Eino ADK: Overview
What is Eino ADK?
Eino ADK, inspired by Google-ADK, provides a flexible composition framework for Agent development in Go, i.e., an Agent and Multi-Agent development framework. Eino ADK has accumulated common capabilities for multi-Agent interaction, including context passing, event stream distribution and conversion, task control transfer, interrupt and resume, and common aspects. It is widely applicable, model-agnostic, and deployment-agnostic, making Agent and Multi-Agent development simpler and more convenient while providing comprehensive production-grade application governance capabilities.
Eino ADK aims to help developers develop and manage Agent applications. It provides a flexible and robust development environment to help developers build various Agent applications such as conversational agents, non-conversational agents, complex tasks, workflows, and more.
ADK Framework
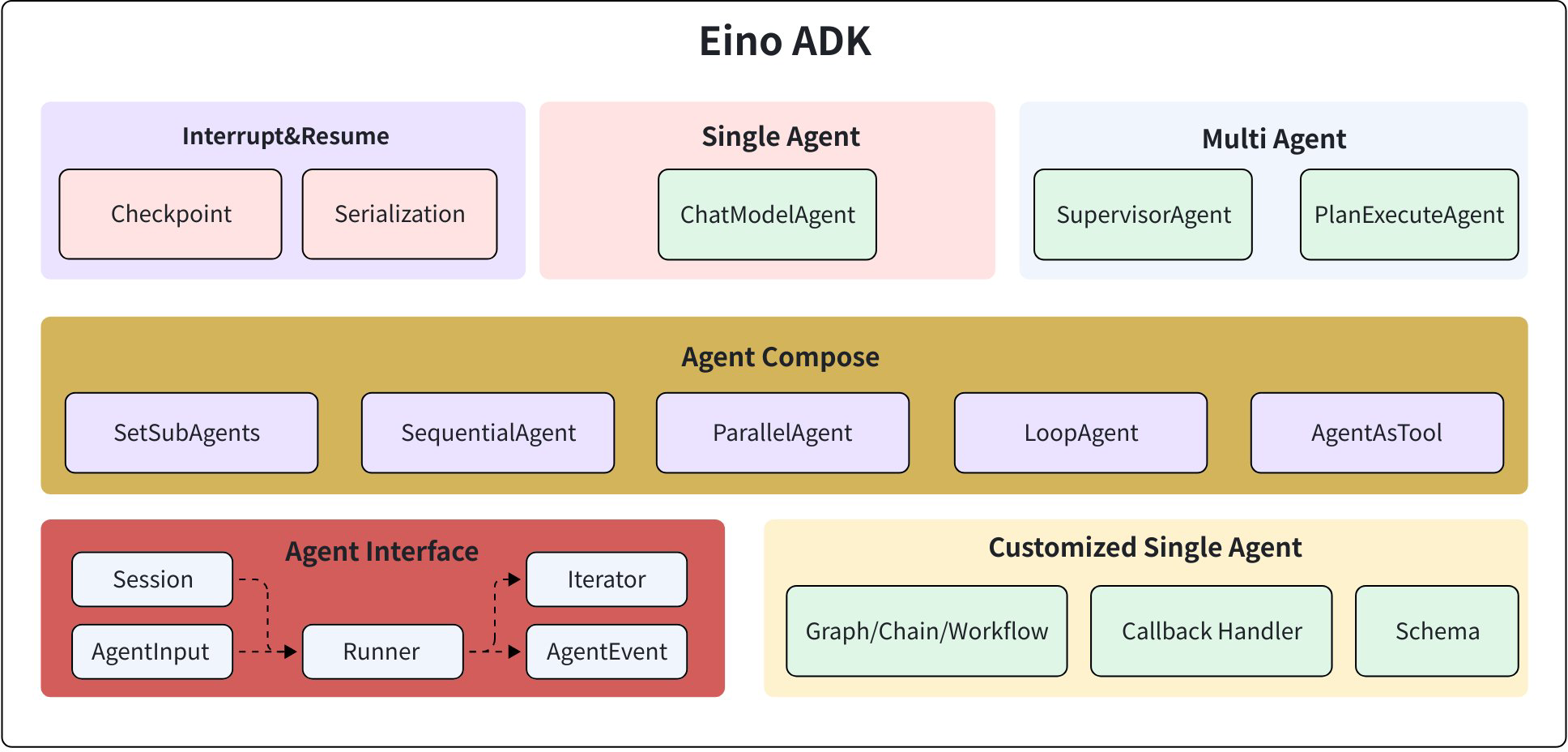
The overall module structure of Eino ADK is shown in the diagram below:
Agent Interface
The core of Eino ADK is the Agent abstraction (Agent Interface). All ADK functionality is designed around the Agent abstraction. For details, see Eino ADK: Agent Interface
type Agent interface {
Name(ctx context.Context) string
Description(ctx context.Context) string
// Run runs the agent.
// The returned AgentEvent within the AsyncIterator must be safe to modify.
// If the returned AgentEvent within the AsyncIterator contains MessageStream,
// the MessageStream MUST be exclusive and safe to be received directly.
// NOTE: it's recommended to use SetAutomaticClose() on the MessageStream of AgentEvents emitted by AsyncIterator,
// so that even the events are not processed, the MessageStream can still be closed.
Run(ctx context.Context, input *AgentInput, options ...AgentRunOption) *AsyncIterator[*AgentEvent]
}
The definition of Agent.Run is:
- Get task details and related data from the input AgentInput, AgentRunOption, and optional Context Session
- Execute the task and write the execution process and results to the AgentEvent Iterator
Agent.Run requires the Agent implementation to execute asynchronously in a Future pattern. The core is divided into three steps. For specifics, refer to the implementation of the Run method in ChatModelAgent:
- Create a pair of Iterator and Generator
- Start the Agent’s asynchronous task and pass in the Generator to process AgentInput. The Agent executes core logic in this asynchronous task (e.g., ChatModelAgent calls LLM) and writes new events to the Generator for the Agent caller to consume from the Iterator
- Return the Iterator immediately after starting the task in step 2
Multi-Agent Collaboration
Around the Agent abstraction, Eino ADK provides various simple, easy-to-use composition primitives for rich scenarios, supporting the development of diverse Multi-Agent collaboration strategies such as Supervisor, Plan-Execute, Group-Chat, and other Multi-Agent scenarios. This enables different Agent division of labor and cooperation patterns to handle more complex tasks. For details, see Eino ADK: Agent Collaboration
The collaboration primitives defined by Eino ADK during Agent collaboration are as follows:
- Collaboration methods between Agents
| Collaboration Method | Description |
| Transfer | Directly transfer the task to another Agent. The current Agent exits after execution and does not care about the task execution status of the transferred Agent |
| ToolCall(AgentAsTool) | Call an Agent as a ToolCall, wait for the Agent's response, and obtain the output result of the called Agent for the next round of processing |
- Context strategies for AgentInput
| Context Strategy | Description |
| Upstream Agent Full Dialogue | Get the complete dialogue record of this Agent's upstream Agent |
| New Task Description | Ignore the complete dialogue record of the upstream Agent and provide a new task summary as the sub-Agent's AgentInput |
- Decision Autonomy
| Decision Autonomy | Description |
| Autonomous Decision | Inside the Agent, based on its available downstream Agents, when assistance is needed, autonomously select downstream Agents for assistance. Generally, the Agent makes decisions based on LLM internally, but even if selection is based on preset logic, it is still considered autonomous decision from outside the Agent |
| Preset Decision | Pre-set the next Agent after an Agent executes a task. The execution order of Agents is predetermined and predictable |
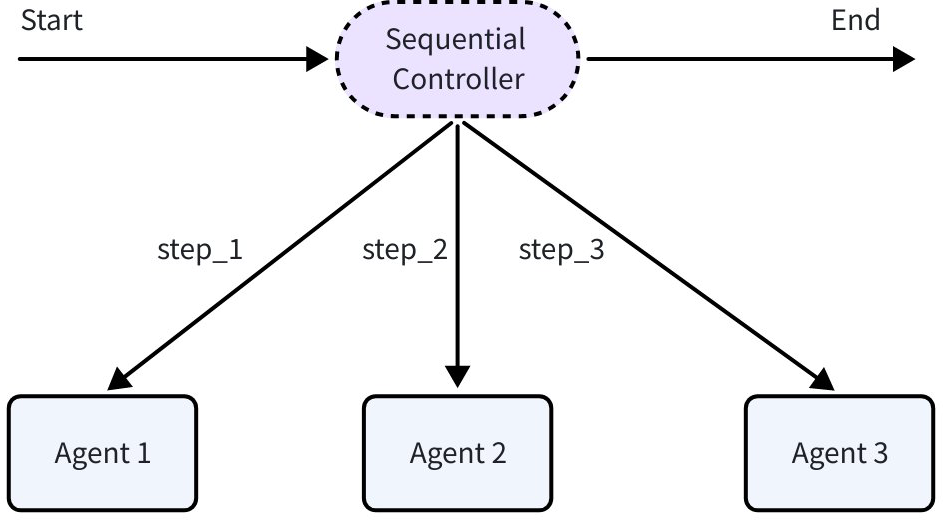
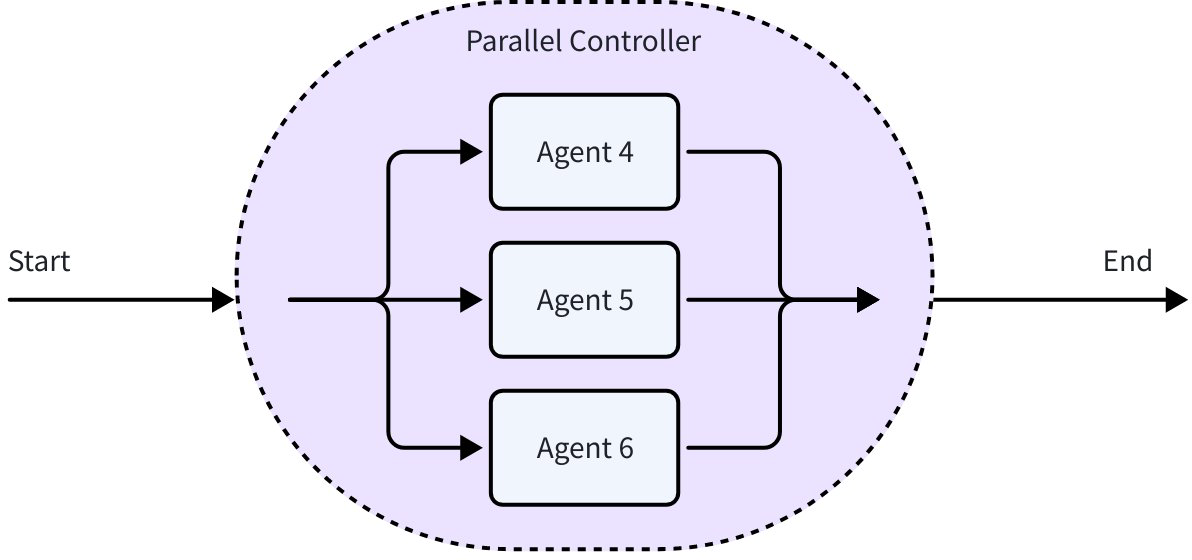
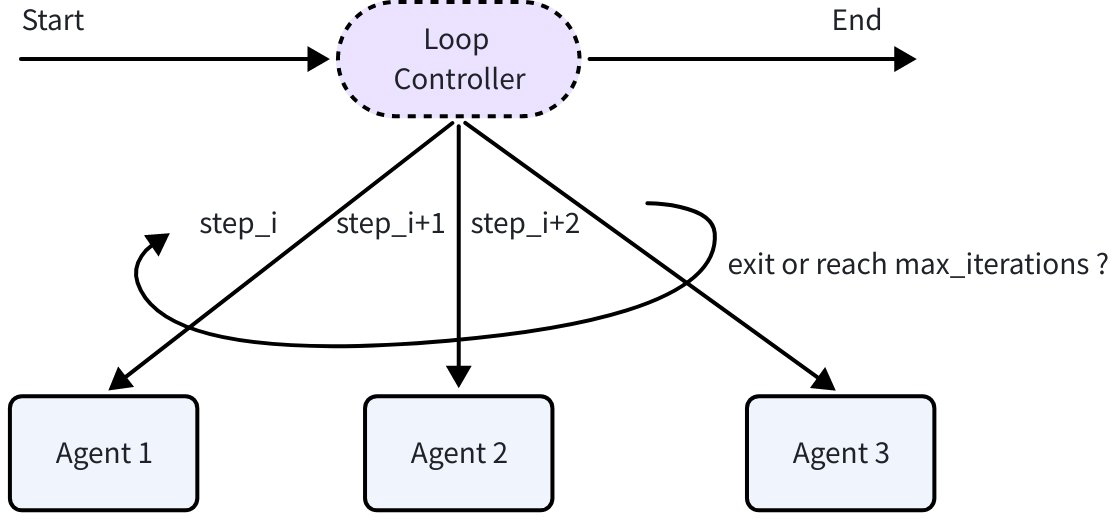
Around the collaboration primitives, Eino ADK provides the following Agent composition primitives:
ChatModelAgent
ChatModelAgent is Eino ADK’s key implementation of Agent. It encapsulates the interaction logic with large language models, implements a ReAct paradigm Agent, orchestrates the ReAct Agent control flow based on Graph in Eino, and exports events generated during ReAct Agent execution through callbacks.Handler, converting them to AgentEvent for return.
To learn more about ChatModelAgent, see: Eino ADK: ChatModelAgent
type ChatModelAgentConfig struct {
// Name of the agent. Better be unique across all agents.
Name string
// Description of the agent's capabilities.
// Helps other agents determine whether to transfer tasks to this agent.
Description string
// Instruction used as the system prompt for this agent.
// Optional. If empty, no system prompt will be used.
// Supports f-string placeholders for session values in default GenModelInput, for example:
// "You are a helpful assistant. The current time is {Time}. The current user is {User}."
// These placeholders will be replaced with session values for "Time" and "User".
Instruction string
Model model.ToolCallingChatModel
ToolsConfig ToolsConfig
// GenModelInput transforms instructions and input messages into the model's input format.
// Optional. Defaults to defaultGenModelInput which combines instruction and messages.
GenModelInput GenModelInput
// Exit defines the tool used to terminate the agent process.
// Optional. If nil, no Exit Action will be generated.
// You can use the provided 'ExitTool' implementation directly.
Exit tool.BaseTool
// OutputKey stores the agent's response in the session.
// Optional. When set, stores output via AddSessionValue(ctx, outputKey, msg.Content).
OutputKey string
// MaxIterations defines the upper limit of ChatModel generation cycles.
// The agent will terminate with an error if this limit is exceeded.
// Optional. Defaults to 20.
MaxIterations int
}
func NewChatModelAgent(_ context.Context, config *ChatModelAgentConfig) (*ChatModelAgent, error) {
// omit code
}
AgentRunner
AgentRunner is the executor for Agents, providing support for extended functionality required by Agent execution. For details, see: Eino ADK: Agent Extension
Only when executing agents through Runner can you use the following ADK features:
Interrupt & Resume
Aspect mechanism (supported in 1226 test version, API compatibility not guaranteed before official release)
Context environment preprocessing
type RunnerConfig struct { Agent Agent EnableStreaming bool CheckPointStore compose.CheckPointStore } func NewRunner(_ context.Context, conf RunnerConfig) *Runner { // omit code }