Eino: ReAct Agent Manual
Introduction
Eino ReAct Agent is an agent framework that implements the ReAct logic, allowing users to quickly and flexibly build and invoke ReAct Agents.
💡 See the code implementation at: Implementation Directory
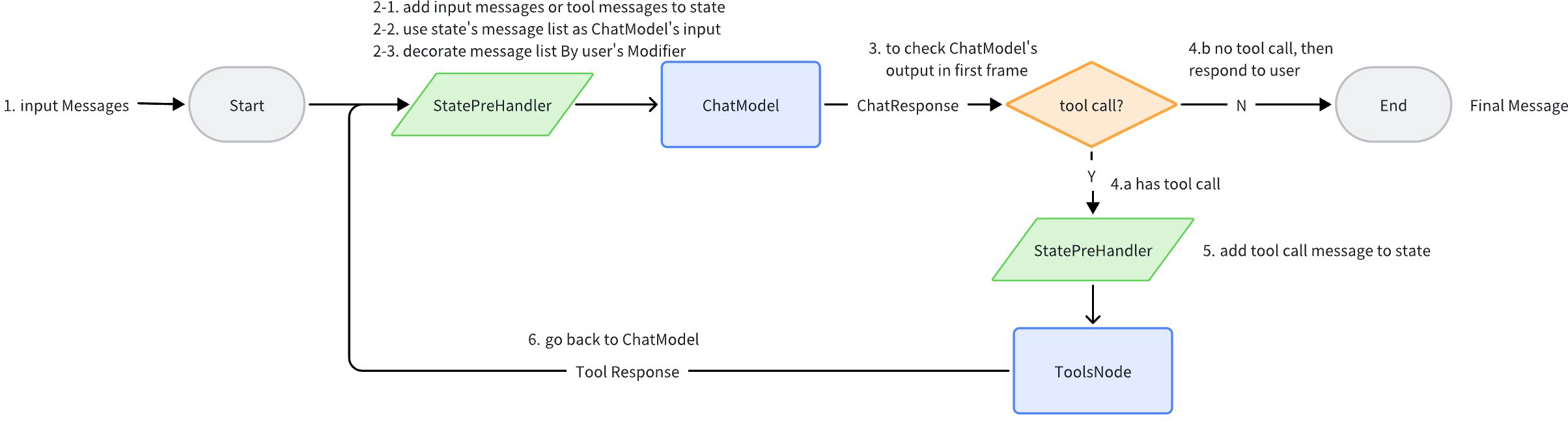
Node Topology & Data Flow Diagram
ReAct Agent uses compose.Graph as its orchestration scheme under the hood. Generally, there are 2 nodes: ChatModel and Tools. All historical messages during the intermediate running process are stored in state. Before passing all historical messages to ChatModel, the messages are copied and processed by MessageModifier, and the processed result is then passed to ChatModel. The process continues until ChatModel returns a message without any tool call, at which point the final message is returned.
When at least one Tool in the Tools list is configured with ReturnDirectly, the ReAct Agent structure becomes more complex: a Branch is added after ToolsNode to determine whether a ReturnDirectly Tool was called. If so, it goes directly to END; otherwise, it proceeds to ChatModel as usual.
Initialization
The ReactAgent initialization function is provided. Required parameters are Model and ToolsConfig. Optional parameters are MessageModifier, MaxStep, ToolReturnDirectly, and StreamToolCallChecker.
go get github.com/cloudwego/eino-ext/components/model/openai@latest
go get github.com/cloudwego/eino@latest
import (
"github.com/cloudwego/eino-ext/components/model/openai"
"github.com/cloudwego/eino/components/model"
"github.com/cloudwego/eino/components/tool"
"github.com/cloudwego/eino/compose"
"github.com/cloudwego/eino/flow/agent/react"
"github.com/cloudwego/eino/schema"
)
func main() {
// first initialize the required chatModel
toolableChatModel, err := openai.NewChatModel(...)
// initialize the required tools
tools := compose.ToolsNodeConfig{
InvokableTools: []tool.InvokableTool{mytool},
StreamableTools: []tool.StreamableTool{myStreamTool},
}
// create agent
agent, err := react.NewAgent(ctx, &react.AgentConfig{
ToolCallingModel: toolableChatModel,
ToolsConfig: tools,
...
}
}
Model
Since ReAct Agent needs to make tool calls, the Model needs to have ToolCall capability, so you need to configure a ToolCallingChatModel.
Inside the Agent, the WithTools interface is called to register the Agent’s tool list with the model. The definition is:
// BaseChatModel defines the basic interface for chat models.
// It provides methods for generating complete outputs and streaming outputs.
// This interface serves as the foundation for all chat model implementations.
//
//go:generate mockgen -destination ../../internal/mock/components/model/ChatModel_mock.go --package model -source interface.go
type BaseChatModel interface {
Generate(ctx context.Context, input []*schema.Message, opts ...Option) (*schema.Message, error)
Stream(ctx context.Context, input []*schema.Message, opts ...Option) (
*schema.StreamReader[*schema.Message], error)
}
// ToolCallingChatModel extends BaseChatModel with tool calling capabilities.
// It provides a WithTools method that returns a new instance with
// the specified tools bound, avoiding state mutation and concurrency issues.
type ToolCallingChatModel interface {
BaseChatModel
// WithTools returns a new ToolCallingChatModel instance with the specified tools bound.
// This method does not modify the current instance, making it safer for concurrent use.
WithTools(tools []*schema.ToolInfo) (ToolCallingChatModel, error)
}
Currently, eino provides implementations such as openai and ark, as long as the underlying model supports tool call.
go get github.com/cloudwego/eino-ext/components/model/openai@latest
go get github.com/cloudwego/eino-ext/components/model/ark@latest
import (
"github.com/cloudwego/eino-ext/components/model/openai"
"github.com/cloudwego/eino-ext/components/model/ark"
)
func openaiExample() {
chatModel, err := openai.NewChatModel(ctx, &openai.ChatModelConfig{
BaseURL: os.Getenv("OPENAI_BASE_URL"),
Key: os.Getenv("OPENAI_ACCESS_KEY"),
ByAzure: true,
Model: "{{model name which support tool call}}",
})
agent, err := react.NewAgent(ctx, react.AgentConfig{
ToolCallingModel: chatModel,
ToolsConfig: ...,
})
}
func arkExample() {
arkModel, err := ark.NewChatModel(context.Background(), ark.ChatModelConfig{
APIKey: os.Getenv("ARK_API_KEY"),
Model: os.Getenv("ARK_MODEL"),
})
agent, err := react.NewAgent(ctx, react.AgentConfig{
ToolCallingModel: arkModel,
ToolsConfig: ...,
})
}
ToolsConfig
toolsConfig type is compose.ToolsNodeConfig. In eino, to build a Tool node, you need to provide the Tool’s information and the function to call the Tool. The tool interface definition is as follows:
type InvokableRun func(ctx context.Context, arguments string, opts ...Option) (content string, err error)
type StreamableRun func(ctx context.Context, arguments string, opts ...Option) (content *schema.StreamReader[string], err error)
type BaseTool interface {
Info() *schema.ToolInfo
}
// InvokableTool the tool for ChatModel intent recognition and ToolsNode execution.
type InvokableTool interface {
BaseTool
Run() InvokableRun
}
// StreamableTool the stream tool for ChatModel intent recognition and ToolsNode execution.
type StreamableTool interface {
BaseTool
Run() StreamableRun
}
Users can implement the required tools according to the tool interface definition. The framework also provides a more convenient method to build tools:
userInfoTool := utils.NewTool(
&schema.ToolInfo{
Name: "user_info",
Desc: "根据用户的姓名和邮箱,查询用户的公司、职位、薪酬信息",
ParamsOneOf: schema.NewParamsOneOfByParams(map[string]*schema.ParameterInfo{
"name": {
Type: "string",
Desc: "用户的姓名",
},
"email": {
Type: "string",
Desc: "用户的邮箱",
},
}),
},
func(ctx context.Context, input *userInfoRequest) (output *userInfoResponse, err error) {
return &userInfoResponse{
Name: input.Name,
Email: input.Email,
Company: "Cool Company LLC.",
Position: "CEO",
Salary: "9999",
}, nil
})
toolConfig := &compose.ToolsNodeConfig{
InvokableTools: []tool.InvokableTool{invokeTool},
}
MessageModifier
MessageModifier is executed before each time all historical messages are passed to ChatModel. The definition is:
// modify the input messages before the model is called.
type MessageModifier func(ctx context.Context, input []*schema.Message) []*schema.Message
Configuring MessageModifier in the Agent can modify the messages passed to the model, commonly used to add a preceding system message:
import (
"github.com/cloudwego/eino/flow/agent/react"
"github.com/cloudwego/eino/schema"
)
func main() {
agent, err := react.NewAgent(ctx, &react.AgentConfig{
Model: toolableChatModel,
ToolsConfig: tools,
MessageModifier: func(ctx context.Context, input []*schema.Message) []*schema.Message {
res := make([]*schema.Message, 0, len(input)+1)
res = append(res, schema.SystemMessage("你是一个 golang 开发专家."))
res = append(res, input...)
return res
},
})
agent.Generate(ctx, []*schema.Message{schema.UserMessage("Write a hello world code")})
// The actual input to the model is:
// []*schema.Message{
// {Role: schema.System, Content:"You are a golang development expert."},
// {Role: schema.Human, Content: "Write a hello world code"}
//}
}
MessageRewriter
MessageRewriter is executed before each ChatModel call and modifies and updates the historical messages saved in the global state:
// MessageRewriter modifies message in the state, before the ChatModel is called.
// It takes the messages stored accumulated in state, modify them, and put the modified version back into state.
// Useful for compressing message history to fit the model context window,
// or if you want to make changes to messages that take effect across multiple model calls.
// NOTE: if both MessageModifier and MessageRewriter are set, MessageRewriter will be called before MessageModifier.
MessageRewriter MessageModifier
Commonly used for context compression, which is a message change that needs to take effect continuously across multiple ReAct loops.
Compared to MessageModifier (which only changes without persisting, thus suitable for system prompts), MessageRewriter’s changes are visible in subsequent ReAct loops.
MaxStep
Specify the Agent’s maximum running step length. Each transition from one node to the next node counts as one step. The default value is node count + 2.
Since one loop in the Agent is ChatModel + Tools, which equals 2 steps, the default value of 12 allows up to 6 loops. However, since the last step must be a ChatModel return (because ChatModel must determine that no tool needs to run before returning the final result), at most 5 tools can be run.
Similarly, if you want to run at most 10 loops (10 ChatModel + 9 Tools), you need to set MaxStep to 20. If you want to run at most 20 loops, MaxStep needs to be 40.
func main() {
agent, err := react.NewAgent(ctx, &react.AgentConfig{
ToolCallingModel: toolableChatModel,
ToolsConfig: tools,
MaxStep: 20,
}
}
ToolReturnDirectly
If you want the Agent to directly return the Tool’s Response ToolMessage after ChatModel selects a specific Tool and executes it, you can configure this Tool in ToolReturnDirectly.
a, err = NewAgent(ctx, &AgentConfig{
Model: cm,
ToolsConfig: compose.ToolsNodeConfig{
Tools: []tool.BaseTool{fakeTool, fakeStreamTool},
},
MaxStep: 40,
ToolReturnDirectly: map[string]struct{}{fakeToolName: {}}, // one of the two tools is return directly
})
StreamToolCallChecker
Different models may output tool calls differently in streaming mode: some models (like OpenAI) output tool calls directly; some models (like Claude) output text first, then output tool calls. Therefore, different methods are needed to determine this. This field is used to specify the function that determines whether the model’s streaming output contains tool calls.
Optional. If not set, the default checks whether the first “non-empty chunk” contains a tool call:
func firstChunkStreamToolCallChecker(_ context.Context, sr *schema.StreamReader[*schema.Message]) (bool, error) {
defer sr.Close()
for {
msg, err := sr.Recv()
if err == io.EOF {
return false, nil
}
if err != nil {
return false, err
}
if len(msg.ToolCalls) > 0 {
return true, nil
}
if len(msg.Content) == 0 { // skip empty chunks at the front
continue
}
return false, nil
}
}
The default implementation is suitable for: models whose Tool Call Message contains only Tool Calls.
The default implementation is NOT suitable for: cases where there are non-empty content chunks before the Tool Call output. In such cases, you need to define a custom tool call checker:
toolCallChecker := func(ctx context.Context, sr *schema.StreamReader[*schema.Message]) (bool, error) {
defer sr.Close()
for {
msg, err := sr.Recv()
if err != nil {
if errors.Is(err, io.EOF) {
// finish
break
}
return false, err
}
if len(msg.ToolCalls) > 0 {
return true, nil
}
}
return false, nil
}
The custom StreamToolCallChecker above may need to check all chunks for ToolCalls in extreme cases, which can cause the “streaming decision” effect to be lost. To preserve the “streaming decision” effect as much as possible, the recommendation is:
💡 Try adding a prompt to constrain the model not to output additional text when calling tools, for example: “If you need to call a tool, output the tool directly, do not output text.”
Different models may be affected differently by prompts, so you need to adjust the prompt and verify the effect in actual use.
Invocation
Generate
agent, _ := react.NewAgent(...)
var outMessage *schema.Message
outMessage, err = agent.Generate(ctx, []*schema.Message{
schema.UserMessage("写一个 golang 的 hello world 程序"),
})
Stream
agent, _ := react.NewAgent(...)
var msgReader *schema.StreamReader[*schema.Message]
msgReader, err = agent.Stream(ctx, []*schema.Message{
schema.UserMessage("写一个 golang 的 hello world 程序"),
})
for {
// msg type is *schema.Message
msg, err := msgReader.Recv()
if err != nil {
if errors.Is(err, io.EOF) {
// finish
break
}
// error
log.Printf("failed to recv: %v\n", err)
return
}
fmt.Print(msg.Content)
}
WithCallbacks
Callback is a callback executed at specific timings during Agent runtime. Since the Agent Graph only has ChatModel and ToolsNode, the Agent’s Callback is the Callback for ChatModel and Tool. The react package provides a helper function to help users quickly build Callback Handlers for these two component types.
import (
template "github.com/cloudwego/eino/utils/callbacks"
)
// BuildAgentCallback builds a callback handler for agent.
// e.g.
//
// callback := BuildAgentCallback(modelHandler, toolHandler)
// agent, err := react.NewAgent(ctx, &AgentConfig{})
// agent.Generate(ctx, input, agent.WithComposeOptions(compose.WithCallbacks(callback)))
func BuildAgentCallback(modelHandler *template.ModelCallbackHandler, toolHandler *template.ToolCallbackHandler) callbacks.Handler {
return template.NewHandlerHelper().ChatModel(modelHandler).Tool(toolHandler).Handler()
}
Options
React agent supports dynamic modification through runtime Options.
Scenario 1: Modify the Model configuration in the Agent at runtime:
// WithChatModelOptions returns an agent option that specifies model.Option for the chat model in agent.
func WithChatModelOptions(opts ...model.Option) agent.AgentOption {
return agent.WithComposeOptions(compose.WithChatModelOption(opts...))
}
Scenario 2: Modify the Tool list at runtime:
// WithToolList returns an agent option that specifies the list of tools can be called which are BaseTool but must implement InvokableTool or StreamableTool.
func WithToolList(tools ...tool.BaseTool) agent.AgentOption {
return agent.WithComposeOptions(compose.WithToolsNodeOption(compose.WithToolList(tools...)))
}
Additionally, you also need to modify the tools bound in ChatModel: WithChatModelOptions(model.WithTools(...))
Scenario 3: Modify the options for a specific Tool at runtime:
// WithToolOptions returns an agent option that specifies tool.Option for the tools in agent.
func WithToolOptions(opts ...tool.Option) agent.AgentOption {
return agent.WithComposeOptions(compose.WithToolsNodeOption(compose.WithToolOption(opts...)))
}
Prompt
Modifying the prompt at runtime is essentially passing different Message lists when calling Generate or Stream.
Get Intermediate Results
If you want to get the *schema.Message generated during the ReAct Agent execution process in real-time, you can first obtain a runtime Option and a MessageFuture through WithMessageFuture:
// WithMessageFuture returns an agent option and a MessageFuture interface instance.
// The option configures the agent to collect messages generated during execution,
// while the MessageFuture interface allows users to asynchronously retrieve these messages.
func WithMessageFuture() (agent.AgentOption, MessageFuture) {
h := &cbHandler{started: make(chan struct{})}
cmHandler := &ub.ModelCallbackHandler{
OnEnd: h.onChatModelEnd,
OnEndWithStreamOutput: h.onChatModelEndWithStreamOutput,
}
toolHandler := &ub.ToolCallbackHandler{
OnEnd: h.onToolEnd,
OnEndWithStreamOutput: h.onToolEndWithStreamOutput,
}
graphHandler := callbacks.NewHandlerBuilder().
OnStartFn(h.onGraphStart).
OnStartWithStreamInputFn(h.onGraphStartWithStreamInput).
OnEndFn(h.onGraphEnd).
OnEndWithStreamOutputFn(h.onGraphEndWithStreamOutput).
OnErrorFn(h.onGraphError).Build()
cb := ub.NewHandlerHelper().ChatModel(cmHandler).Tool(toolHandler).Graph(graphHandler).Handler()
option := agent.WithComposeOptions(compose.WithCallbacks(cb))
return option, h
}
This runtime Option is passed normally to the Generate or Stream method. The MessageFuture can use GetMessages or GetMessageStreams to get the Messages of various intermediate states.
💡 After passing the MessageFuture Option, the Agent will still run in a blocking manner. Receiving intermediate results through MessageFuture needs to be asynchronous with the Agent running (read MessageFuture in a goroutine or run the Agent in a goroutine).
Agent In Graph/Chain
Agent can be embedded into other Graphs as a Lambda:
agent, _ := NewAgent(ctx, &AgentConfig{
ToolCallingModel: cm,
ToolsConfig: compose.ToolsNodeConfig{
Tools: []tool.BaseTool{fakeTool, &fakeStreamToolGreetForTest{}},
},
MaxStep: 40,
})
chain := compose.NewChain[[]*schema.Message, string]()
agentLambda, _ := compose.AnyLambda(agent.Generate, agent.Stream, nil, nil)
chain.
AppendLambda(agentLambda).
AppendLambda(compose.InvokableLambda(func(ctx context.Context, input *schema.Message) (string, error) {
t.Log("got agent response: ", input.Content)
return input.Content, nil
}))
r, _ := chain.Compile(ctx)
res, _ := r.Invoke(ctx, []*schema.Message{{Role: schema.User, Content: "hello"}},
compose.WithCallbacks(callbackForTest))
Demo
Basic Info
Description: This is a Food Recommender with two tools (query_restaurants and query_dishes).
Repository: eino-examples/flow/agent/react
Usage:
- Clone the eino-examples repo and cd to the root directory
- Provide an
OPENAI_API_KEY:export OPENAI_API_KEY=xxxxxxx - Run the demo:
go run flow/agent/react/react.go
Running Process
Running Process Explanation
- Simulating user input:
I'm in Haidian District, recommend some dishes for me, need some spicy dishes, recommend at least 2 restaurants - The agent runs the first node
ChatModel, the LLM determines that a ToolCall needs to be made to query restaurants, with the following parameters:
"function": {
"name": "query_restaurants",
"arguments": "{\"location\":\"Haidian District\",\"topn\":2}"
}
- Entering the
Toolsnode, calling the query_restaurants tool and getting the result. The result returns information about 2 restaurants in Haidian District:
[{"id":"1001","name":"Old Place Restaurant","place":"Beijing Old Hutong 5F, turn left to enter","desc":"","score":3},{"id":"1002","name":"Human Taste Restaurant","place":"Beijing Big World Mall -1F","desc":"","score":5}]
- After getting the tool result, the conversation history now contains the tool result. Running
ChatModelagain, the LLM determines that another ToolCall needs to be made to query what dishes the restaurants have. Note that since there are two restaurants, the LLM returns 2 ToolCalls as follows:
"Message": {
"role": "ai",
"content": "",
"tool_calls": [ // <= there are 2 tool calls here
{
"index": 1,
"id": "call_wV7zA3vGGJBhuN7r9guhhAfF",
"function": {
"name": "query_dishes",
"arguments": "{\"restaurant_id\": \"1002\", \"topn\": 5}"
}
},
{
"index": 0,
"id": "call_UOsp0jRtzEbfxixNjP5501MF",
"function": {
"name": "query_dishes",
"arguments": "{\"restaurant_id\": \"1001\", \"topn\": 5}"
}
}
]
}
- Entering the
Toolsnode again. Since there are 2 tool calls, the Tools node executes these two calls concurrently internally, and both are added to the conversation history. From the callback debug logs, you can see the results as follows:
=========[OnToolStart]=========
{"restaurant_id": "1001", "topn": 5}
=========[OnToolEnd]=========
[{"name":"Braised Pork","desc":"A piece of braised pork","price":20,"score":8},{"name":"Spring Beef","desc":"Lots of boiled beef","price":50,"score":8},{"name":"Stir-fried Pumpkin","desc":"Mushy stir-fried pumpkin","price":5,"score":5},{"name":"Korean Spicy Cabbage","desc":"This is blessed spicy cabbage, very delicious","price":20,"score":9},{"name":"Hot and Sour Potato Shreds","desc":"Sour and spicy potato shreds","price":10,"score":9}]
=========[OnToolStart]=========
{"restaurant_id": "1002", "topn": 5}
=========[OnToolEnd]=========
[{"name":"Braised Spare Ribs","desc":"Piece by piece spare ribs","price":43,"score":7},{"name":"Big Knife Twice-cooked Pork","desc":"Classic twice-cooked pork, big pieces of meat","price":40,"score":8},{"name":"Fiery Kiss","desc":"Cold pig snout, spicy but not greasy","price":60,"score":9},{"name":"Chili Mixed with Preserved Egg","desc":"Pounded chili preserved egg, a rice killer","price":15,"score":8}]
- After getting all the tool call results, entering the
ChatModelnode again. This time the LLM finds that it has all the information needed to answer the user’s question, so it integrates the information and outputs the conclusion. Since theStreammethod was used for the call, the LLM result is returned in a streaming manner.