Eino ADK: Workflow Agents
Workflow Agents Overview
Import Path
import "github.com/cloudwego/eino/adk"
What Are Workflow Agents
Workflow Agents are a special type of Agent in Eino ADK that allows developers to organize and execute multiple sub-agents in a predefined flow.
Unlike the Transfer pattern based on LLM autonomous decision-making, Workflow Agents use predefined decisions, running sub-agents according to the execution flow defined in code, providing a more predictable and controllable multi-agent collaboration approach.
Eino ADK provides three basic Workflow Agent types:
- SequentialAgent: Executes sub-agents sequentially in order
- LoopAgent: Loops through a sequence of sub-agents
- ParallelAgent: Executes multiple sub-agents concurrently
These Workflow Agents can be nested with each other to build more complex execution flows, meeting various business scenario requirements.
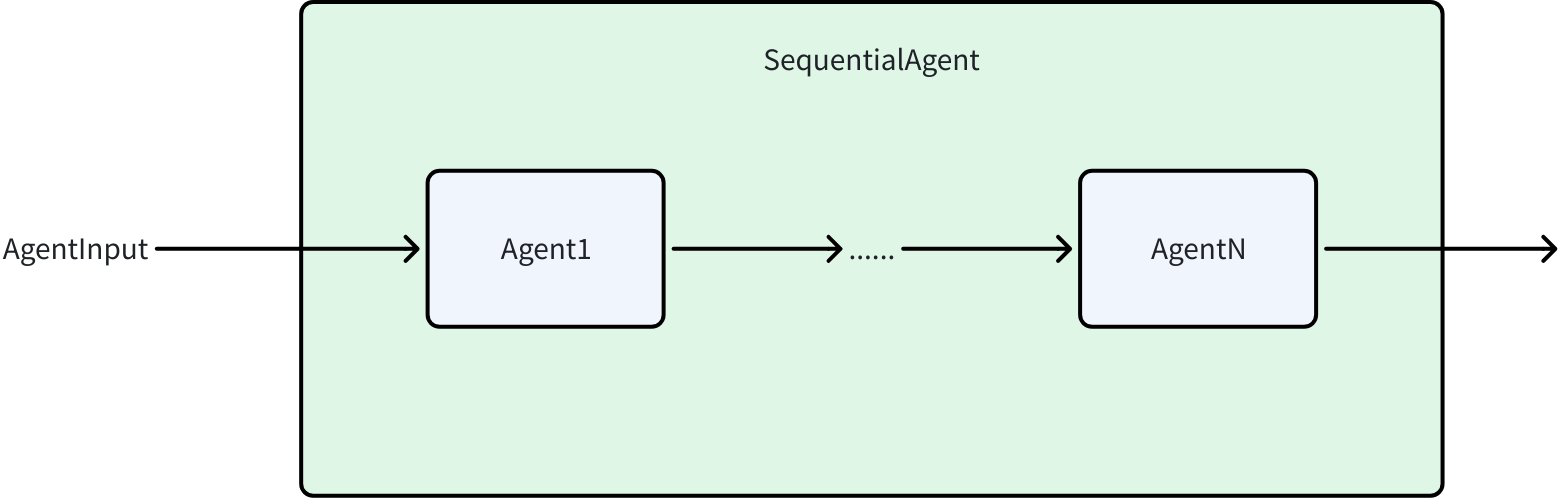
SequentialAgent
Features
SequentialAgent is the most basic Workflow Agent. It executes a series of sub-agents sequentially according to the order provided in the configuration. After each sub-agent completes execution, its output is passed to the next sub-agent through the History mechanism, forming a linear execution chain.
type SequentialAgentConfig struct {
Name string // Agent name
Description string // Agent description
SubAgents []Agent // List of sub-agents, arranged in execution order
}
func NewSequentialAgent(ctx context.Context, config *SequentialAgentConfig) (Agent, error)
SequentialAgent execution follows these rules:
- Linear execution: Strictly follows the order of the SubAgents array
- History passing: Each agent’s execution result is added to History, allowing subsequent agents to access the execution history of previous agents
- Early exit: If any sub-agent produces an ExitAction / Interrupt, the entire Sequential flow terminates immediately
SequentialAgent is suitable for the following scenarios:
- Multi-step processing flows: Such as data preprocessing -> analysis -> report generation
- Pipeline processing: Each step’s output serves as the next step’s input
- Task sequences with dependencies: Subsequent tasks depend on results from previous tasks
Example
This example demonstrates how to use SequentialAgent to create a three-step document processing pipeline:
- DocumentAnalyzer: Analyzes document content
- ContentSummarizer: Summarizes analysis results
- ReportGenerator: Generates the final report
package main
import (
"context"
"fmt"
"log"
"os"
"github.com/cloudwego/eino-ext/components/model/openai"
"github.com/cloudwego/eino/adk"
"github.com/cloudwego/eino/components/model"
"github.com/cloudwego/eino/schema"
)
// Create ChatModel instance
func newChatModel() model.ToolCallingChatModel {
cm, err := openai.NewChatModel(context.Background(), &openai.ChatModelConfig{
APIKey: os.Getenv("OPENAI_API_KEY"),
Model: os.Getenv("OPENAI_MODEL"),
})
if err != nil {
log.Fatal(err)
}
return cm
}
// Document analysis Agent
func NewDocumentAnalyzerAgent() adk.Agent {
a, err := adk.NewChatModelAgent(context.Background(), &adk.ChatModelAgentConfig{
Name: "DocumentAnalyzer",
Description: "Analyzes document content and extracts key information",
Instruction: "You are a document analysis expert. Please carefully analyze the document content provided by the user, extracting key information, main points, and important data.",
Model: newChatModel(),
})
if err != nil {
log.Fatal(err)
}
return a
}
// Content summarization Agent
func NewContentSummarizerAgent() adk.Agent {
a, err := adk.NewChatModelAgent(context.Background(), &adk.ChatModelAgentConfig{
Name: "ContentSummarizer",
Description: "Summarizes analysis results",
Instruction: "Based on the previous document analysis results, generate a concise and clear summary highlighting the most important findings and conclusions.",
Model: newChatModel(),
})
if err != nil {
log.Fatal(err)
}
return a
}
// Report generation Agent
func NewReportGeneratorAgent() adk.Agent {
a, err := adk.NewChatModelAgent(context.Background(), &adk.ChatModelAgentConfig{
Name: "ReportGenerator",
Description: "Generates the final analysis report",
Instruction: "Based on the previous analysis and summary, generate a structured analysis report including an executive summary, detailed analysis, and recommendations.",
Model: newChatModel(),
})
if err != nil {
log.Fatal(err)
}
return a
}
func main() {
ctx := context.Background()
// Create three processing step Agents
analyzer := NewDocumentAnalyzerAgent()
summarizer := NewContentSummarizerAgent()
generator := NewReportGeneratorAgent()
// Create SequentialAgent
sequentialAgent, err := adk.NewSequentialAgent(ctx, &adk.SequentialAgentConfig{
Name: "DocumentProcessingPipeline",
Description: "Document processing pipeline: Analysis → Summary → Report Generation",
SubAgents: []adk.Agent{analyzer, summarizer, generator},
})
if err != nil {
log.Fatal(err)
}
// Create Runner
runner := adk.NewRunner(ctx, adk.RunnerConfig{
Agent: sequentialAgent,
})
// Execute document processing flow
input := "Please analyze the following market report: In Q3 2024, company revenue grew 15%, mainly due to the successful launch of new product lines. However, operating costs also increased by 8%, requiring efficiency optimization."
fmt.Println("Starting document processing pipeline...")
iter := runner.Query(ctx, input)
stepCount := 1
for {
event, ok := iter.Next()
if !ok {
break
}
if event.Err != nil {
log.Fatal(event.Err)
}
if event.Output != nil && event.Output.MessageOutput != nil {
fmt.Printf("\n=== Step %d: %s ===\n", stepCount, event.AgentName)
fmt.Printf("%s\n", event.Output.MessageOutput.Message.Content)
stepCount++
}
}
fmt.Println("\nDocument processing pipeline completed!")
}
Run result:
Starting document processing pipeline...
=== Step 1: DocumentAnalyzer ===
Market Report Key Information Analysis:
1. Revenue Growth:
- In Q3 2024, company revenue grew 15% year-over-year.
- The main driver of revenue growth was the successful launch of new product lines.
2. Cost Situation:
- Operating costs increased by 8%.
- The cost increase reminds the company of the need for efficiency optimization.
Key Points Summary:
- The new product line launch significantly drove revenue growth, showing good results in product innovation.
- Although revenue increased, the rise in operating costs somewhat affected profitability, highlighting the importance of improving operational efficiency.
Important Data:
- Revenue growth rate: 15%
- Operating cost growth rate: 8%
=== Step 2: ContentSummarizer ===
Summary: In Q3 2024, the company achieved 15% revenue growth, mainly attributed to the successful launch of new product lines, demonstrating significant improvement in product innovation capability. However, operating costs also increased by 8%, putting some pressure on profitability and emphasizing the urgent need for operational efficiency optimization. Overall, the company needs to seek a better balance between growth and cost control to ensure sustainable healthy development.
=== Step 3: ReportGenerator ===
Analysis Report
I. Executive Summary
In Q3 2024, the company achieved 15% year-over-year revenue growth, mainly driven by the successful launch of new product lines, demonstrating strong product innovation capability. However, operating costs also increased 8% year-over-year, putting some pressure on profit margins. To ensure continued profitable growth, focus should be on optimizing operational efficiency and promoting balanced development of cost control and revenue growth.
II. Detailed Analysis
1. Revenue Growth Analysis
- The company's 15% revenue growth reflects good market acceptance of new product lines, effectively expanding revenue sources.
- The launch of new product lines demonstrates improved R&D and market responsiveness, laying a foundation for future sustained growth.
2. Operating Cost Situation
- The 8% increase in operating costs may come from various aspects including raw material price increases, decreased production efficiency, or increased sales and promotion expenses.
- This cost increase somewhat offsets the profit gains from revenue growth, affecting overall profitability.
3. Profitability and Efficiency Considerations
- The mismatch between revenue and cost growth indicates room for improvement in current operational efficiency.
- Optimizing supply chain management, improving production automation, and strengthening cost control will become key measures.
III. Recommendations
1. Strengthen follow-up support for new product lines, including marketing and customer feedback mechanisms, to continue driving revenue growth.
2. Conduct in-depth analysis of operating cost composition, identify main cost drivers, and develop targeted cost reduction strategies.
3. Promote internal process optimization and technology upgrades to improve production and operational efficiency and alleviate cost pressure.
4. Establish a dynamic financial monitoring system to achieve real-time tracking and adjustment of revenue and costs, ensuring company financial health.
IV. Conclusion
The company demonstrated good growth momentum in Q3 2024 but also faces challenges from rising costs. Through continuous product innovation combined with effective cost management, there is potential to achieve dual improvement in profitability and market competitiveness, driving steady company development.
Document processing pipeline completed!
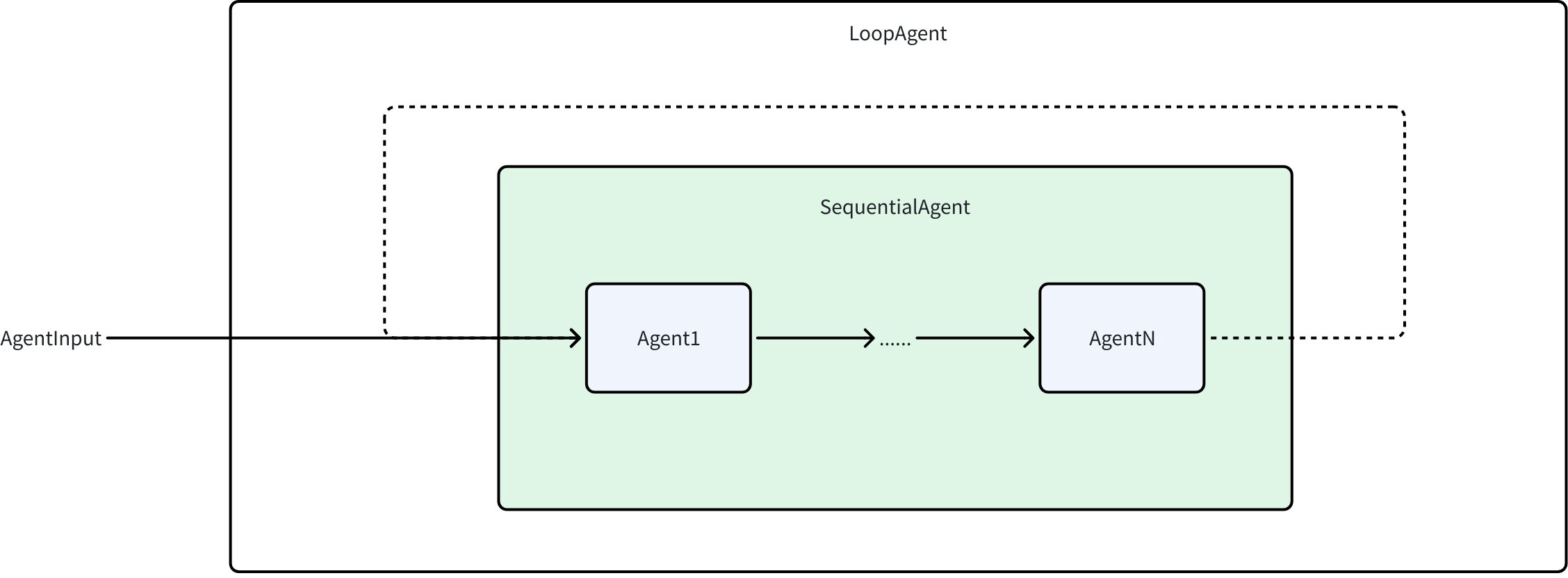
LoopAgent
Features
LoopAgent is built on SequentialAgent. It repeatedly executes the configured sub-agent sequence until the maximum iteration count is reached or a sub-agent produces an ExitAction. LoopAgent is particularly suitable for scenarios requiring iterative optimization, repeated processing, or continuous monitoring.
type LoopAgentConfig struct {
Name string // Agent name
Description string // Agent description
SubAgents []Agent // List of sub-agents
MaxIterations int // Maximum iteration count, 0 means infinite loop
}
func NewLoopAgent(ctx context.Context, config *LoopAgentConfig) (Agent, error)
LoopAgent execution follows these rules:
- Loop execution: Repeatedly executes the SubAgents sequence, with each loop being a complete Sequential execution process
- History accumulation: Results from each iteration accumulate in History, allowing subsequent iterations to access all historical information
- Conditional exit: Supports terminating the loop via ExitAction or reaching maximum iteration count; setting
MaxIterations=0means infinite loop
LoopAgent is suitable for the following scenarios:
- Iterative optimization: Tasks requiring repeated improvement such as code optimization, parameter tuning
- Continuous monitoring: Periodically checking status and executing corresponding operations
- Repeated processing: Tasks that need multiple rounds of processing to achieve satisfactory results
- Self-improvement: Agent continuously improves its output based on previous execution results
Example
This example demonstrates how to use LoopAgent to create a code optimization loop:
- CodeAnalyzer: Analyzes code issues
- CodeOptimizer: Optimizes code based on analysis results
- ExitController: Determines whether to exit the loop
The loop continues until code quality meets standards or maximum iteration count is reached.
package main
import (
"context"
"fmt"
"log"
"os"
"github.com/cloudwego/eino-ext/components/model/openai"
"github.com/cloudwego/eino/adk"
"github.com/cloudwego/eino/components/model"
"github.com/cloudwego/eino/schema"
)
func newChatModel() model.ToolCallingChatModel {
cm, err := openai.NewChatModel(context.Background(), &openai.ChatModelConfig{
APIKey: os.Getenv("OPENAI_API_KEY"),
Model: os.Getenv("OPENAI_MODEL"),
})
if err != nil {
log.Fatal(err)
}
return cm
}
// Code analysis Agent
func NewCodeAnalyzerAgent() adk.Agent {
a, err := adk.NewChatModelAgent(context.Background(), &adk.ChatModelAgentConfig{
Name: "CodeAnalyzer",
Description: "Analyzes code quality and performance issues",
Instruction: `You are a code analysis expert. Please analyze the provided code and identify the following issues:
1. Performance bottlenecks
2. Code duplication
3. Readability issues
4. Potential bugs
5. Non-compliance with best practices
If the code is already excellent, output "EXIT: Code quality has met standards" to end the optimization process.`,
Model: newChatModel(),
})
if err != nil {
log.Fatal(err)
}
return a
}
// Code optimization Agent
func NewCodeOptimizerAgent() adk.Agent {
a, err := adk.NewChatModelAgent(context.Background(), &adk.ChatModelAgentConfig{
Name: "CodeOptimizer",
Description: "Optimizes code based on analysis results",
Instruction: `Based on the previous code analysis results, optimize and improve the code:
1. Fix identified performance issues
2. Eliminate code duplication
3. Improve code readability
4. Fix potential bugs
5. Apply best practices
Please provide the complete optimized code.`,
Model: newChatModel(),
})
if err != nil {
log.Fatal(err)
}
return a
}
// Create a special Agent to handle exit logic
func NewExitControllerAgent() adk.Agent {
a, err := adk.NewChatModelAgent(context.Background(), &adk.ChatModelAgentConfig{
Name: "ExitController",
Description: "Controls the exit of the optimization loop",
Instruction: `Check the previous analysis results. If the code analyst believes the code quality has met standards (contains "EXIT" keyword),
output "TERMINATE" and generate an exit action to end the loop. Otherwise continue to the next optimization round.`,
Model: newChatModel(),
})
if err != nil {
log.Fatal(err)
}
return a
}
func main() {
ctx := context.Background()
// Create optimization flow Agents
analyzer := NewCodeAnalyzerAgent()
optimizer := NewCodeOptimizerAgent()
controller := NewExitControllerAgent()
// Create LoopAgent, execute up to 5 optimization rounds
loopAgent, err := adk.NewLoopAgent(ctx, &adk.LoopAgentConfig{
Name: "CodeOptimizationLoop",
Description: "Code optimization loop: Analysis → Optimization → Check exit condition",
SubAgents: []adk.Agent{analyzer, optimizer, controller},
MaxIterations: 5, // Maximum 5 optimization rounds
})
if err != nil {
log.Fatal(err)
}
// Create Runner
runner := adk.NewRunner(ctx, adk.RunnerConfig{
Agent: loopAgent,
})
// Code example to optimize
codeToOptimize := `
func processData(data []int) []int {
result := []int{}
for i := 0; i < len(data); i++ {
for j := 0; j < len(data); j++ {
if data[i] > data[j] {
result = append(result, data[i])
break
}
}
}
return result
}
`
fmt.Println("Starting code optimization loop...")
iter := runner.Query(ctx, "Please optimize the following Go code:\n"+codeToOptimize)
iteration := 1
for {
event, ok := iter.Next()
if !ok {
break
}
if event.Err != nil {
log.Fatal(event.Err)
}
if event.Output != nil && event.Output.MessageOutput != nil {
fmt.Printf("\n=== Round %d - %s ===\n", iteration, event.AgentName)
fmt.Printf("%s\n", event.Output.MessageOutput.Message.Content)
// Check if exit is needed
if event.AgentName == "ExitController" {
if event.Action != nil && event.Action.Exit {
fmt.Println("\nOptimization loop ended early!")
break
}
iteration++
}
}
}
fmt.Println("\nCode optimization loop completed!")
}
Run result:
Starting code optimization loop...
=== Round 1 - CodeAnalyzer ===
Analyzing the provided code:
```go
func processData(data []int) []int {
result := []int{}
for i := 0; i < len(data); i++ {
for j := 0; j < len(data); j++ {
if data[i] > data[j] {
result = append(result, data[i])
break
}
}
}
return result
}
1. Performance Bottlenecks
- Double nested loop with O(n²) time complexity, poor performance for large datasets.
- Inner loop breaks immediately when condition is met, reducing some unnecessary comparisons, but overall still quadratic complexity.
2. Code Duplication
- No obvious code duplication, but logic can be simplified.
3. Readability Issues
- The code’s intent is not very clear. Based on the code logic, the function filters out elements that have at least one element smaller than them in the array. In other words, it removes all elements that are equal to or are the minimum.
- Readability can be improved through comments or renaming.
4. Potential Bugs
- No obvious bugs currently, but returning an empty array for empty input is expected behavior.
5. Non-compliance with Best Practices
- The process is relatively inefficient, not using Go language features to optimize performance.
- Missing comments or documentation.
Optimization Suggestions
If the goal is indeed to return all elements greater than some element in the array (excluding the minimum element), it can be changed to:
- Find the minimum element minVal in the array.
- Iterate through the array, adding elements greater than minVal to the result.
- This reduces time complexity to O(n).
Optimized code:
func processData(data []int) []int {
if len(data) == 0 {
return nil
}
minVal := data[0]
for _, v := range data[1:] {
if v < minVal {
minVal = v
}
}
result := make([]int, 0, len(data))
for _, v := range data {
if v > minVal {
result = append(result, v)
}
}
return result
}
Optimization Points Explained
- Use one traversal to determine minimum value, O(n).
- Another traversal to construct result, O(n).
- Properly use slice capacity initialization to reduce memory allocation.
- Code intent is clear and performance improvement is significant.
If you expect different logic, please let me know for further adjustments.
=== Round 1 - CodeOptimizer ===
// processData returns all values in the input slice that are greater than the minimum element.
// Returns nil if input is empty.
func processData(data []int) []int {
if len(data) == 0 {
return nil
}
// Find the minimum value in the slice
minVal := data[0]
for _, v := range data[1:] {
if v < minVal {
minVal = v
}
}
// Collect all elements greater than the minimum value
result := make([]int, 0, len(data))
for _, v := range data {
if v > minVal {
result = append(result, v)
}
}
return result
}
=== Round 1 - ExitController === TERMINATE
=== Round 2 - CodeAnalyzer === EXIT: Code quality has met standards
=== Round 2 - CodeOptimizer ===
// processData returns all values in the input slice that are greater than the minimum element.
// Returns nil if input is empty.
func processData(data []int) []int {
if len(data) == 0 {
return nil
}
// Find the minimum value in the slice
minVal := data[0]
for _, v := range data[1:] {
if v < minVal {
minVal = v
}
}
// Collect all elements greater than the minimum value
result := make([]int, 0, len(data))
for _, v := range data {
if v > minVal {
result = append(result, v)
}
}
return result
}
=== Round 2 - ExitController === TERMINATE
=== Round 3 - CodeAnalyzer === EXIT: Code quality has met standards
=== Round 3 - CodeOptimizer ===
// processData returns all values in the input slice that are greater than the minimum element.
// Returns nil if input is empty.
func processData(data []int) []int {
if len(data) == 0 {
return nil
}
minVal := data[0]
for _, v := range data[1:] {
if v < minVal {
minVal = v
}
}
result := make([]int, 0, len(data))
for _, v := range data {
if v > minVal {
result = append(result, v)
}
}
return result
}
=== Round 3 - ExitController === TERMINATE
=== Round 4 - CodeAnalyzer === EXIT: Code quality has met standards
=== Round 4 - CodeOptimizer ===
// processData returns all elements in the slice that are greater than the minimum element.
// Returns nil if input is empty.
func processData(data []int) []int {
if len(data) == 0 {
return nil
}
minVal := data[0]
for _, v := range data[1:] {
if v < minVal {
minVal = v
}
}
result := make([]int, 0, len(data))
for _, v := range data {
if v > minVal {
result = append(result, v)
}
}
return result
}
=== Round 4 - ExitController === TERMINATE
=== Round 5 - CodeAnalyzer === EXIT: Code quality has met standards
=== Round 5 - CodeOptimizer ===
// processData returns all values in the input slice that are greater than the minimum element.
// Returns nil if input is empty.
func processData(data []int) []int {
if len(data) == 0 {
return nil
}
minVal := data[0]
for _, v := range data[1:] {
if v < minVal {
minVal = v
}
}
result := make([]int, 0, len(data))
for _, v := range data {
if v > minVal {
result = append(result, v)
}
}
return result
}
=== Round 5 - ExitController === TERMINATE
Code optimization loop completed!
## BreakLoop
In a Loop Agent, when an Agent needs to interrupt the loop execution, you can use the corresponding Break Action provided by ADK.
```go
// BreakLoopAction is a programmatic-only agent action used to prematurely
// terminate the execution of a loop workflow agent.
// When a loop workflow agent receives this action from a sub-agent, it will stop its
// current iteration and will not proceed to the next one.
// It will mark the BreakLoopAction as Done, signalling to any 'upper level' loop agent
// that this action has been processed and should be ignored further up.
// This action is not intended to be used by LLMs.
type BreakLoopAction struct {
// From records the name of the agent that initiated the break loop action.
From string
// Done is a state flag that can be used by the framework to mark when the
// action has been handled.
Done bool
// CurrentIterations is populated by the framework to record at which
// iteration the loop was broken.
CurrentIterations int
}
// NewBreakLoopAction creates a new BreakLoopAction, signaling a request
// to terminate the current loop.
func NewBreakLoopAction(agentName string) *AgentAction {
return &AgentAction{BreakLoop: &BreakLoopAction{
From: agentName,
}}
}
Break Action achieves the interruption purpose without affecting other Agents outside the Loop Agent, while Exit Action immediately interrupts all subsequent Agent execution.
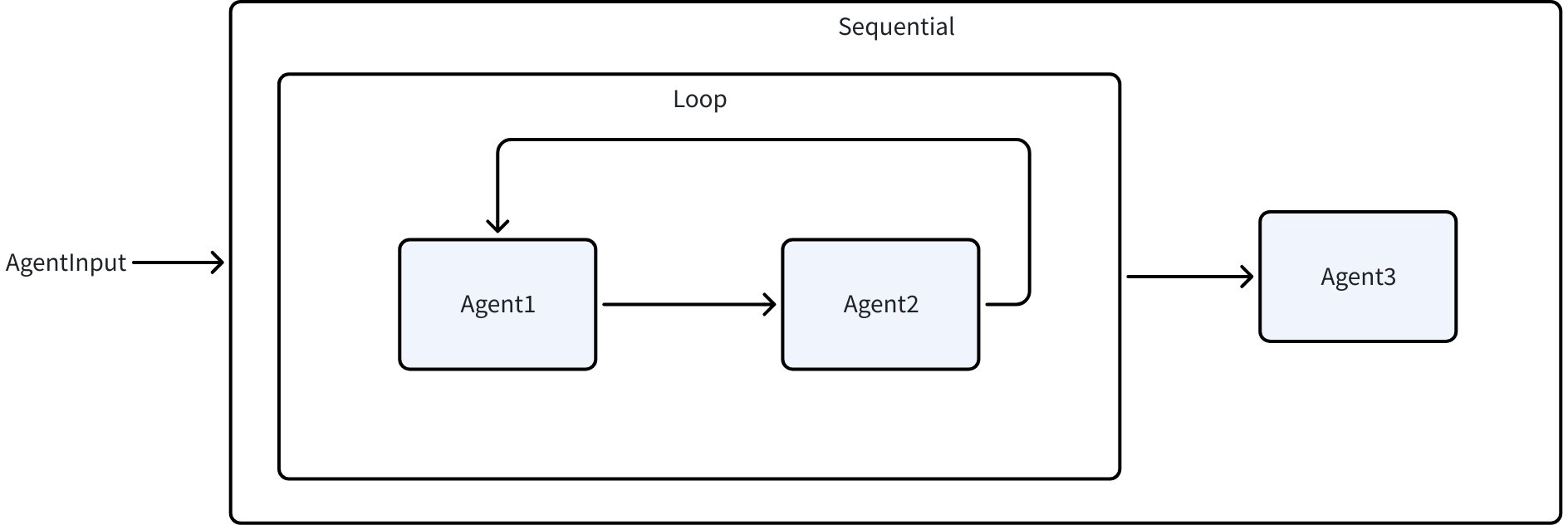
Using the following diagram as an example:
- When Agent1 issues a BreakAction, the Loop Agent will be interrupted, and Sequential continues to run Agent3
- When Agent1 issues an ExitAction, the Sequential execution flow terminates entirely, and neither Agent2 nor Agent3 will run
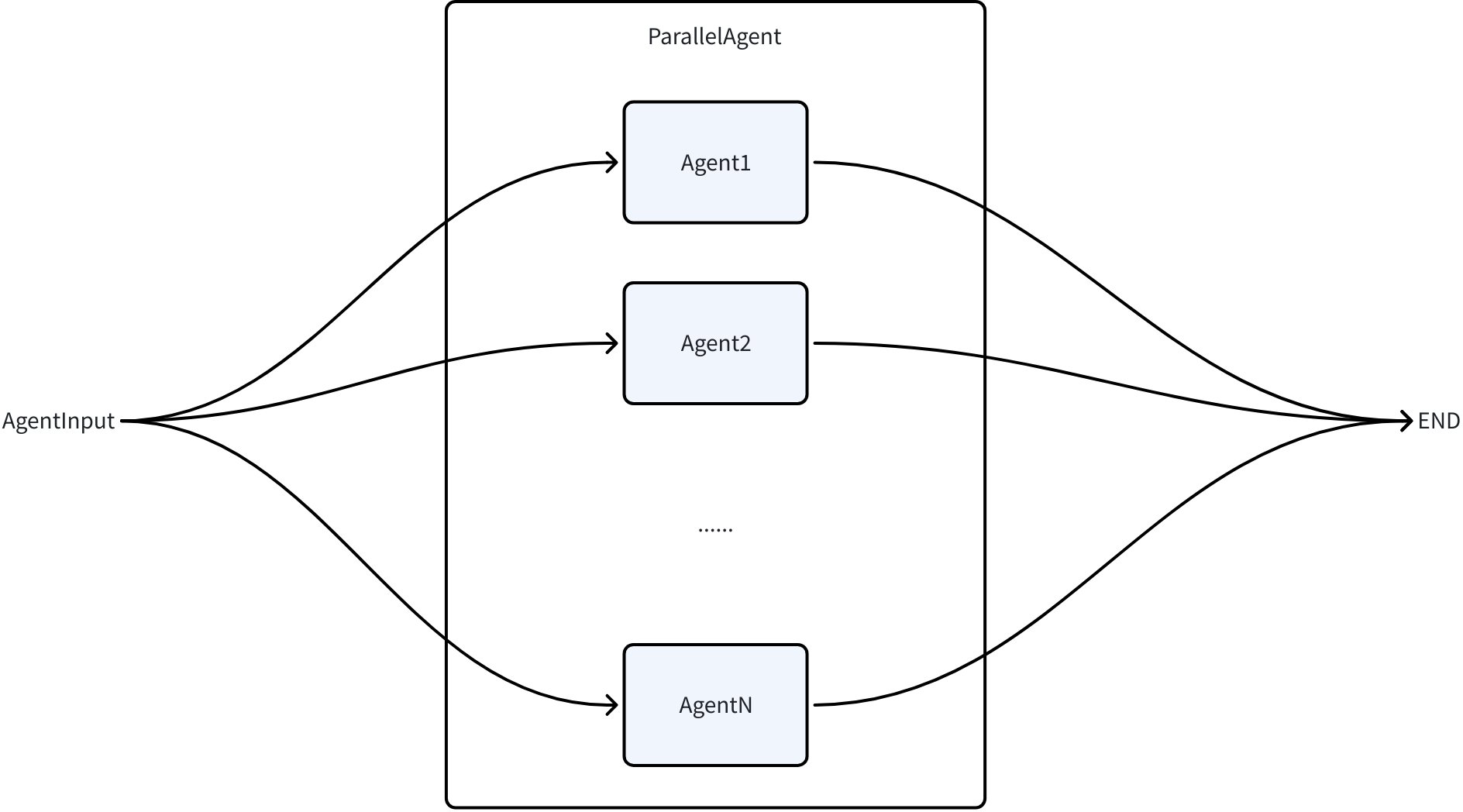
ParallelAgent
Features
ParallelAgent allows multiple sub-agents to execute concurrently based on the same input context. All sub-agents start execution simultaneously and wait for all to complete before ending. This pattern is particularly suitable for tasks that can be processed independently in parallel, significantly improving execution efficiency.
type ParallelAgentConfig struct {
Name string // Agent name
Description string // Agent description
SubAgents []Agent // List of sub-agents to execute concurrently
}
func NewParallelAgent(ctx context.Context, config *ParallelAgentConfig) (Agent, error)
ParallelAgent execution follows these rules:
- Concurrent execution: All sub-agents start simultaneously, executing in parallel in independent goroutines
- Shared input: All sub-agents receive the same initial input and context
- Wait and result aggregation: Internally uses sync.WaitGroup to wait for all sub-agents to complete, collecting all sub-agent execution results and outputting them in the order received
Additionally, Parallel internally includes exception handling mechanisms by default:
- Panic recovery: Each goroutine has independent panic recovery mechanism
- Error isolation: Errors from a single sub-agent do not affect execution of other sub-agents
- Interrupt handling: Supports sub-agent interrupt and resume mechanisms
ParallelAgent is suitable for the following scenarios:
- Independent task parallel processing: Multiple unrelated tasks can execute simultaneously
- Multi-angle analysis: Analyzing the same problem from different angles simultaneously
- Performance optimization: Reducing overall execution time through parallel execution
- Multi-expert consultation: Consulting multiple specialized domain Agents simultaneously
Example
This example demonstrates how to use ParallelAgent to analyze a product proposal from four different angles simultaneously:
- TechnicalAnalyst: Technical feasibility analysis
- BusinessAnalyst: Business value analysis
- UXAnalyst: User experience analysis
- SecurityAnalyst: Security risk analysis
package main
import (
"context"
"fmt"
"log"
"os"
"sync"
"github.com/cloudwego/eino-ext/components/model/openai"
"github.com/cloudwego/eino/adk"
"github.com/cloudwego/eino/components/model"
)
func newChatModel() model.ToolCallingChatModel {
cm, err := openai.NewChatModel(context.Background(), &openai.ChatModelConfig{
APIKey: os.Getenv("OPENAI_API_KEY"),
Model: os.Getenv("OPENAI_MODEL"),
})
if err != nil {
log.Fatal(err)
}
return cm
}
// Technical analysis Agent
func NewTechnicalAnalystAgent() adk.Agent {
a, err := adk.NewChatModelAgent(context.Background(), &adk.ChatModelAgentConfig{
Name: "TechnicalAnalyst",
Description: "Analyzes content from a technical perspective",
Instruction: `You are a technical expert. Please analyze the provided content from technical implementation, architecture design, and performance optimization perspectives.
Focus on:
1. Technical feasibility
2. Architecture rationality
3. Performance considerations
4. Technical risks
5. Implementation complexity`,
Model: newChatModel(),
})
if err != nil {
log.Fatal(err)
}
return a
}
// Business analysis Agent
func NewBusinessAnalystAgent() adk.Agent {
a, err := adk.NewChatModelAgent(context.Background(), &adk.ChatModelAgentConfig{
Name: "BusinessAnalyst",
Description: "Analyzes content from a business perspective",
Instruction: `You are a business analysis expert. Please analyze the provided content from business value, market prospects, and cost-effectiveness perspectives.
Focus on:
1. Business value
2. Market demand
3. Competitive advantages
4. Cost analysis
5. Revenue model`,
Model: newChatModel(),
})
if err != nil {
log.Fatal(err)
}
return a
}
// User experience analysis Agent
func NewUXAnalystAgent() adk.Agent {
a, err := adk.NewChatModelAgent(context.Background(), &adk.ChatModelAgentConfig{
Name: "UXAnalyst",
Description: "Analyzes content from a user experience perspective",
Instruction: `You are a user experience expert. Please analyze the provided content from user experience, usability, and user satisfaction perspectives.
Focus on:
1. User friendliness
2. Operational convenience
3. Learning cost
4. User satisfaction
5. Accessibility`,
Model: newChatModel(),
})
if err != nil {
log.Fatal(err)
}
return a
}
// Security analysis Agent
func NewSecurityAnalystAgent() adk.Agent {
a, err := adk.NewChatModelAgent(context.Background(), &adk.ChatModelAgentConfig{
Name: "SecurityAnalyst",
Description: "Analyzes content from a security perspective",
Instruction: `You are a security expert. Please analyze the provided content from information security, data protection, and privacy compliance perspectives.
Focus on:
1. Data security
2. Privacy protection
3. Access control
4. Security vulnerabilities
5. Compliance requirements`,
Model: newChatModel(),
})
if err != nil {
log.Fatal(err)
}
return a
}
func main() {
ctx := context.Background()
// Create four analysis Agents from different angles
techAnalyst := NewTechnicalAnalystAgent()
bizAnalyst := NewBusinessAnalystAgent()
uxAnalyst := NewUXAnalystAgent()
secAnalyst := NewSecurityAnalystAgent()
// Create ParallelAgent for simultaneous multi-angle analysis
parallelAgent, err := adk.NewParallelAgent(ctx, &adk.ParallelAgentConfig{
Name: "MultiPerspectiveAnalyzer",
Description: "Multi-angle parallel analysis: Technical + Business + User Experience + Security",
SubAgents: []adk.Agent{techAnalyst, bizAnalyst, uxAnalyst, secAnalyst},
})
if err != nil {
log.Fatal(err)
}
// Create Runner
runner := adk.NewRunner(ctx, adk.RunnerConfig{
Agent: parallelAgent,
})
// Product proposal to analyze
productProposal := `
Product Proposal: Intelligent Customer Service System
Overview: Develop an intelligent customer service system based on large language models that can automatically answer user questions, handle common business inquiries, and transfer to human agents when necessary.
Main Features:
1. Natural language understanding and response
2. Multi-turn conversation management
3. Knowledge base integration
4. Sentiment analysis
5. Human agent transfer
6. Conversation history recording
7. Multi-channel access (Web, WeChat, App)
Technical Architecture:
- Frontend: React + TypeScript
- Backend: Go + Gin framework
- Database: PostgreSQL + Redis
- AI Model: GPT-4 API
- Deployment: Docker + Kubernetes
`
fmt.Println("Starting multi-angle parallel analysis...")
iter := runner.Query(ctx, "Please analyze the following product proposal:\n"+productProposal)
// Use map to collect results from different analysts
results := make(map[string]string)
var mu sync.Mutex
for {
event, ok := iter.Next()
if !ok {
break
}
if event.Err != nil {
log.Printf("Error during analysis: %v", event.Err)
continue
}
if event.Output != nil && event.Output.MessageOutput != nil {
mu.Lock()
results[event.AgentName] = event.Output.MessageOutput.Message.Content
mu.Unlock()
fmt.Printf("\n=== %s analysis completed ===\n", event.AgentName)
}
}
// Output all analysis results
fmt.Println("\n" + "============================================================")
fmt.Println("Multi-angle Analysis Results Summary")
fmt.Println("============================================================")
analysisOrder := []string{"TechnicalAnalyst", "BusinessAnalyst", "UXAnalyst", "SecurityAnalyst"}
analysisNames := map[string]string{
"TechnicalAnalyst": "Technical Analysis",
"BusinessAnalyst": "Business Analysis",
"UXAnalyst": "User Experience Analysis",
"SecurityAnalyst": "Security Analysis",
}
for _, agentName := range analysisOrder {
if result, exists := results[agentName]; exists {
fmt.Printf("\n【%s】\n", analysisNames[agentName])
fmt.Printf("%s\n", result)
fmt.Println("----------------------------------------")
}
}
fmt.Println("\nMulti-angle parallel analysis completed!")
fmt.Printf("Received %d analysis results\n", len(results))
}
Run result:
Starting multi-angle parallel analysis...
=== BusinessAnalyst analysis completed ===
=== UXAnalyst analysis completed ===
=== SecurityAnalyst analysis completed ===
=== TechnicalAnalyst analysis completed ===
============================================================
Multi-angle Analysis Results Summary
============================================================
【Technical Analysis】
For this intelligent customer service system proposal, here is a detailed analysis from technical implementation, architecture design, and performance optimization perspectives:
---
### I. Technical Feasibility
1. **Natural Language Understanding and Response**
- Using GPT-4 API for natural language understanding and automatic response is a mature and feasible solution. GPT-4 has strong language understanding and generation capabilities, suitable for handling complex and diverse questions.
2. **Multi-turn Conversation Management**
- Relies on backend to maintain context state, combined with GPT-4 model can handle multi-turn interactions well. Need to design reasonable context management mechanism (such as conversation history maintenance, key slot extraction, etc.) to ensure context information integrity.
3. **Knowledge Base Integration**
- Can add specific knowledge base retrieval results to GPT-4 API (retrieval-augmented generation), or integrate knowledge base through local retrieval interface. Technically feasible, but has high requirements for real-time and accuracy.
4. **Sentiment Analysis**
- Sentiment analysis function can be implemented with independent lightweight models (such as fine-tuned BERT), or try using GPT-4 output, but cost is higher. Sentiment analysis capability helps intelligent customer service better understand user emotions and improve user experience.
5. **Human Agent Transfer**
- Technically achievable through establishing event trigger rules (such as turn count, emotion threshold, keyword detection) to implement automatic transfer to human. System needs to support ticket or session transfer mechanism and ensure seamless session switching.
6. **Multi-channel Access**
- Multi-channel access including web, WeChat, App can all be achieved through unified API gateway, technology is mature, while needing to handle channel differences (message format, authentication, push mechanism, etc.).
---
### II. Architecture Rationality
- **Frontend React + TypeScript**
Very suitable for building responsive customer service interface, mature ecosystem, convenient for multi-channel component sharing.
- **Backend Go + Gin**
Go language has excellent performance, Gin framework is lightweight and high-performance, suitable for high-concurrency scenarios. Backend handles GPT-4 API integration, state management, multi-channel message forwarding and other responsibilities, reasonable choice.
- **Database PostgreSQL + Redis**
- PostgreSQL handles structured data storage, such as user information, conversation history, knowledge base metadata.
- Redis handles session state caching, hot knowledge base, rate limiting, etc., improving access performance.
Architecture design follows common large internet product patterns, with clear component division.
- **AI Model GPT-4 API**
Using mature API reduces development difficulty and model maintenance cost; disadvantage is high dependency on network and API calls.
- **Deployment Docker + Kubernetes**
Containerization and K8s orchestration ensure system elastic scaling, high availability and canary deployment, suitable for production environment, follows modern microservices architecture trends.
---
### III. Performance Considerations
1. **Response Time**
- GPT-4 API calls have inherent latency (usually hundreds of milliseconds to 1 second), significantly affecting response time. Need to handle interface asynchronously and design frontend experience well (such as loading animations, partial progressive response).
2. **Concurrent Processing Capability**
- Backend Go has high concurrent processing advantages, combined with Redis caching hot data, can greatly improve overall throughput.
- But GPT-4 API calls are limited by OpenAI service QPS limits and call costs, need to reasonably design call frequency and degradation strategies.
3. **Caching Strategy**
- Cache user conversation context and common question answers to reduce repeated API calls.
- Match key questions locally first, call GPT-4 only on failure, improving efficiency.
4. **Multi-channel Load Balancing**
- Need to design unified message bus and reliable async queue to prevent traffic spikes from one channel affecting overall system stability.
---
### IV. Technical Risks
1. **GPT-4 API Dependency**
- High dependency on third-party API, risks include service interruption, interface changes and cost fluctuations.
- Recommend designing local cache and limited alternative response logic to handle API exceptions.
2. **Multi-turn Conversation Context Management Difficulty**
- Context too long or complex will reduce answer quality, need to design context length limits and selective important information retention mechanism.
3. **Knowledge Base Integration Complexity**
- How to achieve knowledge base and...
----------------------------------------
【Business Analysis】
Here is the business perspective analysis of the intelligent customer service system product proposal:
1. Business Value
- Improve customer service efficiency: Automatically answer user questions and common inquiries, reduce human agent pressure, lower labor costs.
- Improve user experience: Multi-turn conversation and sentiment analysis make interactions more natural, enhance customer satisfaction and stickiness.
- Data-driven decision support: Conversation history and knowledge base integration provide valuable user feedback and behavior data for enterprises, optimizing products and services.
- Support business expansion: Multi-channel access (web, WeChat, App) meets different customer access habits, improving coverage.
2. Market Demand
- Market demand for intelligent customer service continues to grow, especially in e-commerce, finance, healthcare, education and other industries, customer service automation is an important direction for enterprise digital transformation.
- With the maturity of AI technology, enterprises expect to use large language models to improve customer service intelligence level.
- Users' demand for instant response and 24/7 service is increasing, driving widespread adoption of intelligent customer service systems.
3. Competitive Advantages
- Using advanced GPT-4 large language model, has strong natural language understanding and generation capabilities, improving Q&A accuracy and conversation naturalness.
- Sentiment analysis function helps accurately identify user emotions, dynamically adjust response strategies, improve customer satisfaction.
- Multi-channel access design meets enterprise diversified customer reach needs, enhancing product applicability.
- Technical architecture uses microservices, containerized deployment, convenient for elastic scaling and maintenance, improving system stability and scalability.
4. Cost Analysis
- AI model call cost is high, depends on GPT-4 API, need to adjust budget based on call volume and response speed.
- Technical R&D investment is large, involving frontend and backend, multi-channel integration, AI and knowledge base management.
- Operation and server costs need to consider multi-channel concurrent access.
- In the long term, human agent count can be significantly reduced, saving labor costs.
- Can reduce initial hardware investment through cloud services, but cloud resource usage needs careful management to control costs.
5. Revenue Model
- SaaS subscription service: Charge monthly/yearly service fees to enterprise customers, tiered pricing based on access channels, concurrency, and feature levels.
- Charge by call count or conversation count, suitable for customers with large business fluctuations.
- Value-added services: Data analysis report customization, industry knowledge base integration, human agent collaboration tools, etc.
- For medium and large customers, can provide custom development and technical support, charging project fees.
- Through continuous model and service optimization, increase customer retention and renewal rates.
In summary, this intelligent customer service system based on mature technology and AI advantages has good business value and market potential. Its multi-channel access and sentiment analysis features enhance competitiveness, but need to reasonably control AI call costs and operating expenses. Recommend focusing on SaaS subscription and value-added services, combined with marketing, quickly capture customer resources and improve profitability.
----------------------------------------
【User Experience Analysis】
For this intelligent customer service system proposal, I will analyze from user experience, usability, user satisfaction and accessibility perspectives:
1. User Friendliness
- Natural language understanding and response capability improves user communication experience with the system, allowing users to express needs in natural language, reducing communication barriers.
- Multi-turn conversation management allows the system to understand context, reducing repeated explanations, enhancing conversation coherence, further improving user experience.
- Sentiment analysis function helps the system identify user emotions, making more thoughtful responses, improving interaction personalization and humanization.
- Multi-channel access covers users' commonly used access paths, convenient for users to get service anytime anywhere, improving friendliness.
2. Operational Convenience
- Automatically answering common business inquiries can reduce user waiting time and operational burden, improving response speed.
- Human agent transfer mechanism ensures complex issues can be handled timely, ensuring service continuity and seamless operation handoff.
- Conversation history recording convenient for users to review consultation content, avoiding repeated queries, improving operational convenience.
- Using modern tech stack (React, TypeScript) provides good frontend interaction performance and response speed, indirectly enhancing operational smoothness.
3. Learning Cost
- Based on natural language processing, users don't need to learn special commands, lowering usage threshold.
- Multi-turn conversation natural connection makes it easier for users to understand system response logic, reducing confusion and frustration.
- Consistent interface across different channels (such as keeping similar experience on web and WeChat) helps users get started quickly.
- More precise feedback provided through sentiment analysis reduces time cost of users frequently trying due to misunderstanding.
4. User Satisfaction
- Fast and accurate automatic replies and multi-turn conversation reduce user waiting and repeated input, improving satisfaction.
- Sentiment analysis makes the system better understand user emotions, bringing warmer interaction experience, increasing user stickiness.
- Human agent intervention ensures complex issues are properly handled, improving service quality perception.
- Multi-channel coverage meets different users' usage scenarios, enhancing overall satisfaction.
5. Accessibility
- Multi-channel access covers web, WeChat, App, adapting to different users' devices and environments, improving accessibility.
- The proposal doesn't explicitly mention accessibility design (such as screen reader compatibility, high contrast mode, etc.), which may be an area to supplement in the future.
- Frontend using React and TypeScript is conducive to implementing responsive design and accessibility features, but need to ensure development standards are implemented.
- Backend architecture and deployment solution ensure system stability and scalability, indirectly improving user continuous accessibility.
Summary:
This intelligent customer service system proposal is fairly comprehensive in user experience and usability considerations, using large language models to achieve natural multi-turn conversation, sentiment analysis and knowledge base integration, meeting users' diverse needs. Meanwhile, multi-channel access enhances system coverage. Recommend strengthening accessibility design in specific implementation to achieve more comprehensive accessibility assurance, while continuing to optimize conversation strategies to improve user satisfaction.
----------------------------------------
【Security Analysis】
For this intelligent customer service system proposal, here is the analysis from information security, data protection and privacy compliance perspectives:
I. Data Security
1. Data Transmission Security
- Recommend all client-server communications use TLS/SSL encryption to ensure data confidentiality and integrity during transmission.
- Since multi-channel access is supported (web, WeChat, App), need to ensure each entry point strictly implements encrypted transmission.
2. Data Storage Security
- PostgreSQL stores sensitive information like conversation history and user data, need to enable database encryption (such as transparent data encryption TDE or field-level encryption) to prevent data leakage.
- Redis as cache may store temporary session data, also need to enable access authentication and encrypted transmission.
- Implement minimum storage principle for user sensitive data, avoid storing unrelated data beyond scope.
- Data backup process needs encrypted storage, and backup access should also be controlled.
3. API Call Security
- GPT-4 API calls generate large amounts of user data interaction, should evaluate its data processing and storage policies to ensure compliance with data security requirements.
- Add call permission management, limit API key access scope and permissions to prevent abuse.
4. Log Security
- System logs should avoid storing plaintext sensitive information, especially personal identity information and conversation content. Log access needs strict control.
II. Privacy Protection
1. Personal Data Processing
- Collection and storage of user personal data (name, contact information, account information, etc.) must clearly inform users and obtain user consent.
- Implement data anonymization/de-identification technology, especially for identity information processing in conversation history.
2. User Privacy Rights
- Meet users' rights to access, correct, and delete data in relevant laws and regulations (such as Personal Information Protection Law, GDPR).
- Provide privacy policy clearly disclosing data collection, use and sharing situations.
3. Interaction Privacy
- Multi-turn conversation and sentiment analysis features should consider avoiding excessive invasion of user privacy, such as transparent notification and restriction of sensitive emotion data usage.
4. Third-party Compliance
- GPT-4 API is provided by third party, need to ensure its service complies with relevant privacy compliance requirements and data protection standards.
III. Access Control
1. User Identity Verification
- When system involves user identity information query and management, need to establish reliable identity authentication mechanism.
- Support multi-factor authentication to enhance security.
2. Permission Management
- Backend management interface and human agent transfer module need to use role-based access control (RBAC) to ensure minimum operation permissions.
- Operations accessing sensitive data need detailed audit and monitoring.
3. Session Management
- Need effective session management mechanism for multi-channel sessions to prevent session hijacking.
- Conversation history access permissions should be limited to only relevant users or authorized personnel.
IV. Security Vulnerabilities
1. Application Security
- Frontend React+TypeScript should prevent XSS, CSRF attacks, reasonably use Content Security Policy (CSP).
- Backend Go application needs to prevent SQL injection, request forgery and permission deficiency. Gin framework provides middleware support, recommend fully utilizing security modules.
2. AI Model Risks
- GPT-4 API input/output may have sensitive information leakage or model misuse risks, need to limit input content and filter sensitive information.
- Prevent generating malicious answers or information leakage, establish content review mechanism.
3. Container and Deployment Security
- Docker containers must use secure images and patch timely. Kubernetes cluster network policies and access control need to be complete.
- Container runtime permissions minimized to avoid container escape risks.
V. Compliance Requirements
1. Data Protection Regulations
- Based on operating region, need to comply with Personal Information Protection Law (PIPL), EU General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) or other relevant legal requirements.
- Clearly define user data collection, processing, transmission and storage processes comply with regulations.
2. User Privacy Notice and Consent
- Should provide clear privacy policy and terms of use, explaining data purposes and processing methods.
- Implement user consent management mechanism.
3. Cross-border Data Transfer Compliance
- If system involves cross-border data flow, need to assess compliance risks and take corresponding technical...
----------------------------------------
Multi-angle parallel analysis completed!
Received 4 analysis results
Summary
Workflow Agents provide powerful multi-agent collaboration capabilities for Eino ADK. By reasonably selecting and combining these Workflow Agents, developers can build efficient and reliable multi-agent collaboration systems to meet various complex business requirements.