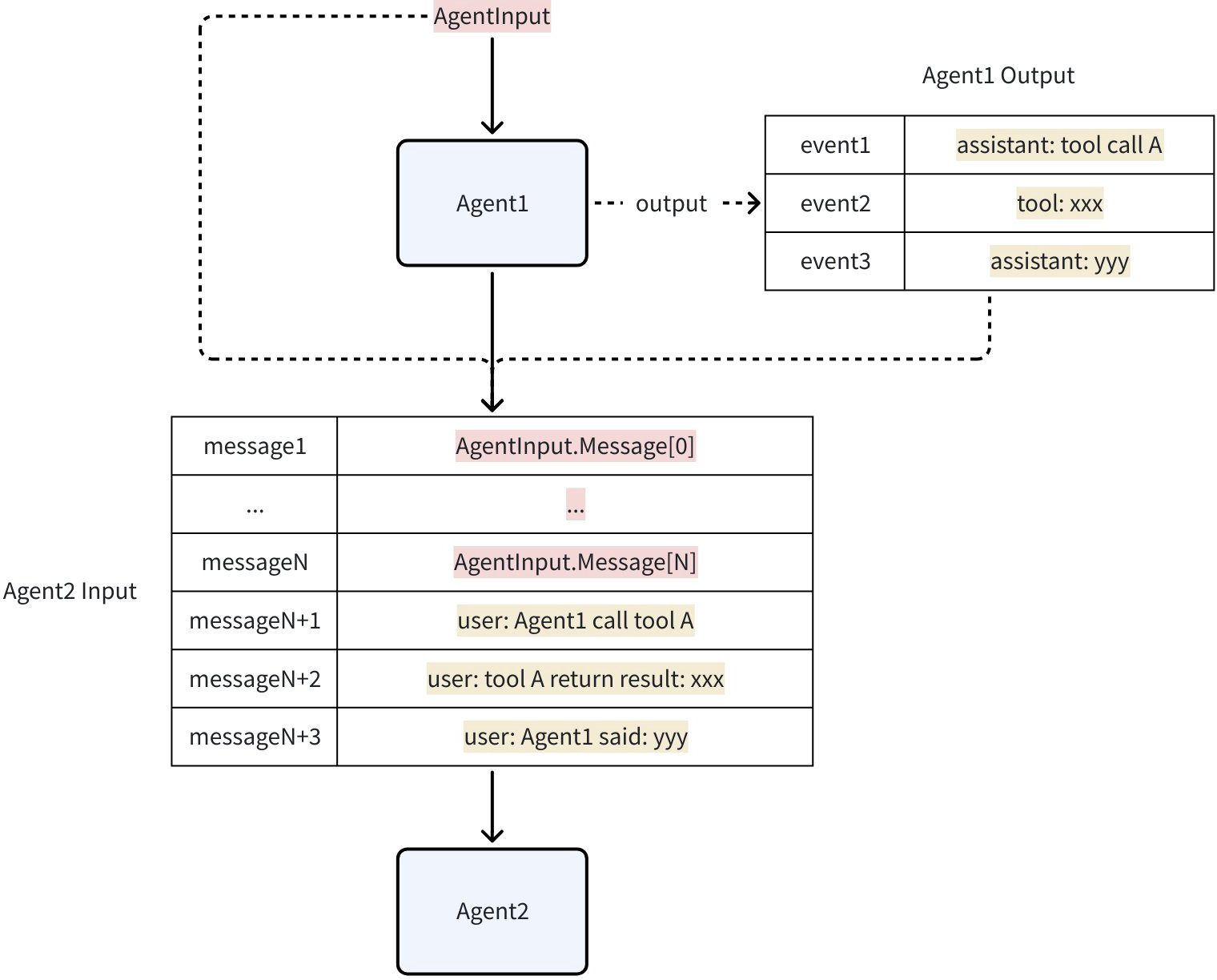
- History: Every AgentEvent produced by an Agent is saved to this hidden History. When calling a new Agent, the AgentEvents in History are converted and concatenated into AgentInput. By default, Assistant or Tool Messages from other Agents are converted to User Messages. This is equivalent to telling the current LLM: “Just now, Agent_A called some_tool and returned some_result. Now, it’s your turn to make a decision.” In this way, other Agents’ behaviors are treated as “external information” or “factual statements” provided to the current Agent, rather than its own behavior, thus avoiding LLM context confusion.
Shared Session: Persistent KV storage during a single execution process, used to support cross-Agent state management and data sharing. Any Agent in a single execution can read and write SessionValues at any time. Taking the Plan-Execute Agent pattern as an example, Planner generates the initial plan and writes it to Session; Executor reads the plan from Session and executes it; Replanner reads the current plan from Session, combines it with execution results, and writes the updated plan back to Session to overwrite the current plan.
// Get all SessionValues within an Agent func GetSessionValues(ctx context.Context) map[string]any // Get value from SessionValues by specified key within an Agent func GetSessionValue(ctx context.Context, key string) (any, bool) // Add SessionValues within an Agent func AddSessionValue(ctx context.Context, key string, value any) // Batch add SessionValues within an Agent func AddSessionValues(ctx context.Context, kvs map[string]any) // WithSessionValues injects SessionValues from outside before Agent execution func WithSessionValues(v map[string]any) AgentRunOption
In addition to comprehensive data passing mechanisms between Agents, Eino ADK provides multiple Agent collaboration patterns based on practical experience:
- Preset Agent Execution Order (Workflow): Execute according to the flow preset in code, the Agent execution order is predetermined and predictable. Corresponds to the three paradigms mentioned in the Workflow Agents section.
- Transfer Execution: Carry the current Agent’s output result context and transfer the task to a sub-Agent for continued processing. Suitable for scenarios where agent functionality can be clearly divided into boundaries and hierarchies, often used in combination with ChatModelAgent for dynamic routing through LLM generation results. Structurally, two Agents collaborating in this way are called parent-child Agents:
// Set parent-child Agent relationship
func SetSubAgents(ctx context.Context, agent Agent, subAgents []Agent) (Agent, error)
// Construct Transfer Event by specifying target Agent name
func NewTransferToAgentAction(destAgentName string) *AgentAction
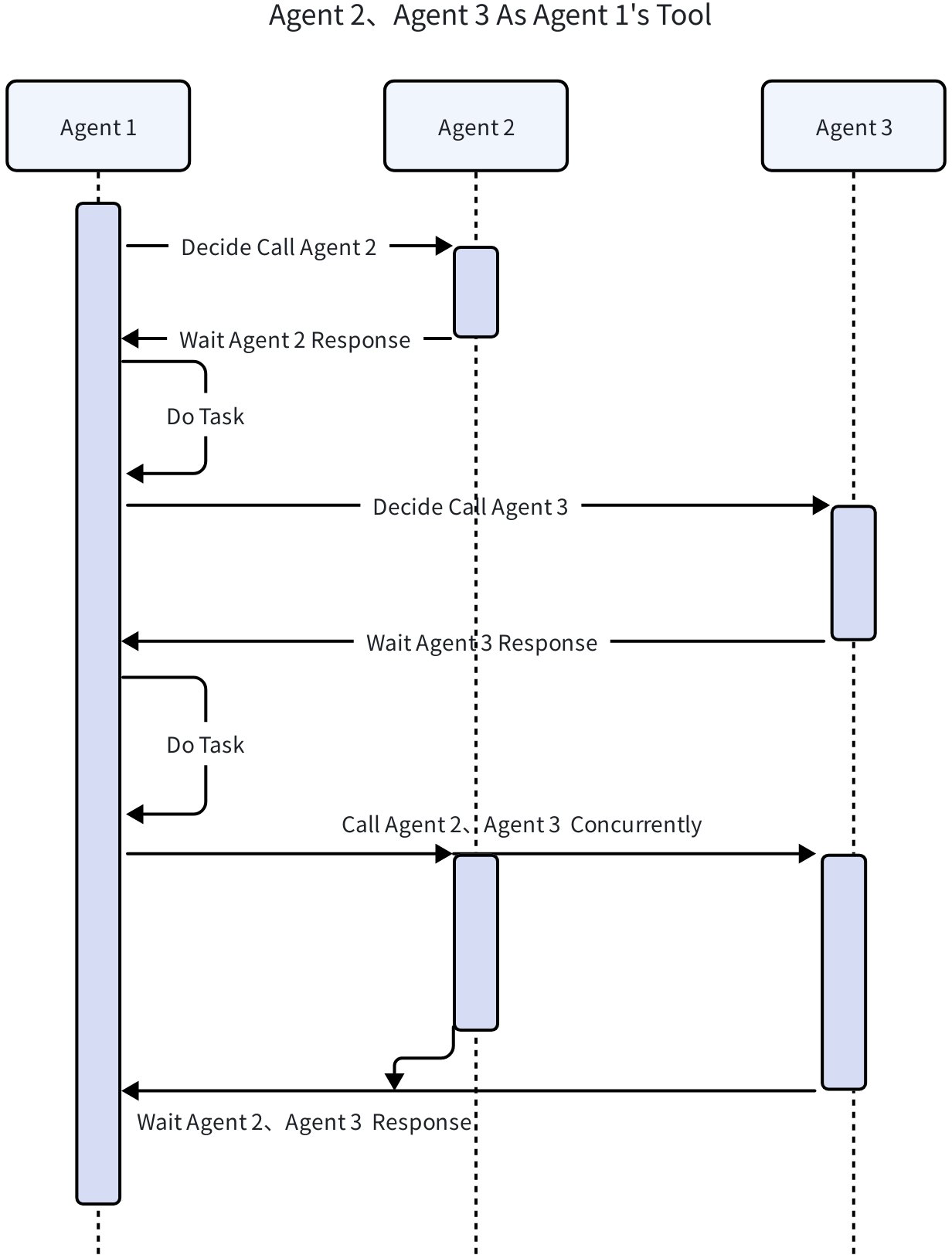
- Explicit Invocation (ToolCall): Treat the Agent as a tool for invocation, suitable for scenarios where Agent execution only requires clear and explicit parameters rather than complete execution context. Often combined with ChatModelAgent, running the Agent as a tool and returning results to ChatModel for continued processing. Additionally, ToolCall also supports calling regular tools that conform to the tool interface construction without containing an Agent.
// Convert Agent to Tool
func NewAgentTool(_ context.Context, agent Agent, options ...AgentToolOption) tool.BaseTool
Excel Agent Example Execution
Configure Environment and Input/Output Paths
Environment Variables: The complete environment variables required for Excel Agent execution can be found in the project README.
Execution Input: Includes a user requirement description and a series of files to be processed, where:
The first line in
main.gorepresents the user’s input requirement description, which you can modify:func main() { // query := schema.UserMessage("Count the recommended novel names and recommendation counts in the attachment file, and write the results to a file. Any content with 《》 is a novel name, form a table with headers for novel name and recommendation count, list same-named novels in one row only, and add up recommendation counts") // query := schema.UserMessage("Read the content in 模拟出题.csv, standardize the format to put question, answer, explanation, options in the same row, for short-answer questions just write the answer into the explanation") query := schema.UserMessage("Please help me extract the first column from the question.csv spreadsheet into a new csv") }adk/multiagent/integration-excel-agent/playground/inputis the default attachment input path. The attachment input path can be configured, refer to README.The
adk/multiagent/integration-excel-agent/playground/test_datapath provides several example files. You can copy files to the attachment input path for test execution:% tree adk/multiagent/integration-excel-agent/playground/test_data adk/multiagent/integration-excel-agent/playground/test_data ├── questions.csv ├── 推荐小说.txt └── 模拟出题.csv 1 directory, 3 files
Execution Output: Input attachments, intermediate artifacts, and final results from Excel Agent execution are all placed in the working path:
adk/multiagent/integration-excel-agent/playground/${uuid}. The output path can be configured, refer to README.
View Execution Results
A single Excel Agent execution creates a new working directory under the output path, completing tasks in that directory. Intermediate artifacts and final results generated during execution are written to that directory.
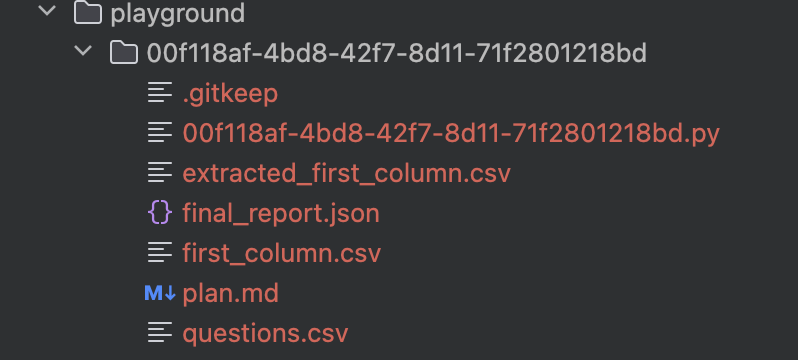
Taking the task Please help me extract the first column from question.csv spreadsheet into a new csv as an example, the files in the working directory after execution include:
Original input:
question.csvobtained from the input pathExecution plan from Planner/Replanner:
plan.md### Task Plan - [x] 1. {"desc":"Read the 'questions.csv' file into a pandas DataFrame."} - [x] 2. Save the extracted first column to a new CSV file.Code written by CodeAgent in Executor:
$uuid.pyimport pandas as pd df = pd.read_csv('questions.csv') first_column = df.iloc[:, _0_] first_column.to_csv('extracted_first_column.csv', index=_False_)Intermediate artifacts:
extracted_first_column.csvandfirst_column.csvtype multiple-choice ... short-answerFinal report:
final_report.json{ "is_success": true, "result": "Successfully extracted the first column from questions.csv and saved it to first_column.csv.", "files": [ { "path": "/User/user/go/src/github.com/cloudwego/eino-examples/adk/multiagent/integration-excel-agent/playground/00f118af-4bd8-42f7-8d11-71f2801218bd/first_column.csv", "desc": "A CSV file containing only the first column data from the original questions.csv." } ] }
Execution Process Output
The Excel Agent outputs the execution results of each step to the log. Below, still using the task Please help me extract the first column from question.csv spreadsheet into a new csv as an example, we will show you several key steps and their outputs during Excel Agent execution, and through explaining the steps, intuitively present the Agent’s execution flow and powerful capabilities:
Planner generates initial plan in JSON format
name: Planner answer: { **"steps"**: [ { **"index"**: **1**, **"desc"**: **"Read the 'questions.csv' file into a pandas DataFrame."** }, { **"index"**: **2**, **"desc"**: **"Extract the first column from the DataFrame."** }, { **"index"**: **3**, **"desc"**: **"Save the extracted first column to a new CSV file."** } ] }Executor calls CodeAgent as a tool to execute the first step in the plan
name: Executor tool name: CodeAgent arguments: {"request":"Read the 'questions.csv' file into a pandas DataFrame using pandas. Use the pandas.read_csv function and store the result in a variable named df."}CodeAgent uses the PythonRunner tool to run code, and uses ReAct pattern for automatic error correction, fixing errors in the code
# CodeAgent uses PythonRunner tool to run code name: Executor tool name: PythonRunner arguments: {"code":"```python\nfirst_column = df.iloc[:, 0]\n```"} # PythonRunner code execution error name: Executor tool response: Traceback (most recent call last): File "/User/user/go/src/github.com/cloudwego/eino-examples/adk/multiagent/integration-excel-agent/playground/00f118af-4bd8-42f7-8d11-71f2801218bd/00f118af-4bd8-42f7-8d11-71f2801218bd.py", line 1, in <module> first_column = df.iloc[:, 0] ^^ NameError: name 'df' is not defined # ReAct pattern automatic error correction, fixing non-executable code name: Executor answer: The error occurs because the DataFrame `df` is not defined. We need to first load the data from the existing CSV file `questions.csv` into `df`. Here's the corrected code: tool name: PythonRunner arguments: {"code":"```python\nimport pandas as pd\ndf = pd.read_csv('questions.csv')\nfirst_column = df.iloc[:, 0]\nprint(first_column.head()) # Verify the result\n```"} # Code execution successful, return execution result name: Executor path: [{SequentialAgent} {plan_execute_replan} {Planner} {execute_replan} {Executor}] tool response: 0 multiple-choice 1 multiple-choice 2 multiple-choice 3 multiple-choice 4 multiple-choice Name: type, dtype: objectReplanner determines plan is complete, submits execution results to ReportAgent
name: Replanner answer: { **"is_success"**: **true**, **"result"**: **"Successfully extracted the first column from 'questions.csv' into the new CSV file 'extracted_first_column.csv'."**, **"files"**: [ { **"desc"**: **"New CSV file containing the first column data from the original spreadsheet"**, **"path"**: **"extracted_first_column.csv"** } ] }ReportAgent generates summary and ends execution
name: Report tool name: SubmitResult arguments: { **"is_success"**: **true**, **"result"**: **"Successfully extracted the first column from questions.csv and saved it to first_column.csv."**, **"files"**: [ { **"path"**: **"/User/user/go/src/github.com/cloudwego/eino-examples/adk/multiagent/integration-excel-agent/playground/00f118af-4bd8-42f7-8d11-71f2801218bd/first_column.csv"**, **"desc"**: **"A CSV file containing only the first column data from the original questions.csv."** } ] }
Summary
What the Excel Agent demonstrates is not the techniques of a “single agent”, but a set of Multi-Agent system engineering methodology based on Eino ADK:
- Built on the ReAct capability of ChatModelAgent as the foundation, enabling the model to “think and call tools”.
- With WorkflowAgents orchestration capabilities, allowing each Agent in the Multi-Agent system to run in the user-expected order.
- With the Planner–Executor–Replanner closed loop, enabling complex tasks to be “decomposable and error-correctable”.
- With History/Session data passing mechanisms, enabling multi-Agent systems to “collaborate and replay”.
💡 Start Your Agent Development Journey Now
- ⌨️ View Excel Agent source code: GitHub Excel Agent Source Code
- 📚 View more documentation: Eino ADK Documentation
- 🛠️ Browse ADK source code: Eino ADK Source Code
- 💡 Explore all ADK examples: Eino ADK Examples
- 🤝 Join the developer community: Exchange experiences and best practices with other developers
Eino ADK makes agent development simple and powerful!