Eino: Callback Manual
Problem Statement
Components (including Lambdas) and Graph orchestration together solve the problem of “defining business logic”. Cross-cutting concerns like logging, tracing, metrics, and UI surfacing need a mechanism to inject functionality into Components (including Lambdas) and Graphs.
On the other hand, users may want to access intermediate information during the execution of a specific Component implementation, such as the DB Name queried by VikingDBRetriever, or parameters like temperature requested by ArkChatModel. A mechanism is needed to expose intermediate state.
Callbacks support both “cross-cutting concern injection” and “intermediate state exposure”. Specifically: users provide and register “functions” (Callback Handlers), and Components and Graphs call back these functions at fixed “timings” (or aspects/points), providing corresponding information.
Core Concepts
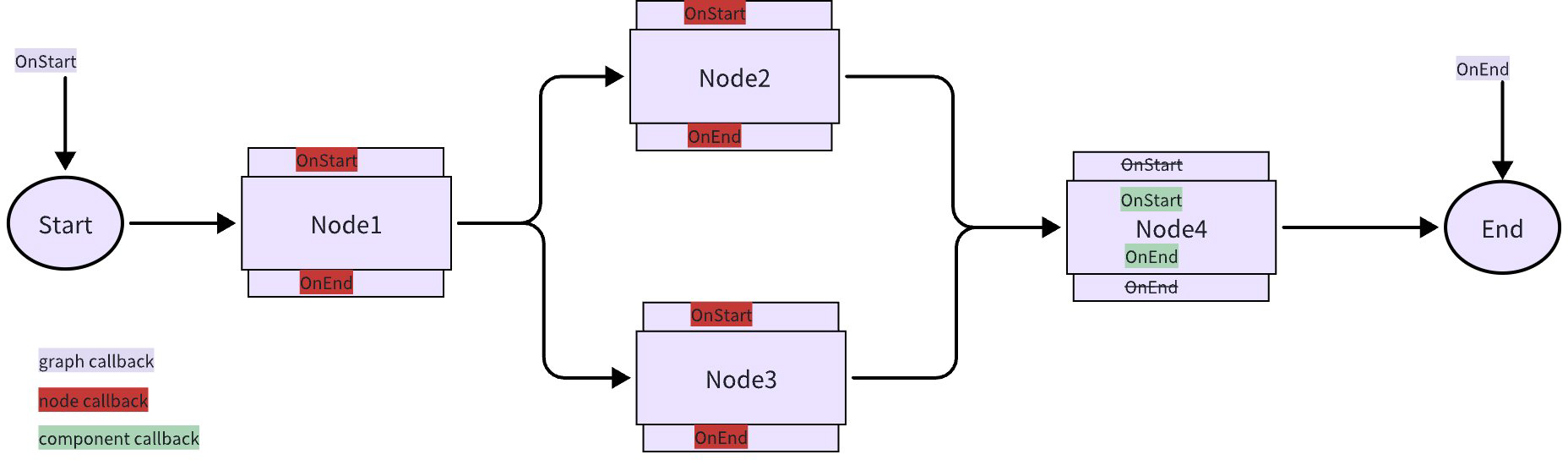
The core concepts connected together: Entities in Eino such as Components and Graphs, at fixed timings (Callback Timing), call back user-provided functions (Callback Handlers), passing who they are (RunInfo) and what happened at that moment (Callback Input & Output).
Triggering Entities
Components (including officially defined component types and Lambdas), Graph Nodes (as well as Chain/Workflow Nodes), and Graphs themselves (as well as Chain/Workflow). All three types of entities have needs for cross-cutting concern injection and intermediate state exposure, so they all trigger callbacks. See the “Triggering Methods” section below for details.
Triggering Timings
// CallbackTiming enumerates all the timing of callback aspects.
type CallbackTiming = callbacks.CallbackTiming
const (
TimingOnStart CallbackTiming = iota // Enter and start execution
TimingOnEnd // Successfully completed and about to return
TimingOnError // Failed and about to return err
TimingOnStartWithStreamInput // OnStart, but input is StreamReader
TimingOnEndWithStreamOutput // OnEnd, but output is StreamReader
)
Different triggering entities, in different scenarios, whether to trigger OnStart or OnStartWithStreamInput (same for OnEnd/OnEndWithStreamOutput), the specific rules are detailed in the “Triggering Methods” section below.
Callback Handler
type Handler interface {
OnStart(ctx context.Context, info *RunInfo, input CallbackInput) context.Context
OnEnd(ctx context.Context, info *RunInfo, output CallbackOutput) context.Context
OnError(ctx context.Context, info *RunInfo, err error) context.Context
OnStartWithStreamInput(ctx context.Context, info *RunInfo,
input *schema.StreamReader[CallbackInput]) context.Context
OnEndWithStreamOutput(ctx context.Context, info *RunInfo,
output *schema.StreamReader[CallbackOutput]) context.Context
}
A Handler is a struct that implements the above 5 methods (corresponding to 5 triggering timings). Each method receives three pieces of information:
- Context: Used to receive custom information that may have been set by preceding timings of the same Handler.
- RunInfo: Metadata of the entity triggering the callback.
- Input/Output/InputStream/OutputStream: Business information at the time of callback triggering.
And all return a new Context: used to pass information between different triggering timings of the same Handler.
If a Handler doesn’t want to focus on all 5 triggering timings, but only some of them, such as only OnStart, it’s recommended to use NewHandlerBuilder().OnStartFn(...).Build(). If you don’t want to focus on all component types, but only specific components like ChatModel, it’s recommended to use NewHandlerHelper().ChatModel(...).Handler(), which only receives ChatModel callbacks and gets typed CallbackInput/CallbackOutput. See the “Handler Implementation Methods” section for details.
There is no guaranteed triggering order between different Handlers.
RunInfo
Describes the metadata of the entity triggering the Callback.
// RunInfo contains information about the running component that triggers callbacks.
type RunInfo struct {
Name string // the 'Name' with semantic meaning for the running component, specified by end-user
Type string // the specific implementation 'Type' of the component, e.g. 'OpenAI'
Component components.Component // the component abstract type, e.g. 'ChatModel'
}
- Name: A name with business meaning, needs to be specified by the user, empty string if not specified. For different triggering entities:
- Component: When in a Graph, uses Node Name. When used standalone outside a Graph, manually set by user. See “Injecting RunInfo” and “Using Components Standalone”
- Graph Node: Uses Node Name
func WithNodeName(n string) GraphAddNodeOpt - Graph itself:
- Top-level graph uses Graph Name
func WithGraphName(graphName string) GraphCompileOption - Nested internal graphs use the Node Name added when joining the parent graph
- Top-level graph uses Graph Name
- Type: Determined by the specific component implementation:
- Components with interfaces: If Typer interface is implemented, uses GetType() method result. Otherwise uses reflection to get Struct/Func name.
- Lambda: If Type is specified with
func WithLambdaType(t string) LambdaOpt, uses that, otherwise empty string. - Graph Node: Uses the value of internal Component/Lambda/Graph.
- Graph itself: Empty string.
- Component:
- Components with interfaces: Whatever interface it is
- Lambda: Fixed value Lambda
- Graph Node: Uses the value of internal Component/Lambda/Graph.
- Graph itself: Fixed value Graph / Chain / Workflow. (Previously there were StateGraph / StateChain, now integrated into Graph / Chain)
Callback Input & Output
Essentially any type, because different Components have completely different inputs/outputs and internal states.
type CallbackInput any
type CallbackOutput any
For specific components, there are more specific types, such as Chat Model:
// CallbackInput is the input for the model callback.
type CallbackInput struct {
// Messages is the messages to be sent to the model.
Messages []*schema.Message
// Tools is the tools to be used in the model.
Tools []*schema.ToolInfo
// Config is the config for the model.
Config *Config
// Extra is the extra information for the callback.
Extra map[string]any
}
// CallbackOutput is the output for the model callback.
type CallbackOutput struct {
// Message is the message generated by the model.
Message *schema.Message
// Config is the config for the model.
Config *Config
// TokenUsage is the token usage of this request.
TokenUsage *TokenUsage
// Extra is the extra information for the callback.
Extra map[string]any
}
In specific implementations of Chat Model, such as OpenAI Chat Model, component authors are recommended to pass specific Input/Output types to Callback Handlers, rather than Any. This exposes more specific, customized intermediate state information.
If a Graph Node triggers the Callback, since the Node cannot access the component’s internal intermediate state information, it can only get the inputs and outputs defined in the component interface, so that’s all it can give to the Callback Handler. For Chat Model, that’s []*schema.Message and *schema.Message.
When Graph itself triggers Callback, the input and output are the overall input and output of the Graph.
Injecting Handlers
Handlers need to be injected into the Context to be triggered.
Injecting Handlers Globally
Inject global Handlers through callbacks.AppendGlobalHandlers. After injection, all callback triggering behaviors will automatically trigger these global Handlers. Typical scenarios are globally consistent, business-scenario-independent functions like tracing and logging.
Not concurrency-safe. It’s recommended to inject once during service initialization.
Injecting Handlers into Graph
Inject Handlers at graph runtime through compose.WithCallbacks, these Handlers will take effect for the entire current run of the graph, including all Nodes within the Graph and the Graph itself (as well as all nested graphs).
Inject Handlers to a specific Node of the top-level Graph through compose.WithCallbacks(...).DesignateNode(...). When this Node itself is a nested Graph, it will be injected into this nested Graph itself and its internal Nodes.
Inject Handlers to a specific Node of an internally nested Graph through compose.WithCallbacks(...).DesignateNodeWithPath(...).
Injecting Handlers Outside Graph
If you don’t want to use Graph but want to use Callbacks:
Obtain a new Context and inject Handlers and RunInfo through InitCallbacks(ctx context.Context, info *RunInfo, handlers ...Handler).
Handler Inheritance
Same as child Context inheriting all Values from parent Context, child Context also inherits all Handlers from parent Context. For example, if the Context passed in when running a Graph already has Handlers, these Handlers will be inherited and take effect for this entire Graph run.
Injecting RunInfo
RunInfo also needs to be injected into the Context to be provided to the Handler when callbacks are triggered.
Graph-Managed RunInfo
Graph automatically injects RunInfo for all internal Nodes. The mechanism is that each Node’s execution is a new child Context, and Graph injects the corresponding Node’s RunInfo into this new Context.
Injecting RunInfo Outside Graph
If you don’t want to use Graph but want to use Callbacks:
Obtain a new Context and inject Handlers and RunInfo through InitCallbacks(ctx context.Context, info *RunInfo, handlers ...Handler).
Obtain a new Context through ReuseHandlers(ctx context.Context, info *RunInfo), reusing the Handlers in the previous Context and setting new RunInfo.
Triggering Methods
Component Implementation Internal Triggering (Component Callback)
In the component implementation code, call OnStart(), OnEnd(), OnError(), OnStartWithStreamInput(), OnEndWithStreamOutput() from the callbacks package. Taking Ark’s ChatModel implementation as an example, in the Generate method:
func (cm *ChatModel) Generate(ctx context.Context, in []*schema.Message, opts ...fmodel.Option) (
outMsg *schema.Message, err error) {
defer func() {
if err != nil {
_ = callbacks.OnError(ctx, err)
}
}()
// omit multiple lines... instantiate req conf
ctx = callbacks.OnStart(ctx, &fmodel.CallbackInput{
Messages: in,
Tools: append(cm.rawTools), // join tool info from call options
ToolChoice: nil, // not support in api
Config: reqConf,
})
// omit multiple lines... invoke Ark chat API and get the response
_ = callbacks.OnEnd(ctx, &fmodel.CallbackOutput{
Message: outMsg,
Config: reqConf,
TokenUsage: toModelCallbackUsage(outMsg.ResponseMeta),
})
return outMsg, nil
}
In the Stream method:
func (cm *ChatModel) Stream(ctx context.Context, in []*schema.Message, opts ...fmodel.Option) ( // byted_s_too_many_lines_in_func
outStream *schema.StreamReader[*schema.Message], err error) {
defer func() {
if err != nil {
_ = callbacks.OnError(ctx, err)
}
}()
// omit multiple lines... instantiate req conf
ctx = callbacks.OnStart(ctx, &fmodel.CallbackInput{
Messages: in,
Tools: append(cm.rawTools), // join tool info from call options
ToolChoice: nil, // not support in api
Config: reqConf,
})
// omit multiple lines... make request to Ark API and convert response stream to StreamReader[model.*CallbackOutput]
_, sr = callbacks.OnEndWithStreamOutput(ctx, sr)
return schema.StreamReaderWithConvert(sr,
func(src *fmodel.CallbackOutput) (*schema.Message, error) {
if src.Message == nil {
return nil, schema.ErrNoValue
}
return src.Message, nil
},
), nil
}
You can see that Generate call triggers OnEnd, while Stream call triggers OnEndWithStreamOutput:
When triggering Callbacks inside component implementations:
- When component input is StreamReader, trigger OnStartWithStreamInput, otherwise trigger OnStart
- When component output is StreamReader, trigger OnEndWithStreamOutput, otherwise trigger OnEnd
Components that implement callback triggering internally should implement the Checker interface, with IsCallbacksEnabled returning true, to communicate “I have implemented callback triggering internally” to the outside:
// Checker tells callback aspect status of component's implementation
// When the Checker interface is implemented and returns true, the framework will not start the default aspect.
// Instead, the component will decide the callback execution location and the information to be injected.
type Checker interface {
IsCallbacksEnabled() bool
}
If a component implementation doesn’t implement the Checker interface, or IsCallbacksEnabled returns false, it can be assumed that the component doesn’t trigger callbacks internally, and Graph Node needs to be responsible for injection and triggering (when used within a Graph).
Graph Node Triggering (Node Callback)
When a Component is orchestrated into a Graph, it becomes a Node. At this point, if the Component itself triggers callbacks, the Node reuses the Component’s callback handling. Otherwise, the Node wraps callback handler trigger points around the Component. These points correspond to the Component’s streaming paradigm. For example, a ChatModelNode wraps OnStart/OnEnd/OnError around the Generate method, and OnStart/OnEndWithStreamOutput/OnError around the Stream method.
At Graph runtime, components run in Invoke or Transform paradigm, and based on the component’s specific business streaming paradigm, call the corresponding component methods. For example, when Graph runs with Invoke, Chat Model Node runs with Invoke, calling the Generate method. When Graph runs with Stream, Chat Model Node runs with Transform, but since Chat Model’s business streaming paradigm doesn’t have Transform, it automatically falls back to calling the Stream method. Therefore:
Which timing point (OnStart vs OnStartWithStreamInput) a Graph Node specifically triggers depends on two factors: the component implementation’s business streaming paradigm and the Graph’s execution mode.
For detailed introduction to Eino streaming programming, see Eino Streaming Programming Essentials
Graph Self-Triggering (Graph Callback)
Graph triggers Callback Handlers at its own start, end, and error timings. If Graph is called in Invoke form, it triggers OnStart/OnEnd/OnError. If called in Stream/Collect/Transform form, it triggers OnStartWithStreamInput/OnEndWithStreamOutput/OnError. This is because Graph internally always executes as Invoke or Transform. See Eino Streaming Programming Essentials
It’s worth noting: graph is also a type of component, so graph callback is also a special form of component callback. According to the Node Callback definition, when the component inside a Node implements awareness and handling of triggering timings, the Node directly reuses the Component’s implementation and won’t implement Node Callback. This means when a graph is added to another Graph as a Node via AddGraphNode, this Node reuses the internal graph’s graph callback.
Parsing Callback Input & Output
From the above, we know that Callback Input & Output’s underlying type is Any, but different component types may pass their own specific types when actually triggering callbacks. And in the Callback Handler interface definition, the parameters of each method are also Any-typed Callback Input & Output.
Therefore, specific Handler implementations need to do two things:
- Determine which component type is currently triggering the callback based on RunInfo, such as RunInfo.Component == “ChatModel”, or RunInfo.Type == “xxx Chat Model”.
- Convert the any-typed Callback Input & Output to the corresponding specific type, taking RunInfo.Component == “ChatModel” as an example:
// ConvCallbackInput converts the callback input to the model callback input.
func ConvCallbackInput(src callbacks.CallbackInput) *CallbackInput {
switch t := src.(type) {
case *CallbackInput: // when callback is triggered within component implementation, the input is usually already a typed *model.CallbackInput
return t
case []*schema.Message: // when callback is injected by graph node, not the component implementation itself, the input is the input of Chat Model interface, which is []*schema.Message
return &CallbackInput{
Messages: t,
}
default:
return nil
}
}
// ConvCallbackOutput converts the callback output to the model callback output.
func ConvCallbackOutput(src callbacks.CallbackOutput) *CallbackOutput {
switch t := src.(type) {
case *CallbackOutput: // when callback is triggered within component implementation, the output is usually already a typed *model.CallbackOutput
return t
case *schema.Message: // when callback is injected by graph node, not the component implementation itself, the output is the output of Chat Model interface, which is *schema.Message
return &CallbackOutput{
Message: t,
}
default:
return nil
}
}
If the Handler needs to add switch cases to determine RunInfo.Component, and for each case, call the corresponding conversion function to convert Any to a specific type, it’s indeed somewhat complex. To reduce the repetitive work of writing glue code, we provide two convenient tool functions for implementing Handlers.
Handler Implementation Methods
Besides directly implementing the Handler interface, Eino provides two convenient Handler implementation tools.
HandlerHelper
If the user’s Handler only focuses on specific component types, such as in ReActAgent scenarios only focusing on ChatModel and Tool, it’s recommended to use HandlerHelper to quickly create typed Callback Handlers:
import ucb "github.com/cloudwego/eino/utils/callbacks"
handler := ucb.NewHandlerHelper().ChatModel(modelHandler).Tool(toolHandler).Handler()
Where modelHandler is Chat Model component’s further encapsulation of callback handler:
// from package utils/callbacks
// ModelCallbackHandler is the handler for the model callback.
type ModelCallbackHandler struct {
OnStart func(ctx context.Context, runInfo *callbacks.RunInfo, input *model.CallbackInput) context.Context
OnEnd func(ctx context.Context, runInfo *callbacks.RunInfo, output *model.CallbackOutput) context.Context
OnEndWithStreamOutput func(ctx context.Context, runInfo *callbacks.RunInfo, output *schema.StreamReader[*model.CallbackOutput]) context.Context
OnError func(ctx context.Context, runInfo *callbacks.RunInfo, err error) context.Context
}
The above ModelCallbackHandler encapsulates three operations:
- No longer need to determine RunInfo.Component to select callbacks triggered by ChatModel, as automatic filtering is already done.
- Only requires implementing the triggering timings supported by Chat Model component, here removing the unsupported OnStartWithStreamInput. Also, if the user only cares about some of the four timings supported by Chat Model, such as only OnStart, they can implement only OnStart.
- Input / Output are no longer Any types, but already converted model.CallbackInput, model.CallbackOutput.
HandlerHelper supports all official components, the current list is: ChatModel, ChatTemplate, Retriever, Indexer, Embedding, Document.Loader, Document.Transformer, Tool, ToolsNode.
For Lambda, Graph, Chain and other “components” with uncertain input/output types, HandlerHelper can also be used, but can only achieve point 1 above, i.e., automatic filtering by component type, points 2 and 3 still need to be implemented by the user:
import ucb "github.com/cloudwego/eino/utils/callbacks"
handler := ucb.NewHandlerHelper().Lambda(callbacks.Handler).Graph(callbacks.Handler)...Handler()
At this point, NewHandlerHelper().Lambda() needs to pass in callbacks.Handler which can be implemented using the HandlerBuilder below.
HandlerBuilder
If the user’s Handler needs to focus on multiple component types, but only needs to focus on some triggering timings, HandlerBuilder can be used:
import "github.com/cloudwego/eino/callbacks"
handler := callbacks.NewHandlerBuilder().OnStartFn(fn)...Build()
Best Practices
Using in Graph
- Actively use Global Handlers to register always-effective Handlers.
package main
import (
"context"
"log"
"github.com/cloudwego/eino/callbacks"
"github.com/cloudwego/eino/compose"
)
func main() {
// Build a simple global handler
handler := callbacks.NewHandlerBuilder().
OnStartFn(func(ctx context.Context, info *callbacks.RunInfo, input callbacks.CallbackInput) context.Context {
log.Printf("[Global Start] component=%s name=%s input=%T", info.Component, info.Name, input)
return ctx
}).
OnEndFn(func(ctx context.Context, info *callbacks.RunInfo, output callbacks.CallbackOutput) context.Context {
log.Printf("[Global End] component=%s name=%s output=%T", info.Component, info.Name, output)
return ctx
}).
OnErrorFn(func(ctx context.Context, info *callbacks.RunInfo, err error) context.Context {
log.Printf("[Global Error] component=%s name=%s err=%v", info.Component, info.Name, err)
return ctx
}).
Build()
// Register as global callbacks (applies to all subsequent runs)
callbacks.AppendGlobalHandlers(handler)
// Example graph usage; the global handler will be invoked automatically
g := compose.NewGraph[string, string]()
// ... add nodes/edges ...
r, _ := g.Compile(context.Background())
_, _ = r.Invoke(context.Background(), "hello") // triggers global callbacks
}
- Inject Handlers at runtime through WithHandlers option, and specify effective Nodes / nested internal Graphs / internal Graph Nodes through DesignateNode or DesignateNodeByPath.
package main
import (
"context"
"github.com/cloudwego/eino/callbacks"
"github.com/cloudwego/eino/compose"
"github.com/cloudwego/eino/components/prompt"
"github.com/cloudwego/eino/schema"
)
func main() {
ctx := context.Background()
top := compose.NewGraph[map[string]any, []*schema.Message]()
sub := compose.NewGraph[map[string]any, []*schema.Message]()
_ = sub.AddChatTemplateNode("tmpl_nested", prompt.FromMessages(schema.FString, schema.UserMessage("Hello, {name}!")))
_ = sub.AddEdge(compose.START, "tmpl_nested")
_ = sub.AddEdge("tmpl_nested", compose.END)
_ = top.AddGraphNode("sub_graph", sub)
_ = top.AddEdge(compose.START, "sub_graph")
_ = top.AddEdge("sub_graph", compose.END)
r, _ := top.Compile(ctx)
optGlobal := compose.WithCallbacks(
callbacks.NewHandlerBuilder().OnEndFn(func(ctx context.Context, _ *callbacks.RunInfo, _ callbacks.CallbackOutput) context.Context { return ctx }).Build(),
)
optNode := compose.WithCallbacks(
callbacks.NewHandlerBuilder().OnStartFn(func(ctx context.Context, _ *callbacks.RunInfo, _ callbacks.CallbackInput) context.Context { return ctx }).Build(),
).DesignateNode("sub_graph")
optNested := compose.WithChatTemplateOption(
prompt.WrapImplSpecificOptFn(func(_ *struct{}) {}),
).DesignateNodeWithPath(
compose.NewNodePath("sub_graph", "tmpl_nested"),
)
_, _ = r.Invoke(ctx, map[string]any{"name": "Alice"}, optGlobal, optNode, optNested)
}
Using Outside Graph
This scenario is: not using Graph/Chain/Workflow orchestration capabilities, but directly calling ChatModel/Tool/Lambda and other components with code, and hoping these components can successfully trigger Callback Handlers.
The problem users need to solve in this scenario is: manually setting correct RunInfo and Handlers, because there’s no Graph to help users automatically set RunInfo and Handlers.
Complete example:
package main
import (
"context"
"github.com/cloudwego/eino/callbacks"
"github.com/cloudwego/eino/compose"
)
func innerLambda(ctx context.Context, input string) (string, error) {
// As ComponentB's implementer: add default RunInfo when entering the component (Name cannot be given a default value)
ctx = callbacks.EnsureRunInfo(ctx, "Lambda", compose.ComponentOfLambda)
ctx = callbacks.OnStart(ctx, input)
out := "inner:" + input
ctx = callbacks.OnEnd(ctx, out)
return out, nil
}
func outerLambda(ctx context.Context, input string) (string, error) {
// As ComponentA's implementer: add default RunInfo when entering the component
ctx = callbacks.EnsureRunInfo(ctx, "Lambda", compose.ComponentOfLambda)
ctx = callbacks.OnStart(ctx, input)
// Recommended: replace RunInfo before calling, ensuring inner component gets correct name/type/component
ctxInner := callbacks.ReuseHandlers(ctx,
&callbacks.RunInfo{Name: "ComponentB", Type: "Lambda", Component: compose.ComponentOfLambda},
)
out1, _ := innerLambda(ctxInner, input) // inner RunInfo.Name = "ComponentB"
// Without replacement: framework clears RunInfo, can only rely on EnsureRunInfo to add default values (Name is empty)
out2, _ := innerLambda(ctx, input) // inner RunInfo.Name == ""
final := out1 + "|" + out2
ctx = callbacks.OnEnd(ctx, final)
return final, nil
}
func main() {
// Using components standalone outside graph: initialize RunInfo and Handlers
h := callbacks.NewHandlerBuilder().Build()
ctx := callbacks.InitCallbacks(context.Background(),
&callbacks.RunInfo{Name: "ComponentA", Type: "Lambda", Component: compose.ComponentOfLambda},
h,
)
_, _ = outerLambda(ctx, "ping")
}
Explanation of the above sample code:
- Initialization: When using components outside graph/chain, use InitCallbacks to set the first RunInfo and Handlers, so subsequent component execution can get the complete callback context.
- Internal calls: Before component A calls component B internally, use ReuseHandlers to replace RunInfo (keeping original handlers), ensuring B’s callbacks get correct Type/Component/Name.
- Consequences of not replacing: After a complete set of Callbacks is triggered, Eino clears the RunInfo in the current ctx. At this point, because RunInfo is empty, Eino won’t trigger Callbacks anymore; Component B’s developer can only use EnsureRunInfo in their own implementation to add default values for Type/Component, to ensure RunInfo is non-empty and roughly correct, thus successfully triggering Callbacks. But cannot give a reasonable Name, so RunInfo.Name will be an empty string.
Component Nesting Usage
Scenario: Inside one component, such as Lambda, manually call another component, such as ChatModel.
At this point, if the outer component’s ctx has callback handlers, because this ctx is also passed to the inner component, the inner component will also receive the same callback handlers.
Distinguishing by “whether you want the inner component to trigger callbacks”:
- Want to trigger: Basically equivalent to the situation in the previous section, it’s recommended to manually set
RunInfofor the inner component throughReuseHandlers.
package main
import (
"context"
"github.com/cloudwego/eino/callbacks"
"github.com/cloudwego/eino/components"
"github.com/cloudwego/eino/components/model"
"github.com/cloudwego/eino/compose"
"github.com/cloudwego/eino/schema"
)
// Outer Lambda, manually calls ChatModel inside
func OuterLambdaCallsChatModel(cm model.BaseChatModel) *compose.Lambda {
return compose.InvokableLambda(func(ctx context.Context, input string) (string, error) {
// 1) Reuse outer handlers and explicitly set RunInfo for inner component
innerCtx := callbacks.ReuseHandlers(ctx, &callbacks.RunInfo{
Type: "InnerCM", // Customizable
Component: components.ComponentOfChatModel, // Mark component type
Name: "inner-chat-model", // Customizable
})
// 2) Build input messages
msgs := []*schema.Message{{Role: schema.User, Content: input}}
// 3) Call ChatModel (internally triggers corresponding callbacks)
out, err := cm.Generate(innerCtx, msgs)
if err != nil {
return "", err
}
return out.Content, nil
})
}
The above code assumes “the inner ChatModel’s Generate method internally has already called OnStart, OnEnd, OnError methods”. If not, you need to call these methods “on behalf of the inner component” inside the outer component:
func OuterLambdaCallsChatModel(cm model.BaseChatModel) *compose.Lambda {
return compose.InvokableLambda(func(ctx context.Context, input string) (string, error) {
// Reuse outer handlers and explicitly set RunInfo for inner component
ctx = callbacks.ReuseHandlers(ctx, &callbacks.RunInfo{
Type: "InnerCM",
Component: components.ComponentOfChatModel,
Name: "inner-chat-model",
})
// Build input messages
msgs := []*schema.Message{{Role: schema.User, Content: input}}
// Explicitly trigger OnStart
ctx = callbacks.OnStart(ctx, msgs)
// Call ChatModel
resp, err := cm.Generate(ctx, msgs)
if err != nil {
// Explicitly trigger OnError
ctx = callbacks.OnError(ctx, err)
return "", err
}
// Explicitly trigger OnEnd
ctx = callbacks.OnEnd(ctx, resp)
return resp.Content, nil
})
}
Don’t want to trigger: This assumes the inner component implements
IsCallbacksEnabled()and returns true, and internally callsEnsureRunInfo. At this point, inner callbacks will trigger by default. If you don’t want them to trigger, the simplest way is to remove handlers from ctx, such as passing a new ctx to the inner component:package main import ( "context" "github.com/cloudwego/eino/components/model" "github.com/cloudwego/eino/compose" "github.com/cloudwego/eino/schema" ) func OuterLambdaNoCallbacks(cm model.BaseChatModel) *compose.Lambda { return compose.InvokableLambda(func(ctx context.Context, input string) (string, error) { // Use a brand new ctx, don't reuse outer handlers innerCtx := context.Background() msgs := []*schema.Message{{Role: schema.User, Content: input}} out, err := cm.Generate(innerCtx, msgs) if err != nil { return "", err } return out.Content, nil }) }- But sometimes users may want to “only not trigger a specific callback handler, but still trigger other callback handlers”. The recommended approach is to add code in this callback handler to filter out inner components by RunInfo:
package main
import (
"context"
"log"
"github.com/cloudwego/eino/callbacks"
"github.com/cloudwego/eino/components"
"github.com/cloudwego/eino/compose"
)
// A handler that filters by RunInfo: does nothing for inner ChatModel (Type=InnerCM, Name=inner-chat-model)
func newSelectiveHandler() callbacks.Handler {
return callbacks.
NewHandlerBuilder().
OnStartFn(func(ctx context.Context, info *callbacks.RunInfo, input callbacks.CallbackInput) context.Context {
if info != nil && info.Component == components.ComponentOfChatModel &&
info.Type == "InnerCM" && info.Name == "inner-chat-model" {
// Filter target: inner ChatModel, return directly without processing
return ctx
}
log.Printf("[OnStart] %s/%s (%s)", info.Type, info.Name, info.Component)
return ctx
}).
OnEndFn(func(ctx context.Context, info *callbacks.RunInfo, output callbacks.CallbackOutput) context.Context {
if info != nil && info.Component == components.ComponentOfChatModel &&
info.Type == "InnerCM" && info.Name == "inner-chat-model" {
// Filter target: inner ChatModel, return directly without processing
return ctx
}
log.Printf("[OnEnd] %s/%s (%s)", info.Type, info.Name, info.Component)
return ctx
}).
Build()
}
// Composition example: outer call wants to trigger, specific handler filters out inner ChatModel through RunInfo
func Example(cm model.BaseChatModel) (compose.Runnable[string, string], error) {
handler := newSelectiveHandler()
chain := compose.NewChain[string, string]().
AppendLambda(OuterLambdaCallsChatModel(cm)) // Internally will ReuseHandlers + RunInfo
return chain.Compile(
context.Background(),
// Mount handler (can also combine with global handlers)
compose.WithCallbacks(handler),
)
}
Reading and Writing Input & Output in Handler
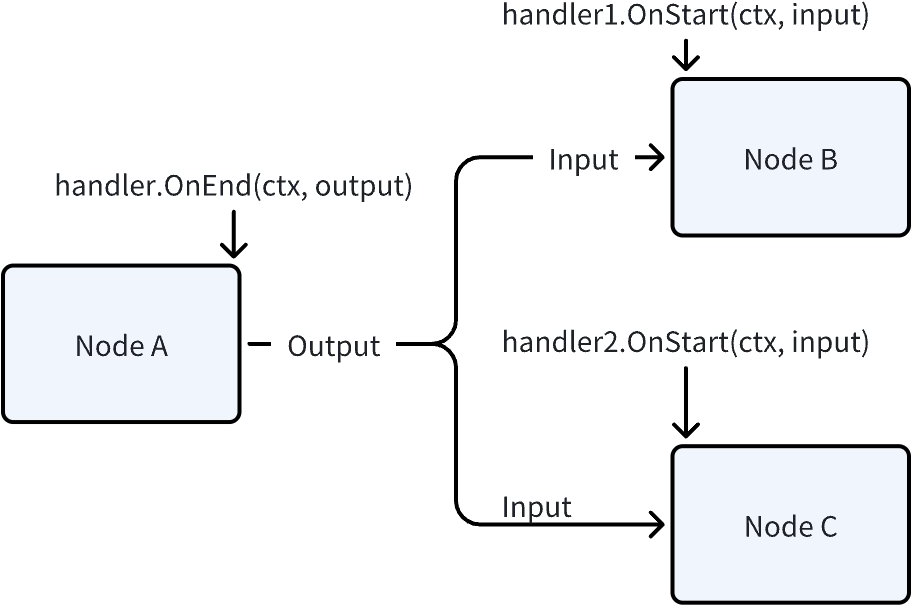
When input & output flow through the graph, they are direct variable assignments. As shown in the figure below, NodeA.Output, NodeB.Input, NodeC.Input, and the input & output obtained in each Handler, if they are reference types like struct pointers or Maps, they are all the same piece of data. Therefore, whether in Node or Handler, it’s not recommended to modify Input & Output, as it will cause concurrency issues: even in synchronous situations, Node B and Node C are concurrent, causing internal handler1 and handler2 to be concurrent. When there’s asynchronous processing logic, there are more possible concurrency scenarios.
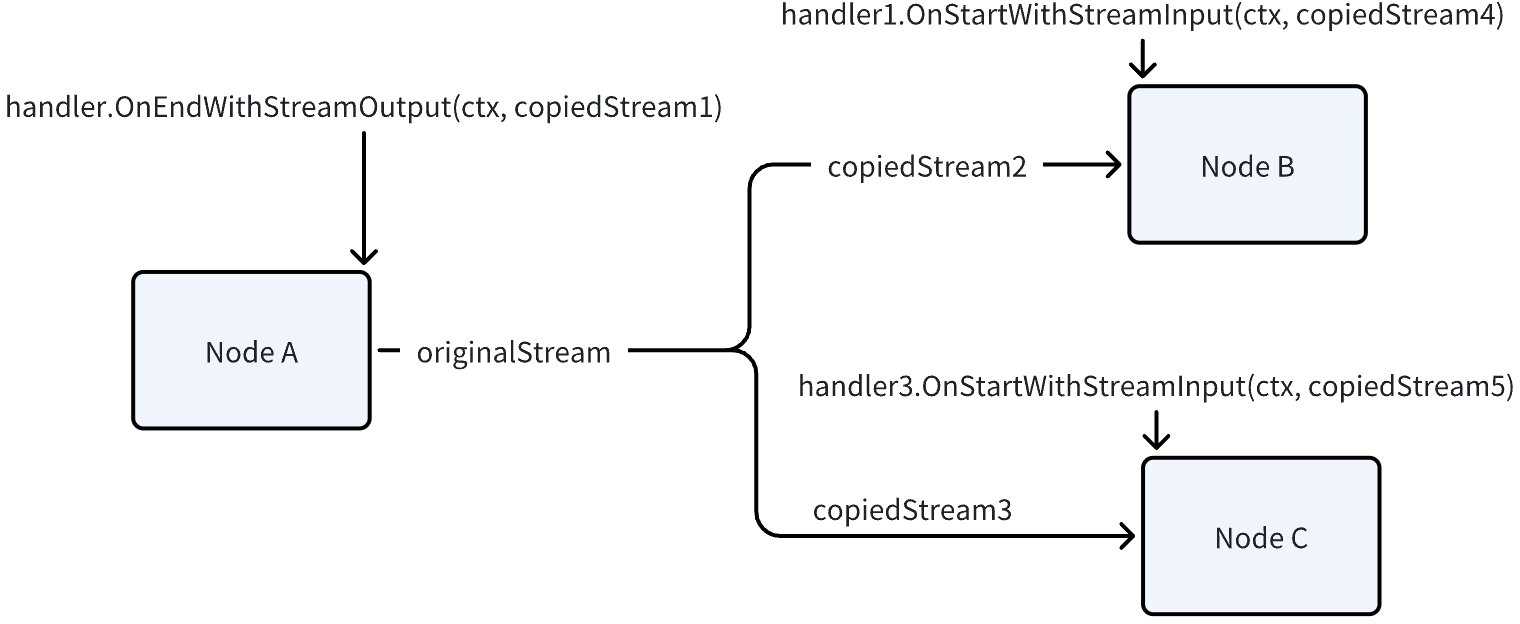
In stream passing scenarios, all downstream nodes and handlers’ input streams are streams obtained from StreamReader.Copy(n), which can be read independently. However, each chunk in the stream is direct variable assignment, if the chunk is a reference type like struct pointer or Map, each copied stream reads the same piece of data. Therefore, in Node and Handler, it’s also not recommended to modify stream chunks, there are concurrency issues.
Passing Information Between Handlers
Between different timings of the same Handler, information can be passed through ctx, such as returning a new context through context.WithValue in OnStart, and then retrieving this value from context in OnEnd.
Between different Handlers, there’s no guarantee of execution order, so it’s not recommended to pass information between different Handlers through the above mechanism. Essentially, there’s no guarantee that the context returned by one Handler will definitely enter the function execution of the next Handler.
If you need to pass information between different Handlers, the recommended approach is to set a global, request-scoped variable in the outermost context (such as the context passed in when graph executes) as a shared space for storing and retrieving common information, and read and update this shared variable as needed in each Handler. Users need to ensure the concurrency safety of this shared variable themselves.
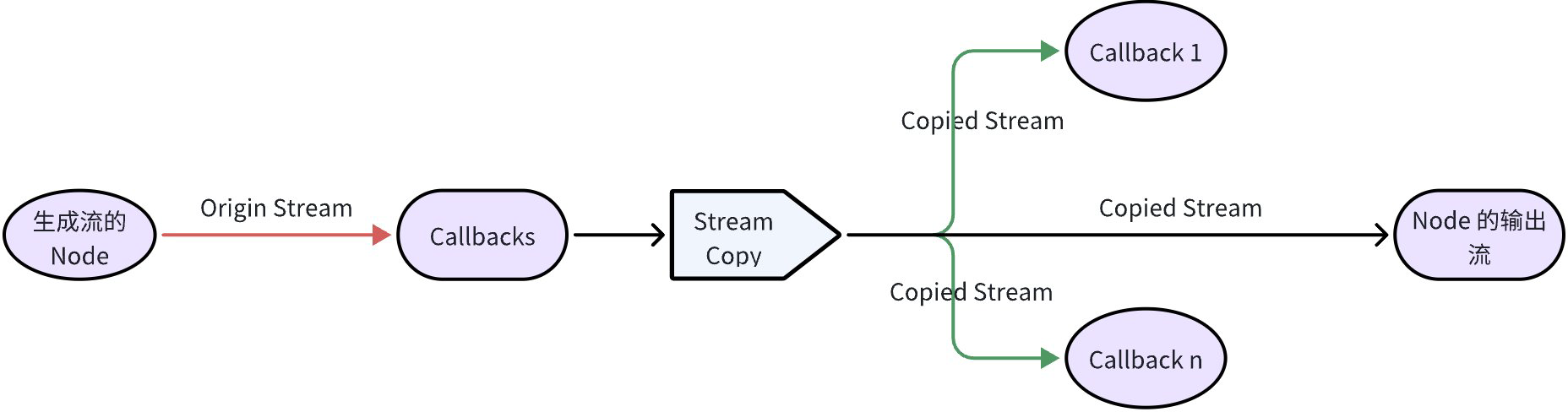
Remember to Close Streams
Taking the existence of ChatModel, a node with true streaming output, as an example, when there are Callback aspects, ChatModel’s output stream:
- Needs to be consumed by downstream nodes as input, and also consumed by Callback aspects
- A frame (Chunk) in a stream can only be consumed by one consumer, i.e., streams are not broadcast models
So at this point, the stream needs to be copied, the copy relationship is as follows:
- If one of the Callback n doesn’t Close the corresponding stream, it may cause the original Stream to be unable to Close and release resources.