Eino: CallOption capabilities and specification
CallOption: A channel for directly passing data to a specific set of nodes (Component, Implementation, Node) when invoking Graph compilation products.
- Difference from Node Config: Node Config is an instance-level configuration, meaning the values in Config are set from instance creation to instance destruction and do not need to change once determined.
- CallOption: This is request-level configuration, where values differ for each request. It is more like node parameters, but these parameters are directly passed from the Graph entrance rather than from upstream nodes.
- Example: Passing a Temperature configuration to a ChatModel node; passing a custom option to a Lambda node.
Component CallOption Form
Component CallOption configuration has two levels:
- CallOption configuration uniformly defined by the abstract (Abstract/Interface) of the component [Component Abstract CallOption]
- CallOption configuration defined by the implementation (Type/Implementation) of the component for that specific type [Component Implementation CallOption]
Taking the ChatModel component as an example, the form of CallOption is introduced
Directory of Model Abstract and Implementation
// Location of the abstract in the code
eino/components/model
├── interface.go
├── option.go // CallOption parameter at the component abstract level
// Location of the abstract implementation in the code
eino-ext/components/model
├── claude
│ ├── option.go // CallOption parameter for one implementation of the component
│ └── chatmodel.go
├── ollama
│ ├── call_option.go // CallOption parameter for one implementation of the component
│ ├── chatmodel.go
Model Abstraction
As mentioned above, when defining the CallOption for a component, it is necessary to distinguish between the [Component Abstract CallOption] and the [Component Implementation CallOption] scenarios. Whether to provide the [Component Implementation CallOption] is determined by the Component Abstraction.
The CallOption extension capabilities provided by the Component Abstraction are as follows (taking Model as an example, other components are similar):
package model
type ChatModel interface {
Generate(ctx context.Context, input []*schema.Message, opts ...Option) (*schema.Message, error)
Stream(ctx context.Context, input []*schema.Message, opts ...Option) (
*schema.StreamReader[*schema.Message], error)
// BindTools bind tools to the model.
// BindTools before requesting ChatModel generally.
// notice the non-atomic problem of BindTools and Generate.
BindTools(tools []*schema.ToolInfo) error
}
// This structure is the unified definition of [Component Abstract CallOption]. The component implementation can extract information from [Component Abstract CallOption] according to its own needs.
// Options is the common options for the model.
type Options struct {
// Temperature is the temperature for the model, which controls the randomness of the model.
Temperature *float32
// MaxTokens is the max number of tokens, if reached the max tokens, the model will stop generating, and mostly return a finish reason of "length".
MaxTokens *int
// Model is the model name.
Model *string
// TopP is the top p for the model, which controls the diversity of the model.
TopP *float32
// Stop is the stop words for the model, which controls the stopping condition of the model.
Stop []string
}
// Option is the call option for the ChatModel component.
type Option struct {
// This field serves the apply method for [Component Abstract CallOption], such as WithTemperature
// If the component abstraction does not want to provide the [Component Abstract CallOption], this field can be omitted, along with the GetCommonOptions() method.
apply func(opts *Options)
// This field serves the apply method for [Component Implementation CallOption], and it is assumed the apply method is: func(*T)
// If the component abstraction does not want to provide [Component Implementation CallOption], this field can be omitted along with the GetImplSpecificOptions() method.
implSpecificOptFn any
}
// WithTemperature is the option to set the temperature for the model.
func WithTemperature(temperature float32) Option {
return Option{
apply: func(opts *Options) {
opts.Temperature = &temperature
},
}
}
// WithMaxTokens is the option to set the max tokens for the model.
func WithMaxTokens(maxTokens int) Option {
return Option{
apply: func(opts *Options) {
opts.MaxTokens = &maxTokens
},
}
}
// WithModel is the option to set the model name.
func WithModel(name string) Option {
return Option{
apply: func(opts *Options) {
opts.Model = &name
},
}
}
// WithTopP is the option to set the top p for the model.
func WithTopP(topP float32) Option {
return Option{
apply: func(opts *Options) {
opts.TopP = &topP
},
}
}
// WithStop is the option to set the stop words for the model.
func WithStop(stop []string) Option {
return Option{
apply: func(opts *Options) {
opts.Stop = stop
},
}
}
// GetCommonOptions extract model Options from Option list, optionally providing a base Options with default values.
func GetCommonOptions(base *Options, opts ...Option) *Options {
if base == nil {
base = &Options{}
}
for i := range opts {
opt := opts[i]
if opt.apply != nil {
opt.apply(base)
}
}
return base
}
// Component implementers can use this method to encapsulate their own Option functions: func WithXXX(xxx string) Option{}
func WrapImplSpecificOptFn[T any](optFn func(*T)) Option {
return Option{
implSpecificOptFn: optFn,
}
}
// GetImplSpecificOptions provides tool authors the ability to extract their own custom options from the unified Option type.
// T: the type of the impl specific options struct.
// This function should be used within the tool implementation's InvokableRun or StreamableRun functions.
// It is recommended to provide a base T as the first argument, within which the tool author can provide default values for the impl specific options.
func GetImplSpecificOptions[T any](base *T, opts ...Option) *T {
if base == nil {
base = new(T)
}
for i := range opts {
opt := opts[i]
if opt.implSpecificOptFn != nil {
optFn, ok := opt.implSpecificOptFn.(func(*T))
if ok {
optFn(base)
}
}
}
return base
}
Claude Implementation
https://github.com/cloudwego/eino-ext/blob/main/components/model/claude/option.go
package claude
import (
"github.com/cloudwego/eino/components/model"
)
type options struct {
TopK *int32
}
func WithTopK(k int32) model.Option {
return model.WrapImplSpecificOptFn(func(o *options) {
o.TopK = &k
})
}
https://github.com/cloudwego/eino-ext/blob/main/components/model/claude/claude.go
func (c *claude) genMessageNewParams(input []*schema.Message, opts ...model.Option) (anthropic.MessageNewParams, error) {
if len(input) == 0 {
return anthropic.MessageNewParams{}, fmt.Errorf("input is empty")
}
commonOptions := model.GetCommonOptions(&model.Options{
Model: &c.model,
Temperature: c.temperature,
MaxTokens: &c.maxTokens,
TopP: c.topP,
Stop: c.stopSequences,
}, opts...)
claudeOptions := model.GetImplSpecificOptions(&options{TopK: c.topK}, opts...)
// omit mulple lines...
return nil, nil
}
CallOption in Composition
https://github.com/cloudwego/eino/blob/main/compose/runnable.go
Graph compilation result is Runnable
type Runnable[I, O any] interface {
Invoke(ctx context.Context, input I, opts ...Option) (output O, err error)
Stream(ctx context.Context, input I, opts ...Option) (output *schema.StreamReader[O], err error)
Collect(ctx context.Context, input *schema.StreamReader[I], opts ...Option) (output O, err error)
Transform(ctx context.Context, input *schema.StreamReader[I], opts ...Option) (output *schema.StreamReader[O], err error)
}
Each method of Runnable accepts a list of compose.Option.
https://github.com/cloudwego/eino/blob/main/compose/graph_call_options.go
Including overall configuration for graph run, configuration of various components, and specific Lambda configurations, etc.
// Option is a functional option type for calling a graph.
type Option struct {
options []any
handler []callbacks.Handler
paths []*NodePath
maxRunSteps int
}
// DesignateNode set the key of the node which will the option be applied to.
// notice: only effective at the top graph.
// e.g.
//
// embeddingOption := compose.WithEmbeddingOption(embedding.WithModel("text-embedding-3-small"))
// runnable.Invoke(ctx, "input", embeddingOption.DesignateNode("my_embedding_node"))
func (o Option) DesignateNode(key ...string) Option {
nKeys := make([]*NodePath, len(key))
for i, k := range key {
nKeys[i] = NewNodePath(k)
}
return o.DesignateNodeWithPath(nKeys...)
}
// DesignateNodeWithPath sets the path of the node(s) to which the option will be applied to.
// You can make the option take effect in the subgraph by specifying the key of the subgraph.
// e.g.
// DesignateNodeWithPath({"sub graph node key", "node key within sub graph"})
func (o Option) DesignateNodeWithPath(path ...*NodePath) Option {
o.paths = append(o.paths, path...)
return o
}
// WithEmbeddingOption is a functional option type for embedding component.
// e.g.
//
// embeddingOption := compose.WithEmbeddingOption(embedding.WithModel("text-embedding-3-small"))
// runnable.Invoke(ctx, "input", embeddingOption)
func WithEmbeddingOption(opts ...embedding.Option) Option {
return withComponentOption(opts...)
}
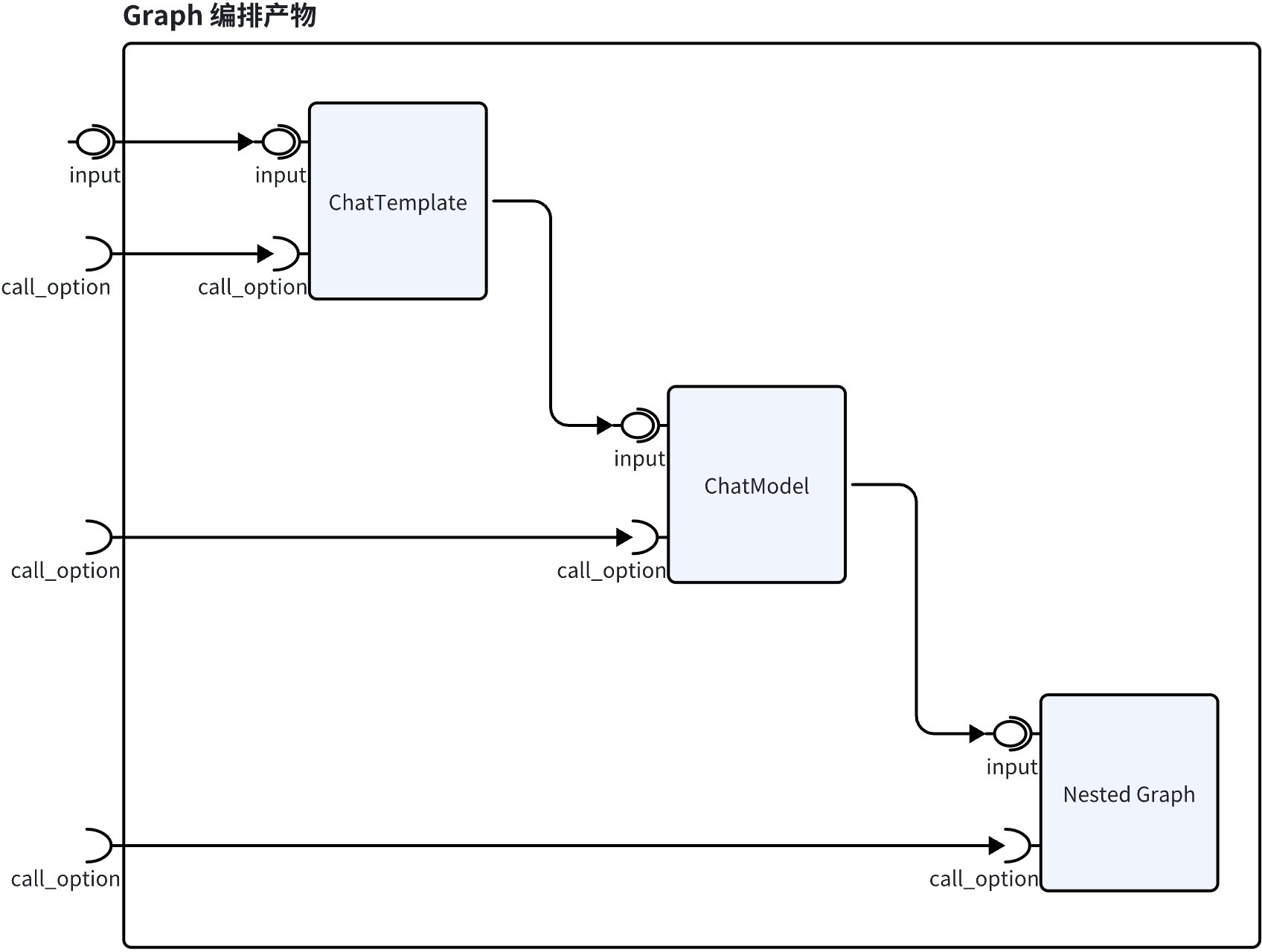
compose.Option can be assigned to different nodes in the Graph as needed.
// Call option effective for all nodes
compiledGraph.Invoke(ctx, input, WithCallbacks(handler))
// Call option effective for specific types of nodes
compiledGraph.Invoke(ctx, input, WithChatModelOption(WithTemperature(0.5))
// Call option effective only for specific nodes
compiledGraph.Invoke(ctx, input, WithCallbacks(handler).DesignateNode("node_1"))
// Call option effective only for specific nested graphs or nodes within them
compiledGraph.Invoke(ctx, input, WithCallbacks(handler).DesignateNodeWithPath(NewNodePath("1", "2"))