Eino ADK: Agent Collaboration
Agent Collaboration
The overview document has provided basic explanations of Agent collaboration. Below we will introduce the design and implementation of collaboration and composition primitives in combination with code:
Collaboration Primitives
Inter-Agent Collaboration Methods
| Collaboration Method | Description |
| Transfer | Directly transfers the task to another Agent. The current Agent exits after execution completes, without concern for the task execution status of the transferred Agent |
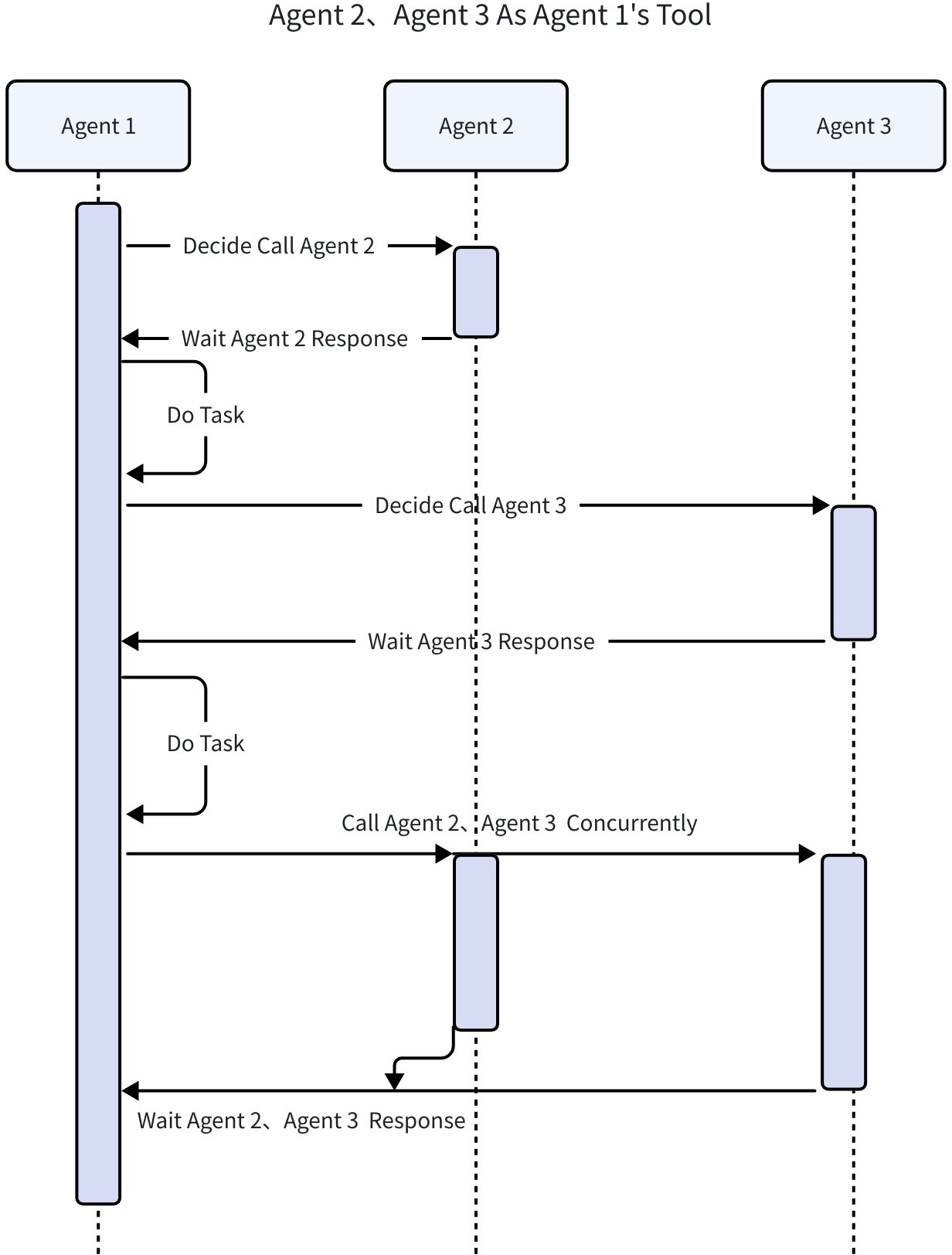
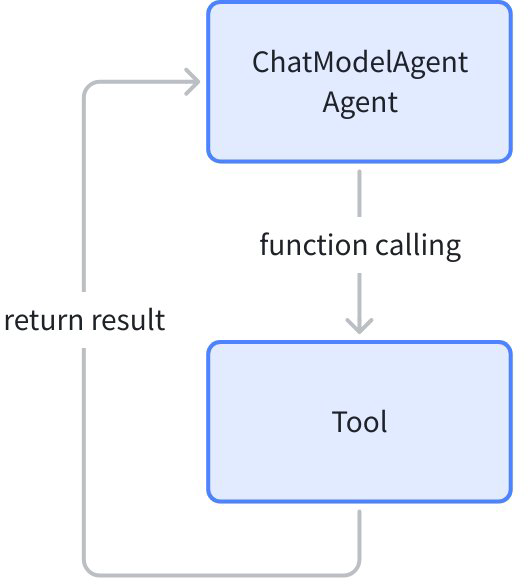
| ToolCall (AgentAsTool) | Invokes the Agent as a ToolCall, waits for the Agent's response, and can obtain the output result of the called Agent for the next round of processing |
AgentInput Context Strategies
| Context Strategy | Description |
| Upstream Agent Full Conversation | Gets the complete conversation history of the current Agent's upstream Agent |
| Fresh Task Description | Ignores the complete conversation history of the upstream Agent and provides a completely new task summary as the AgentInput for the sub-Agent |
Decision Autonomy
| Decision Autonomy | Description |
| Autonomous Decision | Within the Agent, based on its available downstream Agents, when assistance is needed, it autonomously selects a downstream Agent for assistance. Generally, the Agent makes decisions based on LLM internally, but even if selection is based on preset logic, it is still considered autonomous decision from the Agent's external perspective |
| Preset Decision | The next Agent after an Agent executes a task is predetermined. The execution order of Agents is predetermined and predictable |
Composition Primitives
Context Passing
When building multi-Agent systems, efficient and accurate sharing of information between different Agents is crucial. Eino ADK provides two core context passing mechanisms to meet different collaboration needs: History and SessionValues.
History
Concept
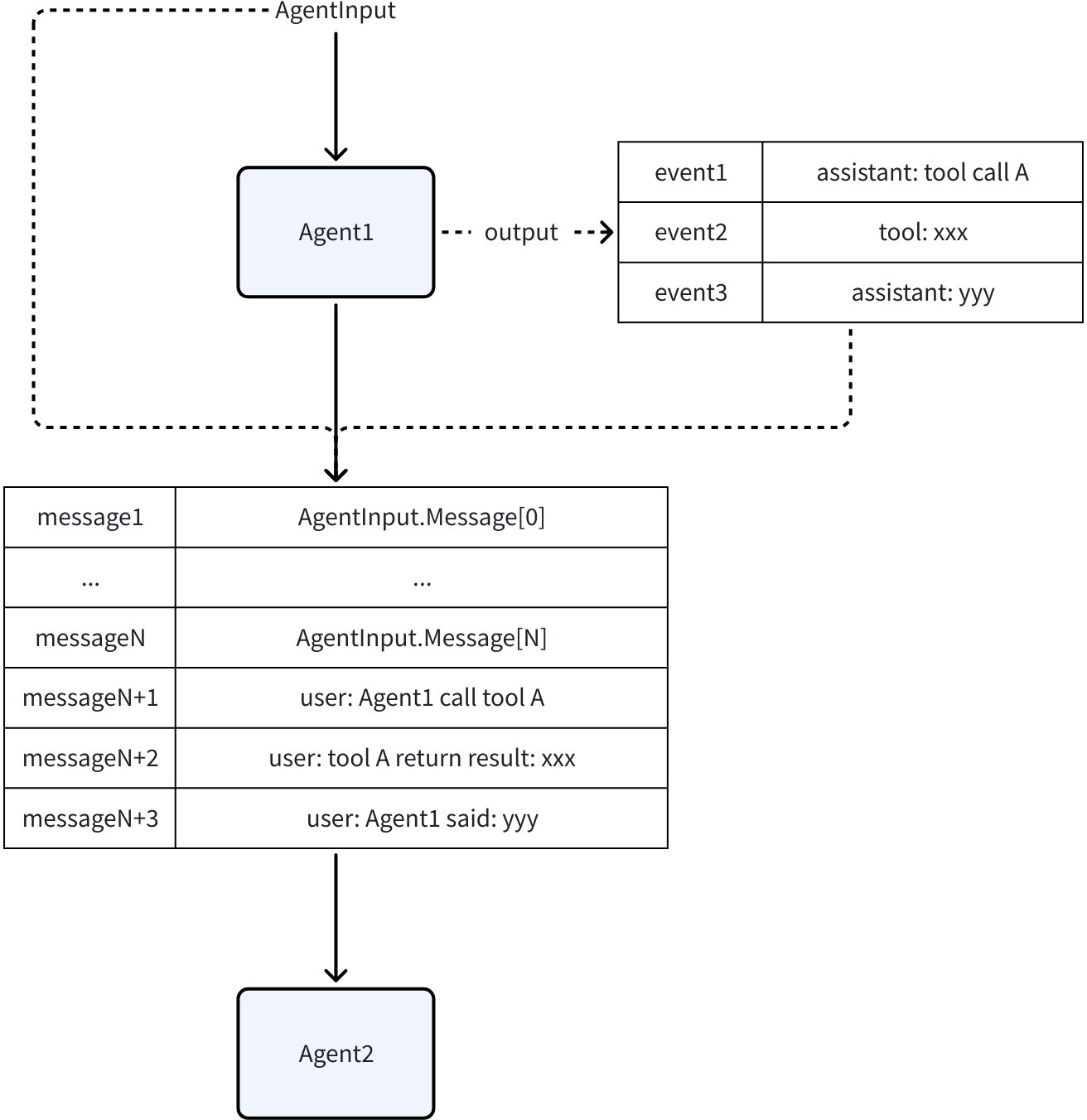
History corresponds to the [Upstream Agent Full Conversation context strategy]. Every AgentEvent produced by each Agent in a multi-Agent system is saved to History. When calling a new Agent (Workflow/Transfer), the AgentEvents in History are converted and concatenated into the AgentInput.
By default, Assistant or Tool Messages from other Agents are converted to User Messages. This is equivalent to telling the current LLM: “Just now, Agent_A called some_tool and returned some_result. Now it’s your turn to make a decision.”
Through this approach, other Agents’ behaviors are treated as “external information” or “factual statements” provided to the current Agent, rather than its own behaviors, thus avoiding LLM context confusion.
In Eino ADK, when building AgentInput for an Agent, the History it can see is “all AgentEvents produced before me”.
Worth mentioning is ParallelWorkflowAgent: two parallel sub-Agents (A, B) cannot see each other’s AgentEvents during parallel execution because neither A nor B precedes the other.
RunPath
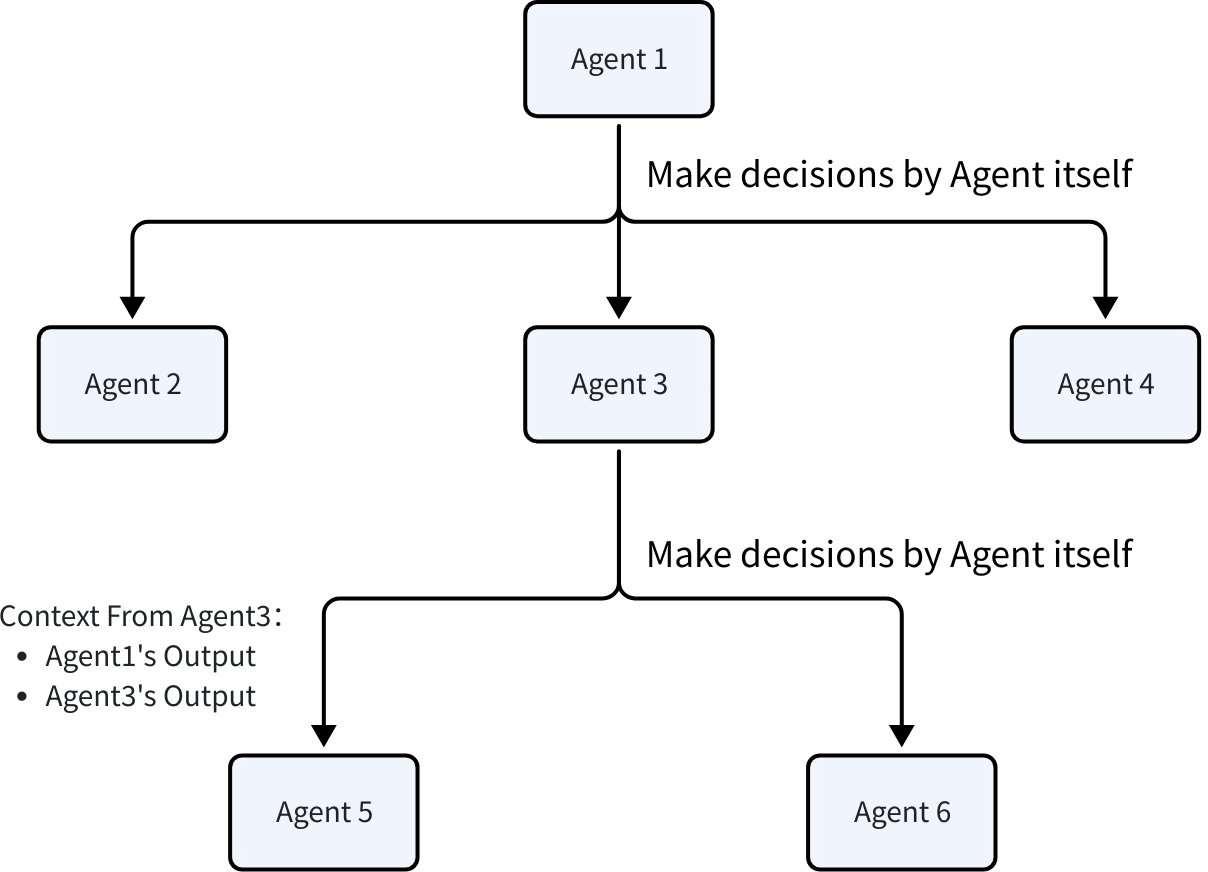
Each AgentEvent in History is “produced by a specific Agent in a specific execution sequence”, meaning AgentEvent has its own RunPath. The purpose of RunPath is to convey this information; it doesn’t carry other functions in the eino framework.
The table below shows the specific RunPath when Agents execute under various orchestration modes:
Customization
In some cases, the History content needs to be adjusted before the Agent runs. At this point, you can customize how the Agent generates AgentInput from History using AgentWithOptions:
// github.com/cloudwego/eino/adk/flow.go
type HistoryRewriter func(ctx context.Context, entries []*HistoryEntry) ([]Message, error)
func WithHistoryRewriter(h HistoryRewriter) AgentOption
SessionValues
Concept
SessionValues is a global temporary KV store that persists throughout a single run, used to support cross-Agent state management and data sharing. Any Agent in a single run can read and write SessionValues at any time.
Eino ADK provides multiple methods for Agents to read and write Session Values in a concurrency-safe manner at runtime:
// github.com/cloudwego/eino/adk/runctx.go
// Get all SessionValues
func GetSessionValues(ctx context.Context) map[string]any
// Batch set SessionValues
func AddSessionValues(ctx context.Context, kvs map[string]any)
// Get a value from SessionValues by specified key. Returns false as the second value if key doesn't exist, otherwise true
func GetSessionValue(ctx context.Context, key string) (any, bool)
// Set a single SessionValue
func AddSessionValue(ctx context.Context, key string, value any)
Note that since the SessionValues mechanism is implemented based on Context, and Runner reinitializes the Context when running, injecting SessionValues via AddSessionValues or AddSessionValue outside of the Run method will not take effect.
If you need to inject data into SessionValues before the Agent runs, you need to use a dedicated Option to assist with this. Usage is as follows:
// github.com/cloudwego/eino/adk/call_option.go
// WithSessionValues injects SessionValues before Agent runs
func WithSessionValues(v map[string]any) AgentRunOption
// Usage:
runner := adk.NewRunner(ctx, adk.RunnerConfig{Agent: agent})
iterator := runner.Run(ctx, []adk.Message{schema.UserMessage("xxx")},
adk.WithSessionValues(map[string]any{
PlanSessionKey: 123,
UserInputSessionKey: []adk.Message{schema.UserMessage("yyy")},
}),
)
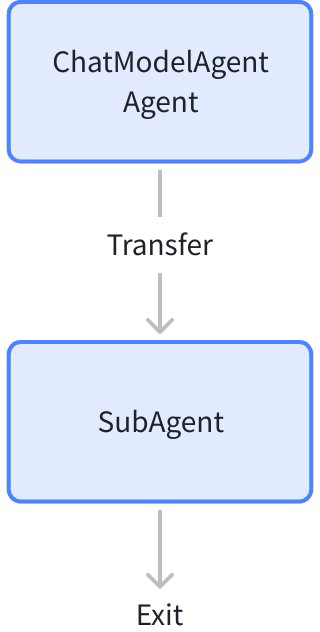
Transfer SubAgents
Concept
Transfer corresponds to the [Transfer collaboration method]. When an Agent produces an AgentEvent containing TransferAction during runtime, Eino ADK calls the Agent specified by the Action. The called Agent is called a SubAgent.
TransferAction can be quickly created using NewTransferToAgentAction:
import "github.com/cloudwego/eino/adk"
event := adk.NewTransferToAgentAction("dest agent name")
For Eino ADK to find and run the SubAgent instance upon receiving TransferAction, you need to first call SetSubAgents to register possible SubAgents with Eino ADK before running:
// github.com/cloudwego/eino/adk/flow.go
func SetSubAgents(ctx context.Context, agent Agent, subAgents []Agent) (Agent, error)
💡 The meaning of Transfer is to hand over the task to the SubAgent, not delegate or assign. Therefore:
- Unlike ToolCall, when calling a SubAgent through Transfer, after the SubAgent finishes running, the parent Agent will not be called again to summarize content or perform the next operation.
- When calling a SubAgent, the SubAgent’s input is still the original input, and the parent Agent’s output serves as context for the SubAgent’s reference.
When triggering SetSubAgents, both parent and child Agents need to process to complete initialization. Eino ADK defines the OnSubAgents interface to support this functionality:
// github.com/cloudwego/eino/adk/interface.go
type OnSubAgents interface {
OnSetSubAgents(ctx context.Context, subAgents []Agent) error
OnSetAsSubAgent(ctx context.Context, parent Agent) error
OnDisallowTransferToParent(ctx context.Context) error
}
If an Agent implements the OnSubAgents interface, SetSubAgents will call the corresponding methods to register with the Agent. For example, ChatModelAgent’s implementation.
Example
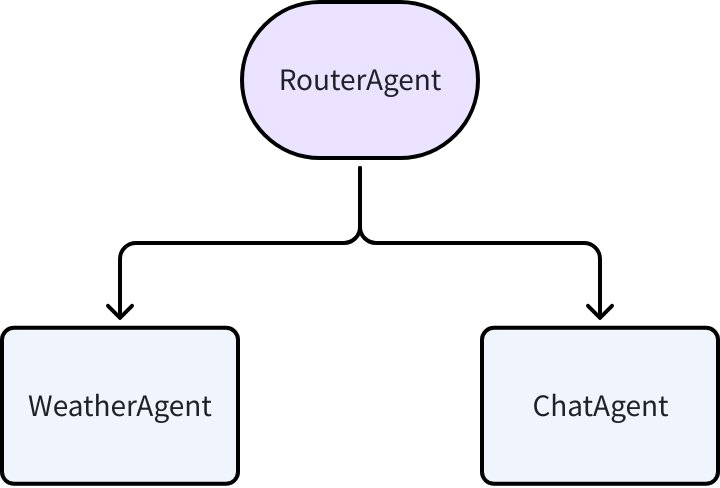
Below we demonstrate the Transfer capability with a multi-functional conversation Agent. The goal is to build an Agent that can query weather or chat with users. The Agent structure is as follows:
All three Agents are implemented using ChatModelAgent:
import (
"context"
"fmt"
"log"
"os"
"github.com/cloudwego/eino-ext/components/model/openai"
"github.com/cloudwego/eino/adk"
"github.com/cloudwego/eino/components/model"
"github.com/cloudwego/eino/components/tool"
"github.com/cloudwego/eino/components/tool/utils"
"github.com/cloudwego/eino/compose"
)
func newChatModel() model.ToolCallingChatModel {
cm, err := openai.NewChatModel(context.Background(), &openai.ChatModelConfig{
APIKey: os.Getenv("OPENAI_API_KEY"),
Model: os.Getenv("OPENAI_MODEL"),
})
if err != nil {
log.Fatal(err)
}
return cm
}
type GetWeatherInput struct {
City string `json:"city"`
}
func NewWeatherAgent() adk.Agent {
weatherTool, err := utils.InferTool(
"get_weather",
"Gets the current weather for a specific city.",
func(ctx context.Context, input *GetWeatherInput) (string, error) {
return fmt.Sprintf(`the temperature in %s is 25°C`, input.City), nil
},
)
if err != nil {
log.Fatal(err)
}
a, err := adk.NewChatModelAgent(context.Background(), &adk.ChatModelAgentConfig{
Name: "WeatherAgent",
Description: "This agent can get the current weather for a given city.",
Instruction: "Your sole purpose is to get the current weather for a given city by using the 'get_weather' tool. After calling the tool, report the result directly to the user.",
Model: newChatModel(),
ToolsConfig: adk.ToolsConfig{
ToolsNodeConfig: compose.ToolsNodeConfig{
Tools: []tool.BaseTool{weatherTool},
},
},
})
if err != nil {
log.Fatal(err)
}
return a
}
func NewChatAgent() adk.Agent {
a, err := adk.NewChatModelAgent(context.Background(), &adk.ChatModelAgentConfig{
Name: "ChatAgent",
Description: "A general-purpose agent for handling conversational chat.",
Instruction: "You are a friendly conversational assistant. Your role is to handle general chit-chat and answer questions that are not related to any specific tool-based tasks.",
Model: newChatModel(),
})
if err != nil {
log.Fatal(err)
}
return a
}
func NewRouterAgent() adk.Agent {
a, err := adk.NewChatModelAgent(context.Background(), &adk.ChatModelAgentConfig{
Name: "RouterAgent",
Description: "A manual router that transfers tasks to other expert agents.",
Instruction: `You are an intelligent task router. Your responsibility is to analyze the user's request and delegate it to the most appropriate expert agent.If no Agent can handle the task, simply inform the user it cannot be processed.`,
Model: newChatModel(),
})
if err != nil {
log.Fatal(err)
}
return a
}
Then use Eino ADK’s Transfer capability to build a Multi-Agent and run it. ChatModelAgent implements the OnSubAgent interface. In the adk.SetSubAgents method, this interface is used to register parent/child Agents with ChatModelAgent, without requiring users to handle TransferAction generation:
import (
"context"
"fmt"
"log"
"os"
"github.com/cloudwego/eino/adk"
)
func main() {
weatherAgent := NewWeatherAgent()
chatAgent := NewChatAgent()
routerAgent := NewRouterAgent()
ctx := context.Background()
a, err := adk.SetSubAgents(ctx, routerAgent, []adk.Agent{chatAgent, weatherAgent})
if err != nil {
log.Fatal(err)
}
runner := adk.NewRunner(ctx, adk.RunnerConfig{
Agent: a,
})
// query weather
println("\n\n>>>>>>>>>query weather<<<<<<<<<")
iter := runner.Query(ctx, "What's the weather in Beijing?")
for {
event, ok := iter.Next()
if !ok {
break
}
if event.Err != nil {
log.Fatal(event.Err)
}
if event.Action != nil {
fmt.Printf("\nAgent[%s]: transfer to %+v\n\n======\n", event.AgentName, event.Action.TransferToAgent.DestAgentName)
} else {
fmt.Printf("\nAgent[%s]:\n%+v\n\n======\n", event.AgentName, event.Output.MessageOutput.Message)
}
}
// failed to route
println("\n\n>>>>>>>>>failed to route<<<<<<<<<")
iter = runner.Query(ctx, "Book me a flight from New York to London tomorrow.")
for {
event, ok := iter.Next()
if !ok {
break
}
if event.Err != nil {
log.Fatal(event.Err)
}
if event.Action != nil {
fmt.Printf("\nAgent[%s]: transfer to %+v\n\n======\n", event.AgentName, event.Action.TransferToAgent.DestAgentName)
} else {
fmt.Printf("\nAgent[%s]:\n%+v\n\n======\n", event.AgentName, event.Output.MessageOutput.Message)
}
}
}
Running result:
>>>>>>>>>query weather<<<<<<<<<
Agent[RouterAgent]:
assistant:
tool_calls:
{Index:<nil> ID:call_SKNsPwKCTdp1oHxSlAFt8sO6 Type:function Function:{Name:transfer_to_agent Arguments:{"agent_name":"WeatherAgent"}} Extra:map[]}
finish_reason: tool_calls
usage: &{201 17 218}
======
Agent[RouterAgent]: transfer to WeatherAgent
======
Agent[WeatherAgent]:
assistant:
tool_calls:
{Index:<nil> ID:call_QMBdUwKj84hKDAwMMX1gOiES Type:function Function:{Name:get_weather Arguments:{"city":"Beijing"}} Extra:map[]}
finish_reason: tool_calls
usage: &{255 15 270}
======
Agent[WeatherAgent]:
tool: the temperature in Beijing is 25°C
tool_call_id: call_QMBdUwKj84hKDAwMMX1gOiES
tool_call_name: get_weather
======
Agent[WeatherAgent]:
assistant: The current temperature in Beijing is 25°C.
finish_reason: stop
usage: &{286 11 297}
======
>>>>>>>>>failed to route<<<<<<<<<
Agent[RouterAgent]:
assistant: I'm unable to assist with booking flights. Please use a relevant travel service or booking platform to make your reservation.
finish_reason: stop
usage: &{206 23 229}
======
The other two methods of OnSubAgents are called when an Agent acts as a SubAgent in SetSubAgents:
- OnSetAsSubAgent is used to register parent Agent information with the Agent
- OnDisallowTransferToParent is called when the Agent sets the WithDisallowTransferToParent option, to inform the Agent not to produce TransferAction to the parent Agent.
adk.SetSubAgents(
ctx,
Agent1,
[]adk.Agent{
adk.AgentWithOptions(ctx, Agent2, adk.WithDisallowTransferToParent()),
},
)
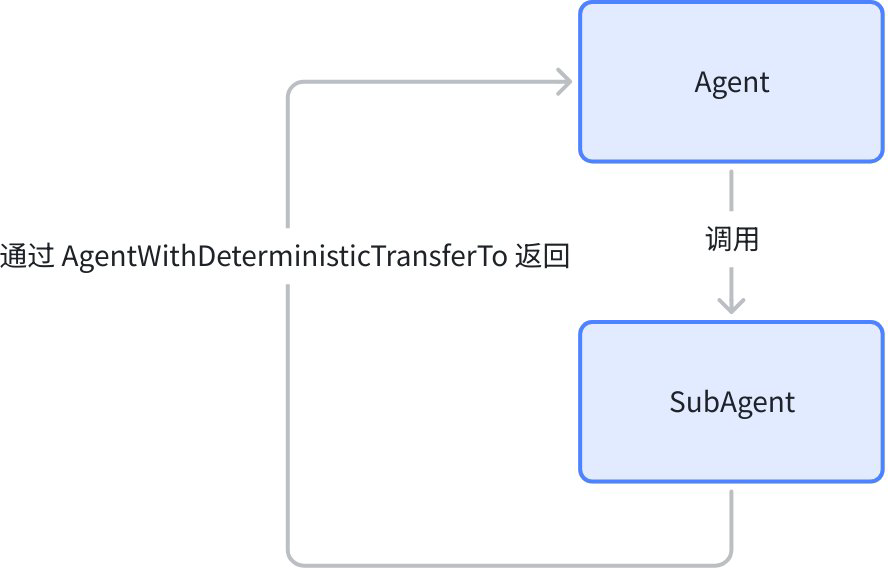
Static Transfer Configuration
AgentWithDeterministicTransferTo is an Agent Wrapper that generates a preset TransferAction after the original Agent executes, enabling static configuration of Agent jumping:
// github.com/cloudwego/eino/adk/flow.go
type DeterministicTransferConfig struct {
Agent Agent
ToAgentNames []string
}
func AgentWithDeterministicTransferTo(_ context.Context, config *DeterministicTransferConfig) Agent
In Supervisor mode, after a SubAgent finishes execution, it always returns to the Supervisor, which generates the next task objective. AgentWithDeterministicTransferTo can be used here:
// github.com/cloudwego/eino/adk/prebuilt/supervisor.go
type SupervisorConfig struct {
Supervisor adk.Agent
SubAgents []adk.Agent
}
func NewSupervisor(ctx context.Context, conf *SupervisorConfig) (adk.Agent, error) {
subAgents := make([]adk.Agent, 0, len(conf.SubAgents))
supervisorName := conf.Supervisor.Name(ctx)
for _, subAgent := range conf.SubAgents {
subAgents = append(subAgents, adk.AgentWithDeterministicTransferTo(ctx, &adk.DeterministicTransferConfig{
Agent: subAgent,
ToAgentNames: []string{supervisorName},
}))
}
return adk.SetSubAgents(ctx, conf.Supervisor, subAgents)
}
Workflow Agents
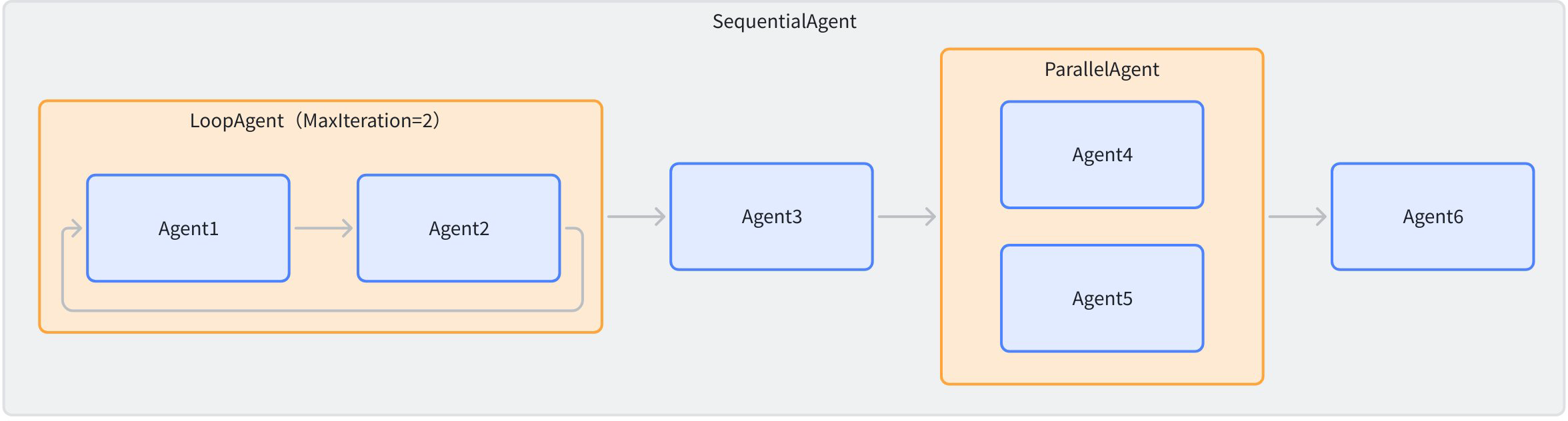
WorkflowAgent supports running Agents according to workflows preset in code. Eino ADK provides three basic Workflow Agents: Sequential, Parallel, and Loop. They can be nested within each other to complete more complex tasks.
By default, the input for each Agent in a Workflow is generated using the method described in the History section. You can customize the AgentInput generation method using WithHistoryRewriter.
When an Agent produces an ExitAction Event, the Workflow Agent will immediately exit, regardless of whether there are other Agents that need to run afterward.
For detailed explanations and use case references, see: Eino ADK: Workflow Agents
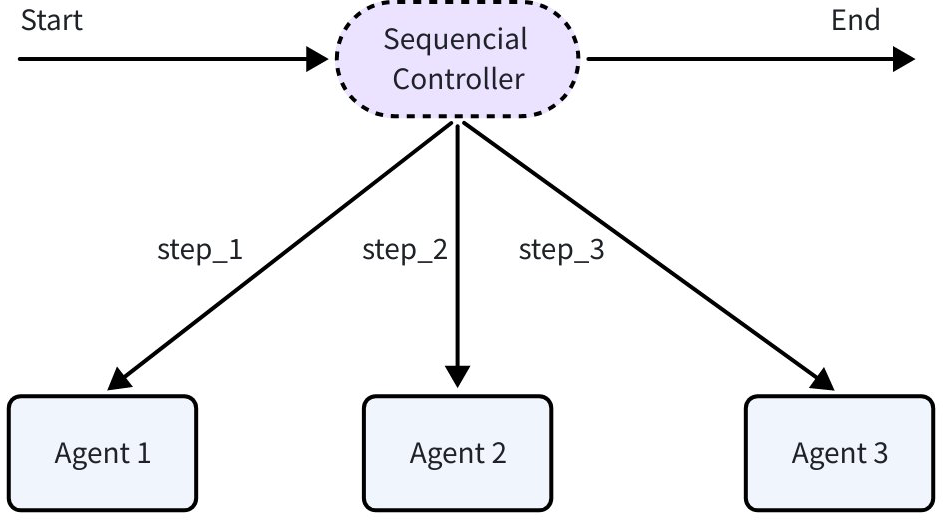
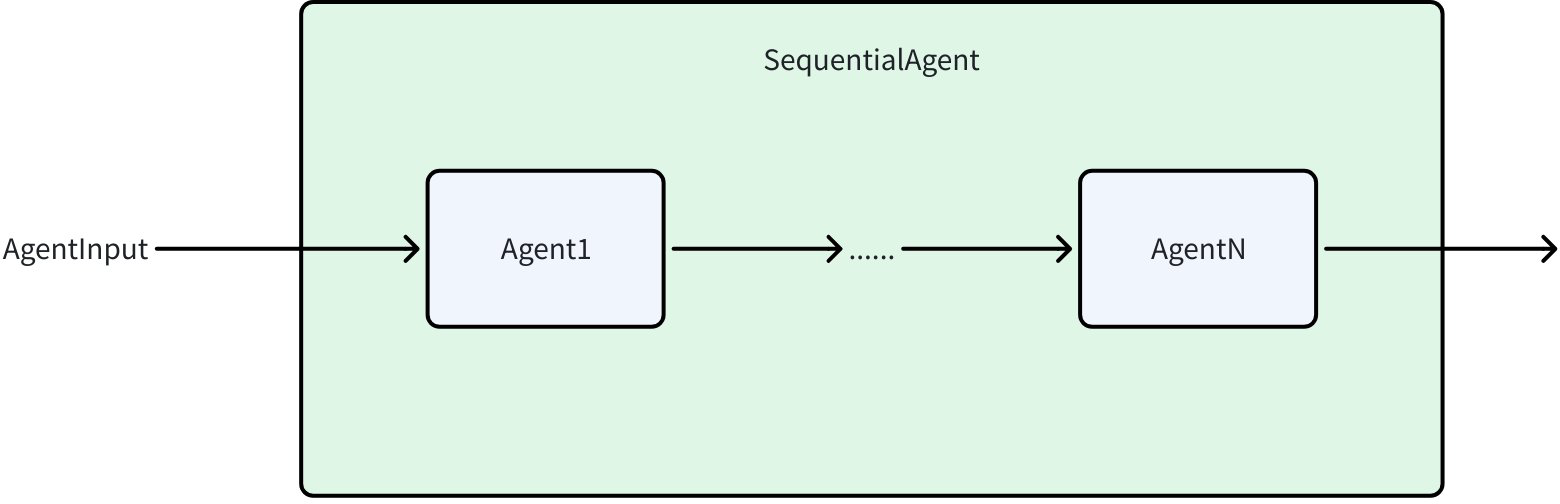
SequentialAgent
SequentialAgent executes a series of Agents in the order you provide:
type SequentialAgentConfig struct {
Name string
Description string
SubAgents []Agent
}
func NewSequentialAgent(ctx context.Context, config *SequentialAgentConfig) (Agent, error)
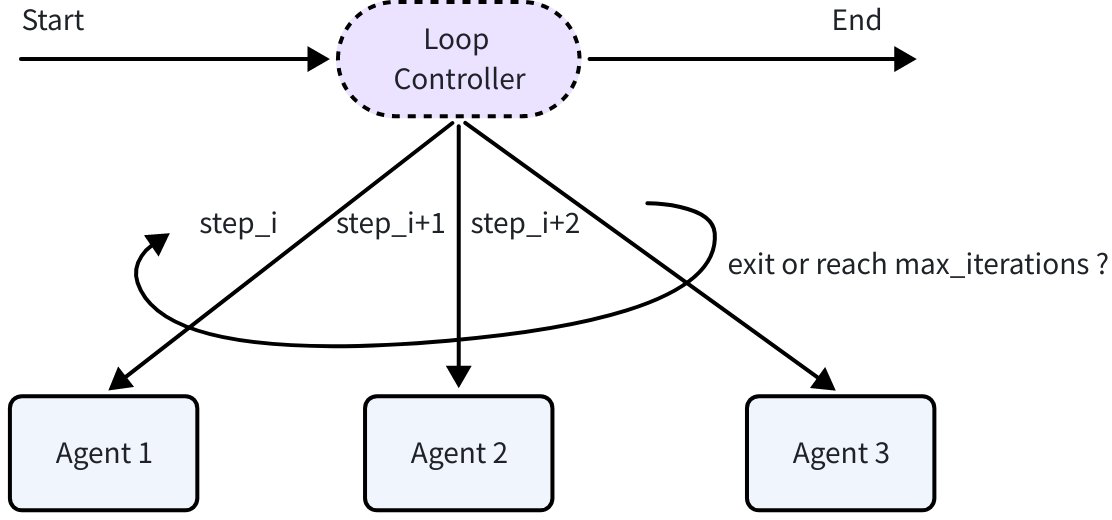
LoopAgent
LoopAgent is implemented based on SequentialAgent. After SequentialAgent completes, it runs from the beginning again:
type LoopAgentConfig struct {
Name string
Description string
SubAgents []Agent
MaxIterations int // Maximum number of loop iterations
}
func NewLoopAgent(ctx context.Context, config *LoopAgentConfig) (Agent, error)
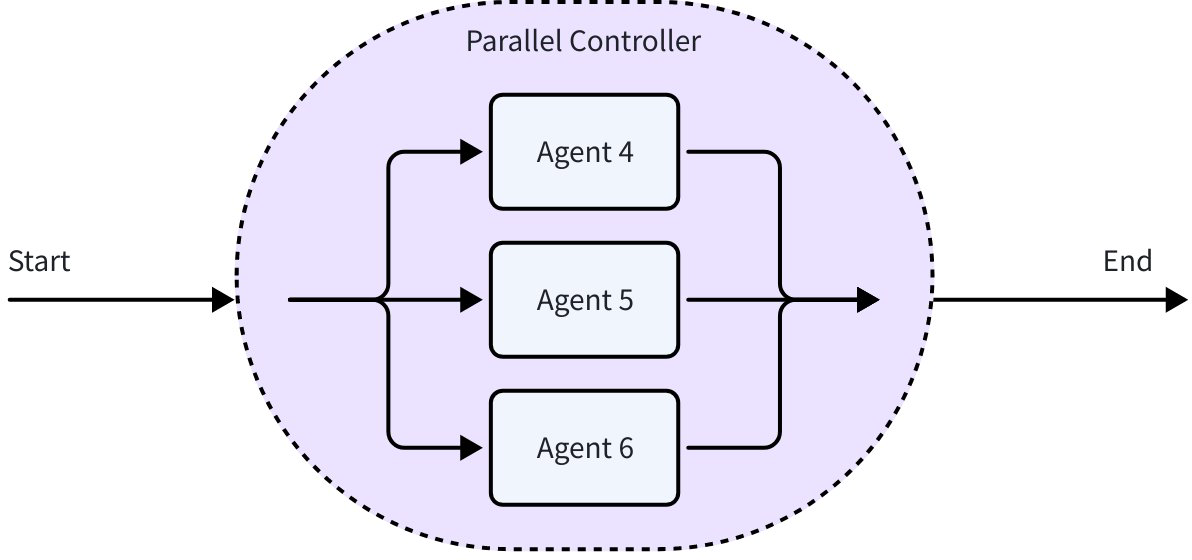
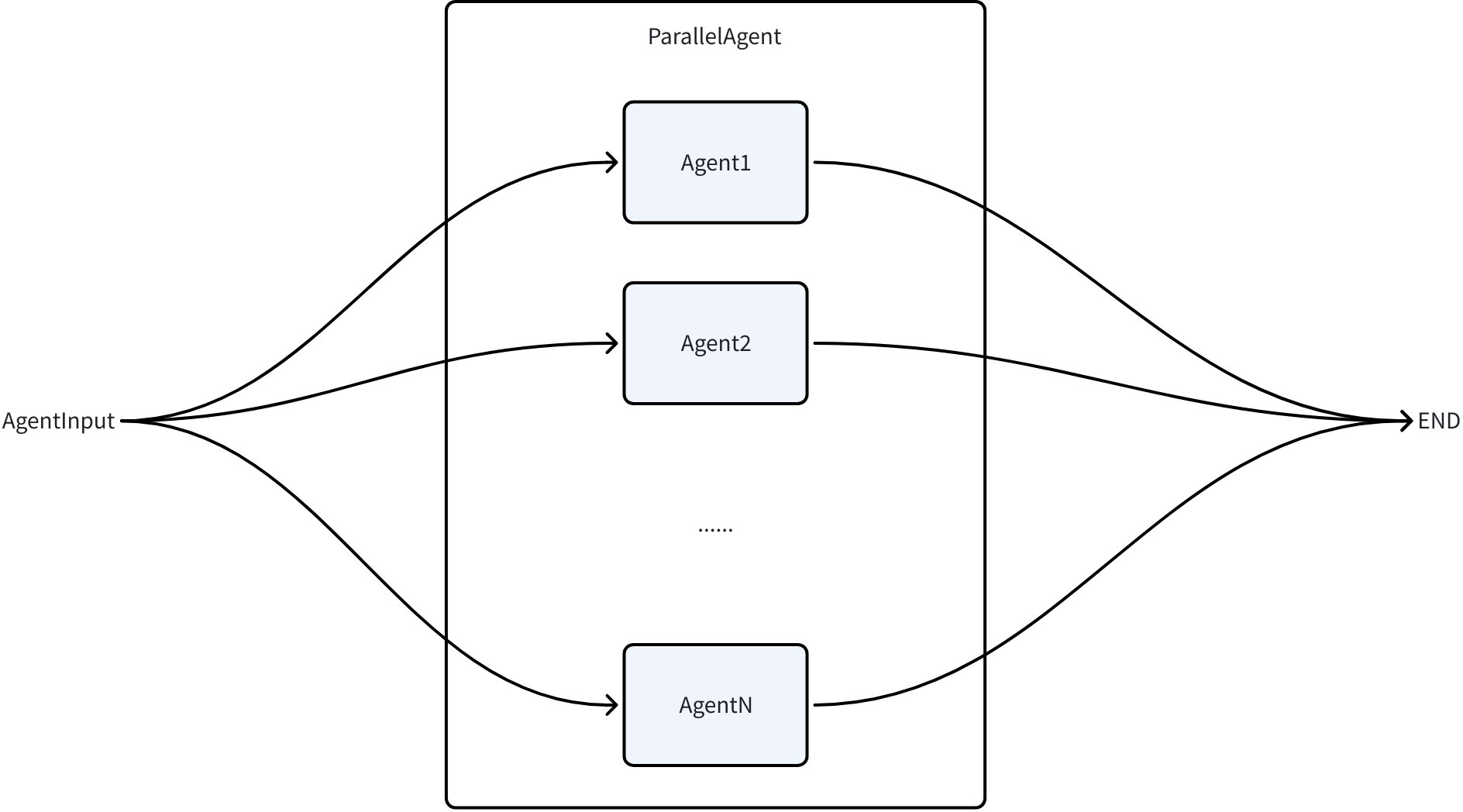
ParallelAgent
ParallelAgent runs multiple Agents concurrently:
type ParallelAgentConfig struct {
Name string
Description string
SubAgents []Agent
}
func NewParallelAgent(ctx context.Context, config *ParallelAgentConfig) (Agent, error)
AgentAsTool
When running an Agent requires only clear and explicit instructions rather than a complete running context (History), the Agent can be converted to a Tool for invocation:
func NewAgentTool(_ context.Context, agent Agent, options ...AgentToolOption) tool.BaseTool
After converting to a Tool, the Agent can be called by ChatModels that support function calling, and can also be called by all LLM-driven Agents. The calling method depends on the Agent implementation.
Message history isolation: An Agent as a Tool does not inherit the message history (History) of the parent Agent.
SessionValues sharing: However, it shares the SessionValues of the parent Agent, i.e., reads and writes the same KV map.
Internal event exposure: An Agent as a Tool is still an Agent and produces AgentEvents. By default, these internal AgentEvents are not exposed through the AsyncIterator returned by Runner. In some business scenarios, if you need to expose the internal AgentTool’s AgentEvents to users, you need to add configuration in the parent ChatModelAgent’s ToolsConfig to enable internal event exposure:
// from adk/chatmodel.go
type ToolsConfig struct {
// other configurations...
// EmitInternalEvents indicates whether internal events from agentTool should be emitted
// to the parent generator via a tool option injection at run-time.
EmitInternalEvents bool
}
These internal events will not enter the parent agent’s context (except for the last message which would enter anyway), and various AgentActions will not take effect (except InterruptAction).